Amoxicillin 875 mg is often prescribed for ear infections, particularly those caused by bacteria. This high dosage helps achieve therapeutic levels in the bloodstream quickly, facilitating faster symptom relief. However, remember that antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, not viral ones. A doctor’s diagnosis is crucial before starting treatment.
Correct dosage is paramount. Never adjust the prescribed dosage or duration without consulting your physician. Incorrect usage can lead to treatment failure or the development of antibiotic resistance. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely, including the timing and method of administration.
Potential side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and rash. If you experience any severe allergic reactions like difficulty breathing or swelling, seek immediate medical attention. While generally safe when used as directed, amoxicillin can interact with certain medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and allergies before beginning treatment.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of ear infections or any medical concerns. Self-treating can be risky; accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan are key to successful recovery.
- Amoxicillin 875 mg for Ear Infections: A Detailed Guide
- Is Amoxicillin 875 mg Right for Your Ear Infection?
- Understanding Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin 875 mg
- Taking Amoxicillin 875 mg
- Missed Dose
- Potential Side Effects
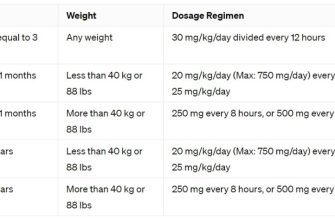
- Dosage Chart (Illustrative – Consult your doctor for personalized guidance):
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Amoxicillin 875 mg
- Completing the Treatment Course and When to Seek Further Medical Advice
- Signs Your Ear Infection Requires Further Attention
- When to Schedule a Follow-up Appointment
- Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Ear Infections
Amoxicillin 875 mg for Ear Infections: A Detailed Guide
Amoxicillin 875 mg is a common prescription for bacterial ear infections (otitis media). This high dose is often prescribed for more severe infections or those resistant to lower doses. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration.
Typical treatment involves taking one 875 mg tablet twice daily, usually with a full glass of water. Finish the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication runs out. Stopping early can lead to recurring infections and antibiotic resistance.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Less frequent, but more serious, side effects include allergic reactions (rash, hives, swelling) and difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any severe reactions.
Amoxicillin may interact with certain medications, including birth control pills and anticoagulants. Discuss all medications you’re taking with your doctor or pharmacist before starting this treatment.
While effective against many bacteria causing ear infections, Amoxicillin isn’t suitable for all types of infections. Your doctor will determine if it’s the right antibiotic for your specific case. They will consider your medical history and the results of any tests performed.
Proper ear hygiene is important. Gently clean the outer ear with a soft cloth, avoiding insertion of anything into the ear canal. This helps prevent future infections.
Pain relief is crucial. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage earache discomfort. Always follow the recommended dosage on the packaging.
Follow-up appointments with your doctor are often recommended to ensure the infection has cleared. This allows your doctor to assess your progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan if necessary.
Remember: This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Is Amoxicillin 875 mg Right for Your Ear Infection?
Amoxicillin 875 mg is a potent antibiotic, often prescribed for ear infections. However, its suitability depends on several factors.
Your Doctor’s Diagnosis: The dosage and antibiotic choice are determined by your physician based on the type and severity of your infection. They’ll consider factors like the bacteria causing the infection and your medical history. Self-treating can be dangerous; always seek professional medical advice.
Your Age and Weight: Amoxicillin dosage is adjusted based on age and weight. An 875 mg dose is generally suitable for adults, but children require lower doses. Your doctor calculates the appropriate amount for your specific needs.
Allergies: Before taking amoxicillin, inform your doctor of any allergies, particularly penicillin allergies. Amoxicillin is a penicillin-derivative, and an allergic reaction can be serious.
Other Medical Conditions: Certain pre-existing conditions can impact the suitability of amoxicillin. Kidney or liver problems, for example, might require dosage adjustments or alternative treatments. Your doctor will carefully consider your complete health profile.
Treatment Duration: Ear infections typically require a course of antibiotics for several days, following your physician’s instructions precisely. Stopping early may lead to recurrence or antibiotic resistance. Completing the prescribed course is critical.
