Amoxicillin 500mg is frequently prescribed for bacterial chest infections. However, it’s crucial to remember this antibiotic targets bacteria, not viruses. A doctor’s diagnosis is always necessary to confirm the infection’s cause before starting treatment.
If your doctor prescribes Amoxicillin 500mg, follow their instructions precisely. This includes the dosage, frequency, and duration of treatment. Failing to complete the course can lead to treatment failure and potential antibiotic resistance.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and stomach upset. Severe allergic reactions, though rare, require immediate medical attention. Symptoms such as rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing necessitate contacting emergency services.
Remember: Amoxicillin 500mg is only one part of managing a chest infection. Rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers often play equally important roles in recovery. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
- Amoxicillin 500mg for Chest Infections: A Detailed Guide
- What is Amoxicillin and How Does it Treat Chest Infections?
- Common Chest Infections Treated with Amoxicillin 500mg
- Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin 500mg for Chest Infections
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Amoxicillin Treatment
- Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Chest Infections
Amoxicillin 500mg for Chest Infections: A Detailed Guide
Amoxicillin 500mg is often prescribed for bacterial chest infections like bronchitis or pneumonia. However, it’s crucial to understand it’s not effective against viral infections. A doctor’s diagnosis is paramount before starting treatment.
Typical dosages involve taking one 500mg tablet twice daily, with or without food, for 7-14 days. Always adhere to your physician’s instructions; adjusting the dosage without medical guidance is risky.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Severe allergic reactions, though rare, can manifest as hives, swelling, or breathing difficulties; seek immediate medical attention if these occur.
Amoxicillin’s effectiveness can be impacted by antibiotic resistance. Factors like prior antibiotic use and specific bacterial strains influence its efficacy. Your doctor will consider these factors when prescribing.
While amoxicillin tackles bacterial infections, managing symptoms like cough and fever requires supportive care. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort.
Never share your medication. Antibiotics should be taken only as prescribed for your specific infection. Improper use contributes to antibiotic resistance.
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are necessary to monitor your progress and ensure the infection clears completely. Report any persistent or worsening symptoms immediately.
Remember, this information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication.
What is Amoxicillin and How Does it Treat Chest Infections?
Amoxicillin is a penicillin-based antibiotic. It combats bacterial chest infections by interfering with the bacteria’s ability to build their cell walls. This process weakens and ultimately kills the bacteria, allowing your body to fight off the infection.
Many chest infections, like bronchitis and pneumonia, are caused by bacteria susceptible to amoxicillin. However, it’s crucial to understand that amoxicillin only works against bacteria; it’s ineffective against viral chest infections. A doctor will determine the cause of your infection before prescribing treatment.
| Type of Infection | Amoxicillin Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Bacterial Pneumonia | Often effective |
| Bacterial Bronchitis | Often effective |
| Viral Pneumonia | Ineffective |
| Viral Bronchitis | Ineffective |
The 500mg dosage is common for adults, but your doctor will adjust the dose based on your individual needs and the severity of your infection. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and treatment duration. Incomplete treatment can lead to antibiotic resistance, making future infections harder to treat. If you experience any side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Common Chest Infections Treated with Amoxicillin 500mg
Amoxicillin 500mg is frequently prescribed for bacterial chest infections. Its effectiveness depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
- Acute Bronchitis: Amoxicillin can treat bacterial bronchitis, characterized by a cough, often with mucus, and sometimes chest discomfort. A doctor’s diagnosis is crucial before starting treatment.
- Pneumonia (certain types): Amoxicillin is effective against some bacteria causing pneumonia, but not all. Many pneumonia cases require stronger antibiotics. Your doctor will determine if amoxicillin is suitable.
- Sinusitis (with secondary bacterial infection): While often viral, sinusitis can sometimes involve a bacterial infection spreading to the chest. Amoxicillin might be prescribed if your doctor identifies this secondary infection.
- Lung Abscess (in some cases): In certain situations, a lung abscess–a pus-filled cavity in the lung–might respond to amoxicillin as part of a broader treatment plan. This is usually a severe condition needing specialist care.
Important Note: Amoxicillin is not effective against viral chest infections like the common cold or influenza. Incorrect use can lead to antibiotic resistance. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and complete the entire course of medication, even if you feel better before finishing it. Consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment before using amoxicillin or any medication.
