Ciprofloxacin 500mg is not the recommended antibiotic for strep throat. Strep throat, caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, requires antibiotics like penicillin or amoxicillin for effective treatment. Ciprofloxacin targets different bacteria and may be ineffective against strep.
Using the wrong antibiotic can lead to treatment failure, allowing the infection to worsen and potentially causing complications like rheumatic fever. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and antibiotic prescription. They will perform a rapid strep test or throat culture to confirm the infection and determine the appropriate antibiotic based on your individual needs and the specific strain of bacteria involved.
Never self-medicate with antibiotics. Incorrect use contributes to antibiotic resistance, making future infections harder to treat. A doctor’s assessment ensures you receive the correct medication and dosage for a complete recovery. This is especially true with strep throat, where timely and accurate treatment is key to preventing further health issues.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek professional medical guidance for any health concerns.
Ciprofloxacin’s Ineffectiveness Against Strep Throat
Ciprofloxacin won’t treat strep throat. This antibiotic targets bacteria by interfering with their DNA replication. Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria causing strep throat, is not susceptible to ciprofloxacin.
Why Ciprofloxacin Fails Against Strep
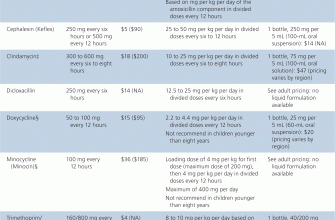
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic; it’s highly effective against many gram-negative bacteria and some gram-positive bacteria. However, S. pyogenes demonstrates significant resistance to fluoroquinolones. This resistance stems from bacterial mutations impacting the drug’s target site within the bacterial cell. Penicillin or amoxicillin are far more appropriate treatments for strep throat.
Appropriate Treatment for Strep Throat
Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. They’ll perform a rapid strep test or throat culture to confirm the infection. Based on the results, they’ll prescribe penicillin or amoxicillin, antibiotics specifically designed to combat S. pyogenes. Ignoring or improperly treating strep throat can lead to serious complications, such as rheumatic fever and kidney inflammation.
Identifying Strep Throat and Appropriate Treatment
See your doctor for diagnosis. They’ll perform a rapid strep test, a quick swab of your throat. This test detects the bacteria responsible for strep throat, Streptococcus pyogenes. A positive result confirms the infection.
If the rapid test is negative but strep throat is suspected based on symptoms, a throat culture may be necessary. This is a more sensitive test, providing a definitive diagnosis. Results typically take 24-48 hours.
Typical symptoms include a sore throat, fever, difficulty swallowing, headache, and sometimes a rash. However, some individuals experience milder symptoms or atypical presentations. Reliable diagnosis requires medical assessment.
Antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin, are the standard treatment for strep throat. Ciprofloxacin is not typically the first-line choice for strep throat due to resistance concerns and penicillin’s superior efficacy. Your doctor will determine the best antibiotic for your specific case.
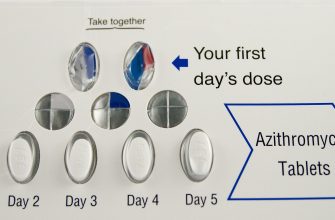
Always complete the full course of prescribed antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This prevents potential complications like rheumatic fever, a serious condition affecting the heart.
If you experience allergic reactions to prescribed medication, contact your doctor immediately. Alternative antibiotics may be necessary.
Potential Risks of Misusing Ciprofloxacin
Don’t take Ciprofloxacin without a doctor’s prescription. Improper use increases your risk of developing antibiotic resistance, meaning future infections will be harder to treat. This resistance affects not only you, but contributes to a global health problem.
Side Effects and Interactions
Ciprofloxacin can cause side effects ranging from mild gastrointestinal upset (nausea, diarrhea) to more serious issues like tendonitis or rupture, particularly in older adults or those on corticosteroids. It can also interact negatively with other medications, including some antacids and blood thinners. Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking.
Allergic reactions, while uncommon, can be severe. Symptoms include hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any allergic reaction.
Long-Term Consequences
Prolonged Ciprofloxacin use can disrupt your gut microbiome, potentially leading to digestive problems and increased susceptibility to other infections. This imbalance can persist even after you stop taking the antibiotic.
Remember, antibiotics are powerful medicines. Use them responsibly, following your doctor’s instructions precisely. Misuse undermines their effectiveness and poses significant health risks. If you have questions or concerns, always consult your physician or pharmacist.