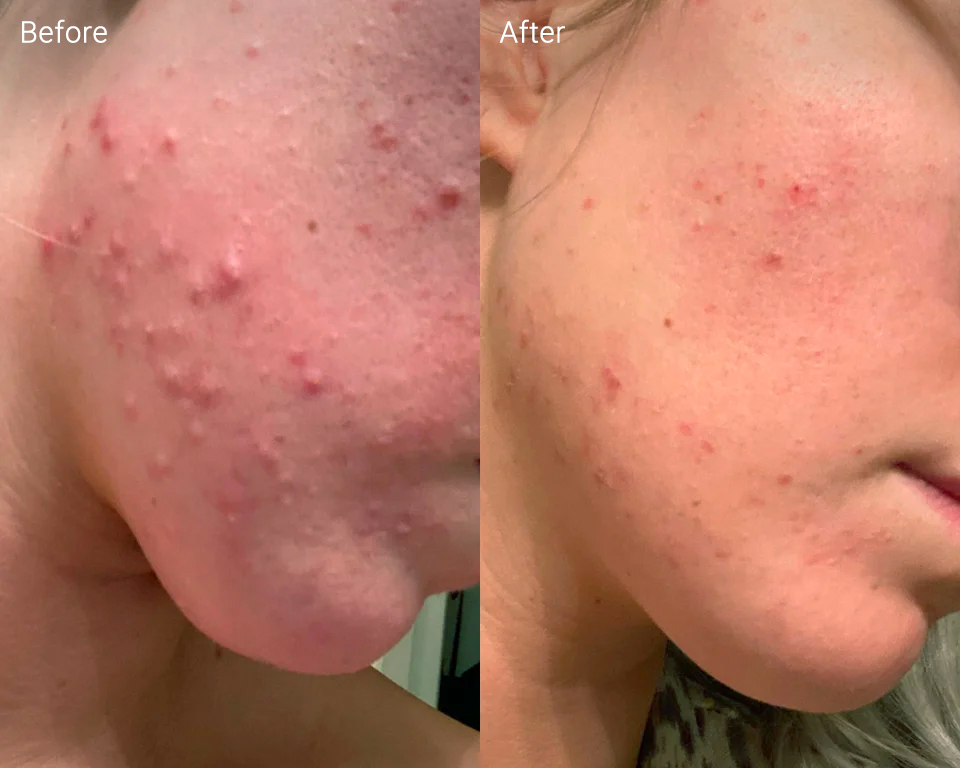
Doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, offers a powerful approach to combating acne, particularly moderate to severe cases unresponsive to topical treatments. It works by reducing inflammation and targeting the bacteria responsible for acne breakouts, Propionibacterium acnes. Expect noticeable improvements within several weeks of starting treatment, though complete clearing may take longer depending on individual responses and severity.
Your dermatologist will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment. Typically, this involves taking doxycycline once or twice daily. Remember to finish the prescribed course of antibiotics, even if your acne clears up sooner; stopping early could lead to recurrence. Consistent medication is key to successful acne management.
While highly effective, doxycycline can cause side effects. These may include nausea, diarrhea, and sun sensitivity. Always inform your doctor about any current medications you’re taking to prevent potential drug interactions. Increased sun sensitivity necessitates careful sun protection, including using sunscreen with a high SPF and limiting sun exposure during peak hours.
Doxycycline isn’t a standalone solution for all acne types. For optimal results, combine it with a proper skincare routine, including gentle cleansers, non-comedogenic moisturizers, and potentially topical retinoids, as prescribed by your doctor. This multifaceted approach targets acne from multiple angles, accelerating healing and minimizing long-term scarring.
Important Note: Doxycycline is a prescription medication. Always consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional before starting any acne treatment, including doxycycline. They can diagnose your specific type of acne, assess your medical history, and recommend the best course of action tailored to your needs.
- Acne Treatment with Doxycycline
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects
- Alternative Treatments and Combining Therapies
- Long-Term Use and Potential Concerns
- What is Doxycycline and How Does it Work for Acne?
- How Doxycycline Reduces Acne Inflammation
- Important Considerations When Using Doxycycline for Acne
- Who is a Good Candidate for Doxycycline Acne Treatment?
- Factors Favoring Doxycycline Use
- Consideration Before Starting Treatment
- When Doxycycline Might Not Be the Best Choice
- Further Discussion
- Common Side Effects of Doxycycline for Acne and How to Manage Them
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Sun Sensitivity
- Yeast Infections
- Other Potential Side Effects
- When to Contact Your Doctor
- Dosage and Duration of Doxycycline Treatment for Acne
- Typical Treatment Length
- Important Considerations
- Doxycycline Dosage Table (Example)
- Follow-Up Appointments
- Doxycycline vs. Other Acne Treatments: Comparing Effectiveness
- Potential Interactions with Other Medications and Supplements
- Medications to Note
- Supplements to Consider
- Important Considerations and Precautions When Using Doxycycline for Acne
- Potential Side Effects
- Medication Adherence
- Specific Patient Groups
Acne Treatment with Doxycycline
Doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, effectively combats acne by targeting the bacteria Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes), a key contributor to acne inflammation. It reduces bacterial load, leading to clearer skin. Remember to finish your prescribed course, even if your acne improves before you complete all the pills. Stopping early may cause the bacteria to become resistant.
