Ciprofloxacin, while a powerful antibiotic, carries a risk of serious lung complications. These adverse reactions, ranging from mild cough to severe pneumonitis, necessitate careful monitoring and understanding. Specifically, watch for shortness of breath, chest pain, or persistent cough after starting Cipro treatment. Report these symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Early detection is paramount. The onset of Cipro-induced lung problems can be subtle initially. Pay close attention to any changes in your breathing patterns, even if seemingly minor. This proactive approach helps ensure timely intervention and prevents complications.
Your doctor will assess your risk factors, including pre-existing lung conditions and other medications you’re taking. Open communication about your medical history is crucial. They might suggest alternative antibiotics if your risk profile warrants it, or implement close monitoring during Cipro treatment. Regular check-ups and pulmonary function tests might be recommended, depending on your individual situation.
Remember, responsible antibiotic use is key. Ciprofloxacin should only be used when absolutely necessary, as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Self-medicating with antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance and increase the likelihood of adverse reactions. Prioritize your respiratory health by following your doctor’s guidance and seeking immediate medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms.
- Cipro and Lung Infections: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin’s Mechanism in Lung Infections
- Ciprofloxacin Dosage and Administration for Lung Infections
- Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Ciprofloxacin for Lung Infections
- When to Seek Medical Attention and Alternative Treatment Options
Cipro and Lung Infections: A Detailed Overview
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic effective against various bacteria, including some causing lung infections like pneumonia. However, its use requires careful consideration.
Cipro is typically prescribed for pneumonia caused by specific bacteria, not all types. Your doctor will determine if Cipro is the right choice based on your specific infection and its causative agent. They will consider factors like your medical history, allergies, and the severity of the illness.
- Bacterial Pneumonia: Cipro targets certain bacteria frequently responsible for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP). However, it’s crucial to note that viral pneumonia is not treatable with antibiotics.
- Resistance: Overuse of antibiotics contributes to bacterial resistance. Therefore, Cipro should only be used when clearly indicated to maintain its efficacy.
- Adverse Effects: Like all medications, Cipro has potential side effects. These can range from mild (diarrhea, nausea) to more serious (tendonitis, nerve damage). Always report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Treatment duration varies, depending on the infection’s severity and your response to treatment. Your doctor will guide you on the appropriate length of therapy. Strict adherence to the prescribed dosage and duration is paramount for successful treatment and to minimize the risk of resistance development.
- Accurate Diagnosis: A precise diagnosis is critical. This involves tests to identify the type of bacteria causing the infection and its susceptibility to Cipro.
- Alternative Treatments: Other antibiotics may be suitable alternatives, depending on the identified bacteria. Your doctor will weigh the risks and benefits of each treatment option.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups are essential to monitor your progress and ensure the infection is resolving effectively.
Remember, self-treating lung infections is dangerous. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure you receive the most appropriate care. This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always seek professional medical assistance.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin’s Mechanism in Lung Infections
Ciprofloxacin combats lung infections by targeting bacterial DNA replication. It achieves this through inhibition of bacterial topoisomerases, specifically DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are crucial for bacterial DNA unwinding and separation–processes necessary for cell division and repair.
By blocking these enzymes, Ciprofloxacin prevents bacteria from replicating their genetic material, halting their growth and ultimately leading to their death. This mechanism is effective against a wide range of gram-negative bacteria commonly causing lung infections, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
However, it’s important to note that Ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness varies depending on the specific bacterial strain and its resistance profile. Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, so appropriate antibiotic selection, guided by culture and sensitivity testing, is paramount. Always consult a physician for diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding medication.
Ciprofloxacin Dosage and Administration for Lung Infections
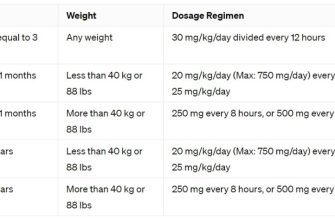
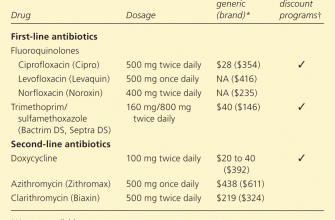
Ciprofloxacin dosage for lung infections depends on the specific infection, its severity, and the patient’s overall health. Always follow your doctor’s prescription exactly. Typical adult dosages for pneumonia range from 500 mg to 750 mg twice daily, administered orally or intravenously. Treatment duration usually lasts 7 to 14 days, but may vary.
For serious infections or those requiring hospitalization, intravenous administration is often preferred. Intravenous dosages are usually higher and determined by the physician based on the patient’s response to treatment. The doctor might adjust the dosage based on blood levels of the antibiotic.
Children require adjusted dosages based on their weight and age. Precise dosing information for pediatric patients should always come directly from a pediatrician or infectious disease specialist. Never administer adult dosages to children.
Potential side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Serious but less common side effects involve tendonitis and allergic reactions. Report any adverse reactions to your doctor immediately.
Ciprofloxacin is not suitable for all lung infections. It’s crucial that your physician accurately diagnoses the infection before prescribing this antibiotic. Your doctor will also consider any existing medical conditions and allergies before treatment begins. Always consult your doctor before taking Ciprofloxacin or any other medication.
Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Ciprofloxacin for Lung Infections
Ciprofloxacin, while effective against many bacterial lung infections, carries potential side effects. These can range from mild to severe, and their likelihood varies by individual.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These usually resolve without intervention. Less frequent, but still possible, are headaches, dizziness, and insomnia.
More serious, though rarer, side effects include tendonitis or tendon rupture, particularly in older adults or those taking steroid medications concurrently. This necessitates immediate medical attention.
Allergic reactions, ranging from skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis, are also possible. If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction (such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing), seek immediate medical help.
Ciprofloxacin can interact negatively with certain medications, including antacids and some blood thinners. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking.
Rare but potentially serious side effects include peripheral neuropathy (numbness or tingling in the extremities) and liver damage. Monitor for any unusual symptoms and report them to your doctor immediately.
Before starting Ciprofloxacin, discuss potential risks and benefits with your physician. They can assess your individual risk factors and determine if Ciprofloxacin is the appropriate treatment for your lung infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention and Alternative Treatment Options
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience shortness of breath, chest pain, or a persistent cough after taking Cipro. These could indicate serious lung complications.
If you suspect a Cipro-related lung reaction, promptly discontinue the medication and seek medical advice. Don’t hesitate; early intervention is key.
Alternative treatments focus on managing symptoms and supporting lung health. These might include bronchodilators to open airways, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, or oxygen therapy to improve breathing.
Lifestyle changes can also help. Prioritize adequate rest, hydration, and a healthy diet. Avoiding irritants like smoke and pollutants is vital.
Complementary therapies like acupuncture or deep breathing exercises may offer some relief from symptoms, but always discuss these with your healthcare provider before starting.
Remember, this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.