Need fast, reliable information on Amoxicillin Capsules IP? Focus on understanding dosage and potential side effects. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Incorrect usage can lead to treatment failure or complications.
Amoxicillin, a penicillin-type antibiotic, effectively combats bacterial infections. Common uses include treating respiratory tract infections, ear infections, and skin infections. However, it’s crucial to remember Amoxicillin only works against bacteria; it’s ineffective against viral infections like the common cold or flu.
Dosage varies greatly depending on factors such as age, weight, and the specific infection. Never adjust your dosage without consulting a physician. Typical adult doses range from 250mg to 500mg every 8 hours, but your prescription will provide the accurate details for your individual needs. Pay close attention to the frequency of administration as directed on your prescription label.
Potential side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and allergic reactions. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe allergic reactions such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Mild side effects often subside once treatment ends. Always report any unusual symptoms to your doctor.
- Amoxicillin Capsules IP: A Detailed Guide
- What is Amoxicillin and How Does it Work?
- Common Uses of Amoxicillin Capsules IP
- Respiratory Tract Infections
- Ear Infections
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Other Applications
- Dental Infections
- Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin Capsules
- Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin
- Less Common Side Effects
- Important Considerations
- Precautions and Contraindications
- Allergies
- Specific Conditions
- Potential Side Effects
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Other Important Considerations
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Storage and Disposal of Amoxicillin Capsules
- Proper Storage Practices
- Safe Disposal
- Summary of Key Storage and Disposal Information
- Further Considerations
- When to Consult a Doctor
Amoxicillin Capsules IP: A Detailed Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Amoxicillin is a penicillin-based antibiotic, effective against a wide range of bacterial infections.
Typical adult dosages range from 250mg to 500mg, taken every 8 hours. Children’s dosages are determined by weight and should be strictly adhered to as prescribed by a pediatrician.
Store capsules in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep them out of reach of children.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. More serious allergic reactions, such as skin rashes or breathing difficulties, are rare but require immediate medical attention.
Do not take amoxicillin if you have a known penicillin allergy. Inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, you are currently taking.
Amoxicillin is typically prescribed for bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, ears, skin, and urinary tract. It’s not effective against viral infections, such as the common cold or flu.
Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before the medication runs out. This prevents the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
If you experience severe or persistent side effects, contact your doctor or seek immediate medical help.
This information is for guidance only and should not replace advice from a healthcare professional. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication.
What is Amoxicillin and How Does it Work?
Amoxicillin is a penicillin-based antibiotic. It fights bacterial infections by preventing bacteria from building cell walls, ultimately leading to their death. This process is highly specific, targeting harmful bacteria without necessarily harming the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
Amoxicillin is effective against a wide range of common bacterial infections, including those affecting the ears, throat, lungs, skin, and urinary tract. Doctors often prescribe it to treat strep throat, pneumonia, bronchitis, and various skin infections.
The specific mechanism involves interfering with the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a crucial component of bacterial cell walls. Without a properly formed cell wall, bacteria cannot maintain their shape and internal pressure, resulting in their demise.
Remember, Amoxicillin only works against bacterial infections, not viral infections like the common cold or influenza. Taking it for a viral infection is ineffective and could contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Completing the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better sooner, is important to ensure complete eradication of the infection and prevent the development of resistant bacteria.
Common Uses of Amoxicillin Capsules IP
Amoxicillin capsules are primarily used to treat bacterial infections. They effectively combat a range of conditions, making them a valuable tool in healthcare.
Respiratory Tract Infections
Amoxicillin effectively targets common respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia caused by susceptible bacteria. It helps reduce symptoms and promotes faster recovery. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Ear Infections
Otitis media, a common middle ear infection, often responds well to amoxicillin treatment. The medication helps clear the infection and alleviate pain and inflammation. Accurate diagnosis from a healthcare professional is crucial.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Amoxicillin proves useful in treating various skin and soft tissue infections caused by bacteria. These can include cellulitis and abscesses. Prompt medical attention is important for appropriate diagnosis and treatment strategy.
