Amoxicillin can effectively treat many bacterial throat infections, but it’s crucial to confirm the infection’s cause before starting treatment. A doctor will typically perform a rapid strep test or throat culture to identify the bacteria responsible for your symptoms. This precise diagnosis ensures you receive the most appropriate antibiotic and avoid unnecessary medication.
If your doctor prescribes amoxicillin, follow their instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration. A typical course lasts 7-10 days. Skipping doses or prematurely stopping treatment can lead to antibiotic resistance and a prolonged infection. Always complete the entire course, even if you feel better before the medication is finished.
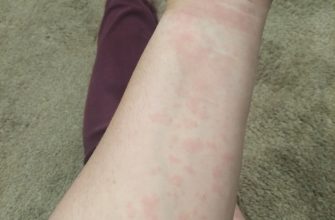
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and a rash. Severe allergic reactions, though rare, are possible and require immediate medical attention. Symptoms of a serious allergic reaction may include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, and hives. Inform your doctor about any existing allergies or medical conditions before starting amoxicillin.
Remember, amoxicillin only works against bacterial infections. Viral infections, like the common cold, are unaffected by antibiotics. If your throat pain is caused by a virus, your doctor might recommend supportive care, such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers. Self-treating with amoxicillin without a proper diagnosis is strongly discouraged.
For accurate diagnosis and treatment, always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional. They can assess your specific situation and provide personalized recommendations.
- Amoxicillin for Throat Infections
- Common Side Effects
- Alternative Treatments
- When is Amoxicillin Appropriate for a Sore Throat?
- Understanding Amoxicillin Dosage and Administration for Throat Infections
- Potential Risks and Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Throat Infections
- Allergic Reactions and Alternatives
- Viral Infections and Treatment Options
- Considering Resistance and Alternatives
- Always Consult a Doctor
Amoxicillin for Throat Infections
Amoxicillin effectively treats most strep throat infections, a bacterial infection causing significant discomfort. Your doctor will confirm the diagnosis with a rapid strep test or throat culture. Always follow your physician’s prescribed dosage and duration, typically 7-10 days. Failure to complete the course can lead to treatment failure and potential complications.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Less common but more serious reactions, such as allergic reactions (rash, hives, swelling), require immediate medical attention. Inform your doctor about any pre-existing allergies, especially penicillin allergies, before starting the medication. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss amoxicillin use with their healthcare provider.
Alternative Treatments
If you’re allergic to penicillin or amoxicillin is ineffective, your doctor may prescribe alternative antibiotics like erythromycin or clindamycin. Viral throat infections, however, don’t respond to antibiotics and require symptomatic treatment with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers. Always consult a medical professional for diagnosis and treatment planning.
When is Amoxicillin Appropriate for a Sore Throat?
Amoxicillin is only appropriate for a sore throat caused by a bacterial infection, specifically Streptococcus pyogenes, also known as Group A Streptococcus (GAS).
Therefore, your doctor will likely perform a rapid strep test or throat culture to confirm the presence of GAS before prescribing amoxicillin. A negative test result means the infection is likely viral and amoxicillin won’t be effective.
- Viral sore throats respond better to rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Bacterial sore throats, confirmed by a positive strep test, often benefit significantly from amoxicillin.
Amoxicillin isn’t a first-line treatment for all sore throats. Consider these factors:
- Your symptoms: Severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, and swollen lymph nodes might suggest a bacterial infection. However, only a medical professional can definitively diagnose the cause.
- Your medical history: Allergies to penicillin or other antibiotics must be discussed with your doctor. Previous antibiotic use can also affect treatment decisions.
- Your doctor’s assessment: A doctor’s examination and test results are critical for determining the best course of treatment.
Never self-medicate. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment of a sore throat. They can determine if amoxicillin is the right antibiotic for your specific condition.
Understanding Amoxicillin Dosage and Administration for Throat Infections
Always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. Dosage depends on your weight and the severity of your infection. Typical adult doses range from 500mg to 1000mg, taken every 8 or 12 hours. Children’s dosages are calculated based on weight, usually in milligrams per kilogram.
Amoxicillin is usually administered orally, as tablets or capsules, with a full glass of water. Take it with food to minimize stomach upset. Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better. Stopping early can lead to recurring infections and antibiotic resistance.
If you experience any side effects like severe diarrhea, allergic reactions (rash, hives, swelling), or unusual bleeding, contact your doctor immediately. Proper storage is important; keep the medication in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Your doctor may recommend a different dosage or antibiotic if you have kidney problems or allergies. Discuss any existing medical conditions or medications you take with your doctor before starting amoxicillin.
Potential Risks and Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Throat Infections
Amoxicillin, while effective for many bacterial throat infections, carries potential side effects. These include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and allergic reactions, ranging from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis. A penicillin allergy necessitates avoiding amoxicillin entirely.
Allergic Reactions and Alternatives
If you have a penicillin allergy, your doctor will likely prescribe a different antibiotic, such as azithromycin or clarithromycin (macrolides), or a cephalosporin like cefuroxime. These antibiotics target bacteria differently and are usually suitable for patients with penicillin allergies, though cross-reactivity is possible. Always inform your doctor about any allergies before starting treatment.
Viral Infections and Treatment Options
Importantly, many throat infections are viral, not bacterial. Amoxicillin is ineffective against viruses. If your doctor determines the infection is viral, they may recommend symptomatic treatment focusing on rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Gargling with salt water can also soothe a sore throat.
Considering Resistance and Alternatives
Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern. Overuse of antibiotics contributes to this. Your doctor may choose a different antibiotic based on local resistance patterns to ensure effective treatment. They will consider factors like the specific bacteria causing your infection, its sensitivity to various antibiotics, and your medical history when selecting the most appropriate treatment.
Always Consult a Doctor
This information should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor before starting any medication, including antibiotics, to ensure the most appropriate and safest treatment plan for your specific situation.