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment, typically ranging from several weeks to months. Commonly prescribed dosages for acne are 50-100mg, taken once or twice daily with food. This minimizes potential stomach upset. Always follow your physician’s instructions precisely.
Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, doxycycline may cause side effects, including nausea, diarrhea, and increased sun sensitivity. Inform your doctor about any adverse reactions immediately. Avoiding excessive sun exposure and using sunscreen with a high SPF are crucial. Also, this medication may interact with other drugs; ensure your doctor knows all medications you’re taking.
Alternative Treatments and Combining Therapies
Doxycycline is often used in conjunction with topical treatments like retinoids or benzoyl peroxide for optimal results. Your dermatologist can advise on the most suitable combination therapy for your specific acne type and severity. Consider lifestyle modifications like proper cleansing and a balanced diet for synergistic improvements.
Long-Term Use and Potential Concerns
Prolonged doxycycline use may increase the risk of yeast infections or antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Regular check-ups with your doctor are vital to monitor progress and address any potential concerns. Your doctor will assess if continued treatment is necessary or if other approaches are more suitable.
What is Doxycycline and How Does it Work for Acne?
Doxycycline is a tetracycline antibiotic. For acne, it works by targeting the bacteria Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes), a key player in acne development. This bacteria contributes to inflammation and the formation of pimples.
How Doxycycline Reduces Acne Inflammation
Doxycycline inhibits bacterial protein synthesis, preventing C. acnes from multiplying and causing further inflammation. This leads to a reduction in the number and severity of acne lesions. Additionally, it possesses anti-inflammatory properties, further calming the skin.
Important Considerations When Using Doxycycline for Acne
Doxycycline is typically prescribed as a short-term treatment, often alongside topical treatments. Remember to always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Common side effects can include nausea, diarrhea, and sun sensitivity. Inform your doctor about any medications you are currently taking, as interactions may occur. Doxycycline isn’t suitable for everyone, particularly pregnant or breastfeeding women. Your doctor will assess your suitability for this medication.
Who is a Good Candidate for Doxycycline Acne Treatment?
Doxycycline is a great option for individuals with moderate to severe acne, particularly inflammatory acne with papules and pustules. It’s especially helpful for those who haven’t seen improvement with topical treatments alone.
Factors Favoring Doxycycline Use
- Moderate to severe acne: Doxycycline is generally prescribed when topical treatments prove insufficient.
- Inflammatory acne: It effectively reduces inflammation, targeting red, swollen pimples.
- Acne unresponsive to topical therapies: If you’ve tried benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, or other topical treatments without satisfactory results, doxycycline can be a viable next step.
- Nodular acne: This severe form of acne, characterized by large, painful lumps, often responds well to doxycycline.
Consideration Before Starting Treatment
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Doxycycline is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Discuss alternative options with your dermatologist.
- Sun sensitivity: Doxycycline can increase sun sensitivity, so consistent sunscreen use is crucial.
- Interactions with other medications: Inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you are taking to avoid potential interactions. This includes birth control pills.
- Allergies: Let your doctor know about any allergies, particularly to tetracyclines.
- Age: While used in adults, doxycycline is generally not recommended for children under 8, due to possible effects on tooth development.
When Doxycycline Might Not Be the Best Choice
Doxycycline may not be the ideal choice for those with mild acne, those who are pregnant or breastfeeding, or individuals with specific medical conditions or allergies. Always consult a dermatologist to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
Further Discussion
Your dermatologist will consider your medical history, the severity of your acne, and your overall health before prescribing doxycycline. A thorough evaluation helps ensure the safest and most effective treatment approach.
Common Side Effects of Doxycycline for Acne and How to Manage Them
Doxycycline, while effective for acne, can cause side effects. Understanding these and knowing how to manage them is key to successful treatment.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Upset stomach, nausea, and diarrhea are common. To minimize these, take doxycycline with food or milk. If symptoms persist or worsen, contact your doctor.
- Nausea: Try taking the medication with a bland food like toast or crackers.
- Diarrhea: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. Consider over-the-counter anti-diarrheal medication, but consult your doctor first.
- Upset Stomach: Smaller, more frequent doses might help.
Sun Sensitivity
Doxycycline increases your skin’s sensitivity to sunlight. Always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days. Wear protective clothing, such as hats and long sleeves, when spending time outdoors.