Urinary Tract Infections
Amoxicillin can be effective in addressing uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs). However, the choice of antibiotic depends on the specific bacteria involved and the severity of the infection, as determined by a doctor.
Other Applications
Amoxicillin, in combination with other medications, is sometimes used to treat certain types of stomach ulcers and other infections.
| Infection Type | Typical Amoxicillin Use | Important Note |
|---|---|---|
| Bronchitis | Treats bacterial bronchitis | Requires doctor’s prescription |
| Pneumonia | Combats bacterial pneumonia | Part of a broader treatment plan |
| Otitis Media | Reduces pain and clears infection | Dosage depends on age and severity |
| Cellulitis | Treats bacterial skin infections | Requires prompt medical attention |
Dental Infections
Amoxicillin can be prescribed to treat certain dental infections, particularly those following procedures or associated with gum disease. Always follow the dentist’s instructions for dosage and duration.
Dosage and Administration of Amoxicillin Capsules
Always follow your doctor’s prescription. Dosage depends on your specific condition, weight, and age. Do not alter the prescribed dosage without consulting your doctor.
Amoxicillin capsules are typically taken orally. Swallow the capsules whole with a glass of water. Avoid chewing or crushing them, as this can affect absorption.
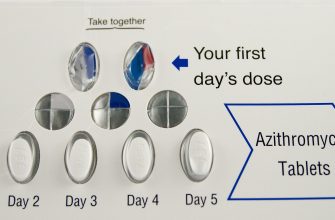
- Typical Adult Dosage: Ranges from 250mg to 500mg, taken every 8 or 12 hours, depending on the infection.
- Typical Child Dosage: Varies significantly based on weight and infection; your doctor will provide specific instructions.
- Frequency: Commonly prescribed as twice-daily or three-times-daily doses, according to your doctor’s instructions.
Duration of Treatment: Complete the full course of treatment prescribed by your doctor, even if you feel better before finishing the medication. Stopping early can lead to recurring infection.
Food and Intake: Generally, Amoxicillin can be taken with or without food, but consistency is key. Choose one method and stick to it for optimal absorption.
Missed Dose: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s nearly time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
Possible Side Effects: Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe allergic reactions like rash, hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Storage: Store Amoxicillin capsules at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight.
- Disposal: Properly dispose of any unused medication as per your local guidelines.
Important Note: This information is for general knowledge and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance regarding Amoxicillin usage.
Potential Side Effects of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin, while generally safe, can cause side effects. The most common are diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These usually are mild and resolve without treatment. However, if diarrhea becomes severe or persistent, contact your doctor immediately, as it could indicate a serious infection like *Clostridium difficile* colitis.
Less Common Side Effects
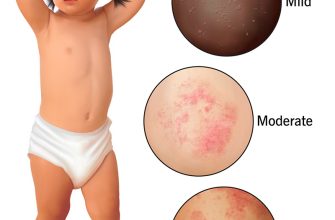
Less frequently, you might experience skin rashes, including hives. These rashes can range from mild irritation to more serious reactions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a rare but potentially life-threatening condition. Seek immediate medical attention if you develop a severe rash, swelling of your face, lips, or tongue, or difficulty breathing. These are signs of a severe allergic reaction.
Other less common side effects include yeast infections (thrush), especially in women, and changes in your blood counts, which your doctor can monitor through blood tests. A rare side effect is a neurological complication, such as seizures, which necessitates immediate medical intervention.
Important Considerations
Before starting Amoxicillin, inform your doctor of any existing allergies, especially penicillin allergies, as cross-reactivity is possible. Also mention other medications you’re taking, as interactions can occur. If you experience any concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider for advice. They can help assess the severity of your symptoms and provide appropriate management.
Precautions and Contraindications
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, before starting amoxicillin. This helps prevent potential drug interactions.
Allergies
Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic. If you have a penicillin allergy, you should avoid amoxicillin. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can range from mild skin rash to severe anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention. Discuss your allergy history thoroughly with your doctor.
