Ciprofloxacin, commonly known as Cipro, treats various bacterial infections. However, it’s crucial to understand that Cipro isn’t a universal solution and its effectiveness depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection. Your doctor will determine the appropriate course of treatment based on lab results identifying the infecting organism and its susceptibility to Cipro.
Typical treatment involves oral or intravenous administration, with dosage and duration varying greatly depending on the infection’s severity and location. For example, uncomplicated urinary tract infections might require a shorter course than a severe pneumonia case. Always adhere to the prescribed regimen; prematurely stopping treatment can lead to treatment failure and the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Potential side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. More serious, though less common, reactions may involve tendon damage or allergic reactions. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any unusual symptoms during treatment. Regular monitoring might be necessary, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
Alternatives to Cipro exist if it’s inappropriate or ineffective. Your physician will consider alternative antibiotics based on the bacterial profile and your medical history. Remember, self-treating infections with Cipro or other antibiotics without professional guidance is dangerous and can have significant health consequences.
- Ciprofloxacin for Bacterial Infections: A Guide
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin’s Role in Infection Treatment
- Spectrum of Activity
- Administration and Dosage
- Potential Side Effects
- Antibiotic Resistance
- Common Side Effects and Potential Risks of Ciprofloxacin
- When to Consult a Doctor and Alternative Treatment Options
- When to See a Doctor Sooner Rather Than Later
- Exploring Alternative Treatments
- Disclaimer
Ciprofloxacin for Bacterial Infections: A Guide
Ciprofloxacin targets a wide range of bacteria, making it effective against various infections. It’s a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, meaning it works by interfering with bacterial DNA replication.
Common uses include treating: urinary tract infections (UTIs), pneumonia, skin infections, bone and joint infections, and some sexually transmitted infections. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration based on your specific infection and health status.
Important note: Ciprofloxacin isn’t effective against viral infections like the common cold or flu. Taking it for these won’t help and can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Possible side effects: While generally well-tolerated, some people experience diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. Less common side effects include headache, dizziness, and allergic reactions. Severe side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention.
Before starting Ciprofloxacin: Inform your doctor about all medications you currently take, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Also, discuss any allergies or medical conditions you have, particularly tendon problems.
During treatment: Drink plenty of fluids to help prevent dehydration and aid in eliminating the medication from your system. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. Complete the prescribed course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before finishing the medication, to prevent recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
After treatment: Monitor for any lingering symptoms and contact your doctor if they persist or worsen. Your doctor might order follow-up tests to ensure the infection has cleared.
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin’s Role in Infection Treatment
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, targets bacteria by interfering with their DNA replication. This action effectively stops bacterial growth and kills the bacteria, leading to infection resolution.
Spectrum of Activity
Ciprofloxacin treats a wide range of bacterial infections, including those caused by Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Its effectiveness varies depending on the specific bacteria and their susceptibility to the drug. Always consult a doctor to determine if Ciprofloxacin is the right choice for your infection.
Administration and Dosage
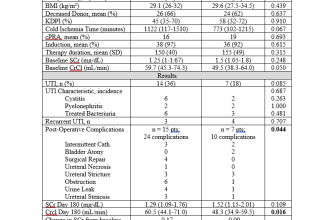
Ciprofloxacin is available in oral and intravenous forms. Dosage depends on the type and severity of infection, as well as the patient’s age and kidney function. Your physician will determine the appropriate dose and duration of treatment. Complete the prescribed course, even if you feel better sooner, to prevent recurrence.
Potential Side Effects
Like all medications, Ciprofloxacin can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Less common, but potentially serious, side effects include tendonitis, peripheral neuropathy, and Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Antibiotic Resistance
Overuse of antibiotics contributes to antibiotic resistance. Ciprofloxacin should only be used when necessary and as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Inappropriate use increases the risk of bacterial resistance, making future infections harder to treat.
Common Side Effects and Potential Risks of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, while effective, can cause several side effects. Understanding these potential issues helps you make informed decisions with your doctor.
Gastrointestinal Issues: These are among the most frequent side effects. You might experience nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. Severe diarrhea, potentially indicating Clostridium difficile infection, requires immediate medical attention.
- Tip: Stay hydrated and discuss any persistent or severe digestive problems with your doctor.
Nervous System Effects: Some individuals experience dizziness, headache, or lightheadedness. Less common, but serious, are seizures and peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage in the extremities), characterized by numbness, tingling, or pain.
- Caution: Report any neurological symptoms to your doctor promptly. Avoid driving or operating machinery if you experience dizziness or lightheadedness.
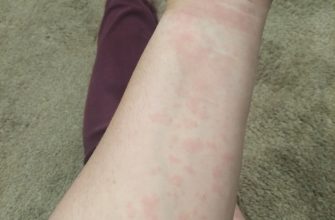
Skin Reactions: Rashes, itching, and hives are possible. A severe allergic reaction, including anaphylaxis (a life-threatening condition), is rare but demands immediate medical care.
- Action: Stop taking Ciprofloxacin and seek immediate medical help if you experience a severe allergic reaction.
Tendinitis and Tendon Rupture: This is a significant risk, particularly in older adults, those with kidney problems, or those taking steroid medications. Pain and inflammation in tendons (especially in the Achilles tendon) can occur.
- Prevention: Discuss this risk with your doctor, especially if you fall into a high-risk category.
- Action: Report any tendon pain immediately.
Other Potential Risks: Ciprofloxacin can affect blood sugar levels, potentially worsening diabetes. It can also interact with other medications; therefore, always inform your doctor of all medications and supplements you are taking. Rare but serious side effects include liver damage and kidney problems.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment. Never stop or change medication without consulting your doctor.
When to Consult a Doctor and Alternative Treatment Options
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe symptoms like high fever (above 101°F), persistent vomiting, severe diarrhea, or signs of dehydration (dark urine, dizziness). These could indicate a serious complication requiring hospitalization.
When to See a Doctor Sooner Rather Than Later
Consult your doctor if Cipro isn’t improving your symptoms after a week of treatment. A change in antibiotic may be necessary. Also, report any new or worsening symptoms, such as persistent pain, unusual bruising, or allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling).
Exploring Alternative Treatments
Note: Alternative treatments should never replace prescribed antibiotics. They may offer supportive care, but antibiotics are often necessary to eradicate bacterial infection. Always discuss any alternative approaches with your doctor before starting them.
Some patients find relief from Cipro’s side effects through dietary adjustments. Probiotics may help restore gut health following antibiotic use. Adequate hydration is vital. Rest is also crucial for recovery. Specific herbal remedies, like echinacea (for immune support), have been suggested by some, but their effectiveness for Cipro-treated infections needs more research and medical oversight.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.