Yeast Infections
Doxycycline can disrupt the balance of your gut bacteria, potentially leading to yeast infections (such as oral thrush). Watch for symptoms like white patches in your mouth or vagina. If you notice these, seek medical attention.
Other Potential Side Effects
- Headache: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may provide relief. If headaches are severe or persistent, consult your doctor.
- Dizziness: Avoid activities requiring alertness, such as driving or operating machinery, until you know how the medication affects you.
- Photosensitivity: Avoid prolonged sun exposure.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or severe allergic reactions.
Dosage and Duration of Doxycycline Treatment for Acne
Your dermatologist will determine the right doxycycline dosage and treatment length based on your specific needs. Commonly, acne treatment involves daily doses ranging from 50 to 100 mg, taken twice a day with food.
Typical Treatment Length
Treatment usually lasts for several weeks or months, often continuing until your acne clears significantly. In some cases, particularly for severe acne, longer treatment may be necessary. Your doctor will monitor your progress and adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
Important Considerations
Consistent medication intake is vital. Missing doses can hinder treatment efficacy. Report any side effects to your doctor promptly. Certain medications and health conditions may affect doxycycline’s use; be sure to discuss your complete medical history with your doctor.
Doxycycline Dosage Table (Example)
| Age Group | Typical Dosage (mg/day) | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Adults (18+) | 50-100 | Twice daily |
| Children (consult a pediatrician) | Variable based on weight and age | As prescribed by pediatrician |
Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring your response to treatment. This allows for timely adjustments to your medication or treatment plan if needed.
Doxycycline vs. Other Acne Treatments: Comparing Effectiveness
Doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic, frequently combats acne by reducing P. acnes bacteria. Studies show it’s highly successful for moderate to severe acne, often clearing skin significantly within weeks. However, it’s not a first-line treatment for all.
Benzoyl peroxide, a topical treatment, directly kills P. acnes. It’s generally well-tolerated and often used in combination with other therapies. While effective for mild to moderate acne, it may cause skin dryness or irritation.
Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, work by increasing skin cell turnover, preventing clogged pores. They are highly effective long-term, addressing both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne. However, initial side effects like dryness and redness are common, requiring gradual introduction.
Salicylic acid, a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA), exfoliates the skin, unclogging pores and reducing inflammation. It’s a gentler option than retinoids, suitable for sensitive skin, though its impact is generally milder.
Oral isotretinoin, a powerful retinoid, is a last resort for severe, resistant acne. It’s very effective, but carries potential side effects requiring close medical supervision.
Choosing the right treatment depends on acne severity, skin type, and individual response. A dermatologist can assess your specific needs and recommend the most appropriate approach, possibly combining therapies for optimal results. Always discuss potential interactions with other medications.
Potential Interactions with Other Medications and Supplements
Doxycycline can interact with several medications and supplements, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Always inform your doctor about all medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs. This includes birth control pills; doxycycline can decrease their effectiveness, leading to unplanned pregnancy. Consider using a backup method of contraception while on doxycycline.
Medications to Note
Certain antacids containing aluminum or magnesium can decrease doxycycline absorption. Separate the administration of these medications by at least two hours. Similarly, dairy products, iron supplements, and multivitamins containing minerals can also interfere with doxycycline absorption. Space their intake from doxycycline by several hours for optimal absorption. Methotrexate, a medication for autoimmune diseases and some cancers, may have increased toxicity when used concurrently with doxycycline. This combination requires close monitoring by your physician.
Supplements to Consider
Some herbal supplements, such as St. John’s wort, are known to interact with numerous medications, including doxycycline. Discuss the use of any herbal supplements with your doctor before starting or continuing doxycycline treatment. This also applies to any other supplements you are taking. Accurate reporting of all substances consumed is key for safe and effective treatment.
Important Considerations and Precautions When Using Doxycycline for Acne
Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible. This is especially important with birth control pills, as doxycycline can reduce their effectiveness.
Protect yourself from the sun. Doxycycline increases sun sensitivity; use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and wear protective clothing when outdoors.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and upset stomach. Less frequent, but possible, side effects include yeast infections, photosensitivity reactions, and esophageal irritation. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Medication Adherence
Take doxycycline as prescribed. Don’t stop taking it prematurely, even if your acne seems to clear up. Finishing the full course is key to preventing antibiotic resistance and ensuring the best outcome. Also, take it with a full glass of water and avoid lying down for at least 30 minutes after taking a dose to minimize esophageal irritation.
Regularly check in with your dermatologist for progress monitoring. They can assess your response to treatment and adjust your plan as needed. Proper diagnosis and management are critical.
Specific Patient Groups
Doxycycline is generally not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Women of childbearing age should discuss contraceptive options with their physician. People with kidney or liver problems should also inform their doctor before taking doxycycline.