- Seek professional medical advice: A doctor will diagnose the infection and prescribe the right medication and dosage.
- Follow prescribed dosage and duration: Completing the antibiotic course is vital to prevent recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
- Report any adverse reactions immediately: Contact your doctor if you experience any side effects.
Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin 500mg for Chest Infections
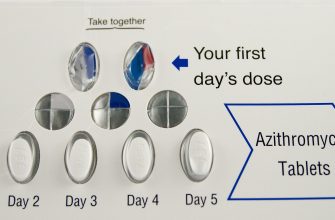
Amoxicillin 500mg is typically prescribed as one tablet twice daily, or as your doctor directs. This means taking one tablet every 12 hours, consistently, for the full course of treatment.
Take the medicine with a full glass of water. Avoid taking it with acidic beverages like orange juice, as this can affect absorption. Taking it with food might reduce stomach upset for some people, but this isn’t always necessary.
The duration of treatment varies depending on the severity of your infection and your doctor’s assessment. Typical courses last between 5 to 14 days. Always finish the entire course, even if you start feeling better before the medication is gone. Stopping early can lead to recurrent infections.
Do not crush, chew, or break the tablets unless specifically instructed by your doctor or pharmacist. Swallowing them whole ensures proper absorption.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular schedule. Never take a double dose.
Side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or rash. If you experience severe or persistent side effects, contact your doctor immediately. Allergic reactions such as hives or difficulty breathing are serious and require immediate medical attention.
This information is for general guidance only. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions and consult them before making any changes to your medication regimen.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Amoxicillin, while generally safe and effective, can cause side effects. Most are mild and temporary, but some require medical attention.
Common side effects include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stomach upset
- Rash
Less common, but more serious side effects need immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- Dark urine
- Clay-colored stools
- Unusual bleeding or bruising
- Severe stomach pain
Precautions to take:
- Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Interactions can occur.
- Tell your doctor about any allergies, particularly penicillin allergies. Amoxicillin is a penicillin-type antibiotic.
- Drink plenty of water while taking amoxicillin to stay hydrated and help prevent stomach upset.
- Finish the entire course of medication, even if you feel better. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
- Monitor for side effects and contact your doctor if you experience any concerns.
- If you develop diarrhea that is severe or bloody, seek immediate medical advice as it could be Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any medication.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Amoxicillin Treatment
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience a severe allergic reaction, including hives, swelling of your face or throat, or difficulty breathing. These are signs of a serious allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention.
Seek medical advice if your symptoms worsen or don’t improve after 72 hours of taking Amoxicillin. This suggests the antibiotic may not be effectively treating the infection.
If you develop new symptoms, such as a high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C), severe headache, or persistent vomiting, contact your physician. These could indicate a complication or a different infection.
Report any side effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, or abdominal pain, to your doctor. While some mild side effects are common, severe or persistent gastrointestinal issues need evaluation.
If you experience persistent or worsening chest pain, shortness of breath, or coughing up blood, seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms could indicate a more serious condition requiring urgent care.
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Amoxicillin. This helps avoid potential drug interactions.
Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Chest Infections
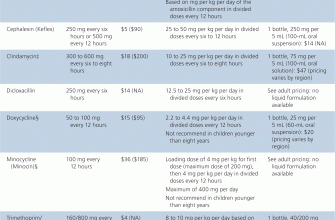
If amoxicillin isn’t suitable, your doctor might prescribe doxycycline, a broad-spectrum antibiotic effective against many bacteria causing chest infections. It’s often used for pneumonia and bronchitis.
Clarithromycin is another option, a macrolide antibiotic frequently used for treating respiratory infections, including those caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It targets bacteria amoxicillin might miss.
For severe or complicated chest infections, your physician might consider levofloxacin or moxifloxacin, fluoroquinolone antibiotics. These are powerful but are reserved for cases unresponsive to other treatments due to potential side effects.
Always discuss treatment options with your doctor. They will consider your medical history, the severity of your infection, and potential drug interactions before prescribing an alternative to amoxicillin. They can also advise on over-the-counter remedies to manage symptoms such as cough and fever.
Remember, self-treating can be harmful. Professional medical guidance is key to effective treatment and preventing complications.