Amoxicillin 500mg can effectively treat many gum infections, but it’s crucial to consult a dentist for diagnosis and personalized treatment. Self-treating can delay proper care and worsen the infection.
A dentist will determine the specific type and severity of your gum infection. This helps ensure the right antibiotic dosage and duration for complete healing. They may also recommend additional treatments like scaling and root planing to address underlying dental issues contributing to the infection.
While amoxicillin is often prescribed, your dentist might choose a different antibiotic depending on your medical history, allergies, and the bacteria causing the infection. Always inform your dentist about all medications you currently take to prevent drug interactions.
Remember, antibiotics treat bacterial infections. If your gum problem stems from a viral infection or other causes, amoxicillin won’t be helpful. Accurate diagnosis is paramount for successful treatment. Follow your dentist’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and treatment duration to achieve optimal results and prevent recurrence.
Common side effects of amoxicillin include diarrhea, nausea, and rash. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe or persistent side effects. Never discontinue amoxicillin without consulting your dentist.
- Amoxicillin 500mg: Effective Against Gum Infections?
- Understanding Gum Infections and Their Causes
- Amoxicillin’s Mechanism of Action Against Bacteria in Gums
- Targeting Gram-Positive Bacteria
- Limited Effect on Gram-Negative Bacteria
- Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin 500mg for Gum Infections
- Taking Your Medication
- Additional Considerations
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Amoxicillin
- When to Seek Professional Dental Care
- Severe Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
Amoxicillin 500mg: Effective Against Gum Infections?
Amoxicillin 500mg is frequently prescribed for gum infections, particularly those caused by susceptible bacteria. Its effectiveness depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Most common gum infection culprits, such as Streptococcus and Prevotella species, are usually sensitive to amoxicillin. However, resistance is increasing, so a proper diagnosis is vital.
Your dentist or doctor should determine the specific bacteria causing your infection via a culture and sensitivity test. This test identifies the bacteria and determines its susceptibility to various antibiotics. This ensures the most appropriate treatment.
If your gum infection is severe or doesn’t improve after a few days of amoxicillin treatment, contact your healthcare provider immediately. They may recommend a different antibiotic or additional treatments.
Remember, amoxicillin treats the infection; however, proper oral hygiene remains critical for preventing future occurrences. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups are vital for maintaining healthy gums.
Amoxicillin can cause side effects. Common ones include diarrhea, nausea, and rash. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor.
Understanding Gum Infections and Their Causes
Gum infections, or periodontal diseases, stem primarily from bacterial plaque buildup. This sticky film of bacteria constantly forms on your teeth. Failing to remove it through proper brushing and flossing allows the bacteria to irritate your gums, leading to gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease.
Gingivitis manifests as red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Left untreated, it progresses to periodontitis. Periodontitis involves deeper infection, damaging the gums and bone supporting your teeth. This can result in loose teeth, tooth loss, and even serious health complications like heart disease or diabetes.
Several factors increase your risk of gum disease. Smoking significantly raises your chances. Poor oral hygiene is a major contributor. Genetic predisposition plays a role, as some individuals are genetically more susceptible to gum disease than others. Certain medical conditions, like diabetes, also increase vulnerability. Stress can exacerbate existing gum problems.
Regular dental checkups are critical for early detection and treatment. Your dentist can professionally clean your teeth, removing plaque and tartar buildup. They can also diagnose problems early, preventing more severe complications. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is your best defense – brush twice daily, floss daily, and use an antimicrobial mouthwash as directed by your dentist.
Amoxicillin’s Mechanism of Action Against Bacteria in Gums
Amoxicillin combats gum infection by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis. Specifically, it inhibits the formation of peptidoglycan, a crucial component of bacterial cell walls. This process weakens the bacterial structure, leading to cell lysis (rupture) and bacterial death.
Targeting Gram-Positive Bacteria
Amoxicillin is particularly effective against gram-positive bacteria, common culprits in gum infections. These bacteria possess a thick peptidoglycan layer, making them highly susceptible to amoxicillin’s inhibitory effects. Examples include Streptococcus and Actinomyces species, frequently involved in gingivitis and periodontitis.
Limited Effect on Gram-Negative Bacteria
Amoxicillin’s activity against gram-negative bacteria, which also contribute to gum disease, is less potent. Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer, protected by an outer membrane. This membrane partially blocks amoxicillin’s access to its target. Therefore, for infections involving significant gram-negative bacterial populations, a different antibiotic might be necessary.
Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin 500mg for Gum Infections
Amoxicillin dosage for gum infections depends on the severity and your doctor’s assessment. Typically, the prescribed dose is 500mg, taken three times daily.
Taking Your Medication
- Frequency: Take the medication at evenly spaced intervals throughout the day (e.g., every 8 hours).
- Timing: Consume with a full glass of water. Taking it with food can minimize stomach upset, but it shouldn’t significantly impact absorption.
- Duration: Complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve. Stopping early may lead to recurring infection.
Additional Considerations
Certain factors influence the dosage and duration:
- Infection Severity: More severe infections may require a higher dosage or a longer treatment period. Your dentist or doctor will determine the appropriate course.
- Patient Factors: Age, weight, and kidney function can all impact how your body processes the medication. Always inform your doctor about any pre-existing health conditions.
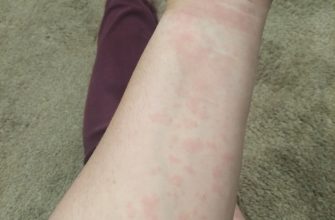
- Allergic Reactions: If you experience an allergic reaction (rash, hives, difficulty breathing), discontinue use and seek immediate medical attention.
Always follow your doctor’s or dentist’s instructions carefully. They’ll provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation. Do not adjust the dosage without consulting them first.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin, while generally safe, can cause side effects. Common ones include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Less frequent but possible reactions are skin rashes, which warrant immediate medical attention. Severe allergic reactions, though rare, are serious and require immediate emergency medical care. Symptoms include swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, and difficulty breathing.
Before starting Amoxicillin, inform your doctor about any allergies, particularly penicillin allergies, as cross-reactivity is possible. Discuss current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid interactions. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their physician before taking Amoxicillin.
During treatment, drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and help prevent side effects. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. Do not stop taking Amoxicillin without consulting your doctor, even if you feel better. Completing the prescribed course ensures the infection is fully eradicated.
Amoxicillin can interact with certain medications, such as birth control pills, so discuss potential interactions with your physician. Follow the prescribed dosage carefully. Incorrect usage can reduce effectiveness and increase the risk of side effects or antibiotic resistance.
When to Seek Professional Dental Care
See a dentist immediately if your gum infection shows no improvement after 72 hours of taking amoxicillin, or if it worsens. This includes increased pain, swelling, bleeding, or fever.
Severe Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
Seek emergency dental care if you experience severe pain, difficulty swallowing or breathing, spreading infection to your face or neck, or if you develop a high fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C). These are signs of a potentially serious infection that requires urgent treatment.
Regular dental checkups are key to preventing gum infections. Schedule appointments every six months for professional cleaning and early detection of any issues.