If you have an ear infection, consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. They will determine if Amoxicillin 875 mg, or another antibiotic or treatment, is the best option for you.
Understanding Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin 875 mg
Amoxicillin 875 mg is typically prescribed as one tablet twice daily, 12 hours apart. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely, as dosage may vary depending on your specific infection and overall health. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Taking Amoxicillin 875 mg
Take the medication with a full glass of water. You can take it with or without food, but consistency is key. Choose one method and stick with it. If you experience upset stomach, try taking it with food. Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before finishing the prescription.
Missed Dose
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses. Contact your doctor or pharmacist if you have questions about missed doses.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Severe allergic reactions are rare but possible. Stop taking the medication and seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms like rash, swelling, difficulty breathing, or hives.
Dosage Chart (Illustrative – Consult your doctor for personalized guidance):
| Age Group | Typical Dosage (Amoxicillin 875 mg tablets) | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Adults | 1 tablet | Twice daily |
| Children (Dosage determined by weight and age – Consult physician) | Variable | Variable |
This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any medication.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Amoxicillin 875 mg
Amoxicillin, while generally safe, can cause side effects. Common ones include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These usually are mild and resolve without treatment. However, severe diarrhea may indicate Clostridium difficile infection, requiring immediate medical attention.
Less common, but more serious, side effects include allergic reactions. These range from skin rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Stop taking Amoxicillin and seek immediate medical help if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, or tongue, or hives.
Amoxicillin can interact with certain medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are currently taking. This includes blood thinners, like warfarin. Your doctor may need to adjust your dosage or recommend alternative treatments.
Before starting Amoxicillin, discuss your medical history with your doctor. This includes any allergies, kidney or liver problems, or a history of digestive issues. This will help determine if Amoxicillin is the right treatment for you and if any dosage adjustments are needed.
If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, or new symptoms develop during treatment, contact your doctor immediately. They will evaluate your condition and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
Proper hydration is important while on Amoxicillin. Drink plenty of fluids to help prevent dehydration, especially if you experience diarrhea.
Complete the entire course of Amoxicillin prescribed by your doctor, even if you feel better before finishing the medication. Stopping early may lead to recurrence of the infection.
Completing the Treatment Course and When to Seek Further Medical Advice
Finish your entire Amoxicillin 875 mg prescription, even if you feel better before the medication runs out. Stopping early can lead to a recurrence of the infection, making it harder to treat.
Signs Your Ear Infection Requires Further Attention
While Amoxicillin is usually effective, some symptoms indicate you need to contact your doctor immediately:
- Severe ear pain that worsens despite medication.
- High fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C) that persists or increases.
- Pus or drainage from your ear.
- Hearing loss or changes in hearing.
- Facial swelling or weakness.
- No improvement in symptoms after 72 hours of taking Amoxicillin.
When to Schedule a Follow-up Appointment
Schedule a follow-up appointment with your doctor after completing the course of Amoxicillin. This allows your doctor to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and ensure the infection is fully resolved. They may also want to discuss any lingering symptoms.
- Your doctor will determine the appropriate timing for this appointment, based on your individual case.
- They might conduct a further examination or order additional tests.
Remember, prompt medical attention is key to successful treatment and preventing complications.
Alternatives to Amoxicillin for Ear Infections
If amoxicillin isn’t suitable, your doctor might prescribe azithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic. This is often a good choice for children with mild to moderate ear infections.
Cefuroxime axetil, a cephalosporin antibiotic, represents another effective option. It’s generally well-tolerated and offers broad coverage against common ear infection bacteria.
For penicillin allergies, clindamycin, a lincosamide, provides a strong alternative. However, it’s less effective against certain bacteria compared to amoxicillin.
In some cases, your doctor may recommend a combination of antibiotics, or they might choose to wait and observe the infection’s progress, especially if it’s mild. This watchful waiting approach sometimes allows the body to fight the infection naturally.
Always discuss treatment options with your doctor. They will consider your medical history, allergy status, and the severity of the infection to determine the best course of action for you.