Specific Conditions
- Kidney disease: Amoxicillin is primarily excreted through the kidneys. People with kidney problems may need a reduced dosage or a different antibiotic altogether. Your doctor will assess your kidney function before prescribing.
- Liver disease: While rare, liver problems can occur. Your doctor will monitor you for any signs of liver damage if you have pre-existing liver conditions.
- Infectious mononucleosis (mono): Amoxicillin use during mono can sometimes cause a rash. Your physician will determine the most appropriate treatment.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Less common, but potentially serious, effects include severe allergic reactions, seizures, and colitis (inflammation of the colon). Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience any serious or concerning side effects.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Pregnancy: Amoxicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy, but your doctor will weigh the risks and benefits based on your individual circumstances.
- Breastfeeding: Amoxicillin passes into breast milk. Your doctor can advise on the best course of action, considering the potential impact on the infant.
Other Important Considerations
- Dosage: Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
- Missed dose: Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
- Storage: Store amoxicillin capsules as directed on the label to maintain their effectiveness.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, or a severe skin rash. These could indicate a serious allergic reaction.
Interactions with Other Medications
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, before starting amoxicillin. This helps prevent potentially harmful interactions.
Amoxicillin can interact with several medications. Here are some key examples:
- Oral contraceptives: Amoxicillin may decrease the effectiveness of some birth control pills. Consider using additional contraceptive methods while taking amoxicillin.
- Methotrexate: Amoxicillin can increase the risk of methotrexate toxicity. Your doctor might need to adjust your methotrexate dosage.
- Warfarin: This blood thinner interacts with amoxicillin, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding. Close monitoring of your INR levels is crucial.
- Probenecid: This medication can increase amoxicillin levels in your blood, potentially leading to side effects. Your doctor will consider this interaction when prescribing.
Specific interactions vary depending on individual factors and other medications involved. This list is not exhaustive. Always discuss potential drug interactions with your doctor or pharmacist before starting or stopping any medication.
Never stop taking prescribed medication without consulting your doctor, even if you believe a drug interaction is occurring.
- Report any unusual symptoms you experience while taking amoxicillin.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
- Maintain an updated list of all your medications.
Storage and Disposal of Amoxicillin Capsules
Store amoxicillin capsules in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Ideal storage temperature is between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). Keep the capsules in their original container to maintain their quality and protect them from degradation.
Proper Storage Practices
Always check the expiry date printed on the packaging. Discard expired amoxicillin. Avoid storing the capsules in damp areas like bathrooms. Extreme temperatures can affect the drug’s potency.
Safe Disposal
Never flush unused medications down the toilet or drain. This can contaminate water supplies. Follow local guidelines for medication disposal. Many pharmacies offer drug take-back programs. Alternatively, you can mix the capsules with undesirable substances, such as used coffee grounds, and then seal them in a plastic bag before discarding in your household trash.
Summary of Key Storage and Disposal Information
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Storage Temperature | 15°C – 30°C (59°F – 86°F) |
| Storage Location | Cool, dry place, away from sunlight and moisture |
| Container | Original container |
| Disposal Method | Do not flush; use take-back program or mix with undesirable substances before trash disposal |
Further Considerations
If you have any concerns about storing or disposing of your amoxicillin, consult your pharmacist or doctor for personalized advice. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation.
When to Consult a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience a severe allergic reaction, characterized by difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, or hives. These symptoms require emergency treatment.
Contact your doctor if your symptoms worsen or don’t improve after completing the prescribed course of amoxicillin. This includes persistent fever, ongoing diarrhea, or a new rash.
Report any new or unusual symptoms developing while taking amoxicillin, such as dark urine, pale stools, or yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice).
If you experience severe stomach pain, persistent vomiting, or bloody diarrhea, contact your doctor immediately. These could indicate a serious complication.
Consult your doctor before taking amoxicillin if you have a history of allergic reactions to penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics. They will assess your risk and advise accordingly.
If you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant, discuss the use of amoxicillin with your doctor before starting treatment.
Always inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are currently taking before starting amoxicillin.