Always follow your doctor’s instructions, but for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), a common Bactrim dosage is two double-strength tablets (1600mg sulfamethoxazole/400mg trimethoprim) once daily for three days. This is a widely used regimen, but your individual needs may differ.
For other infections, such as bronchitis or ear infections, the prescribed dose and duration will vary. Expect higher daily dosages, possibly split into two doses per day, and treatment durations extending to 7-14 days depending on the severity and type of infection. Precise instructions are crucial. Carefully review your prescription label, or contact your physician or pharmacist for clarification if needed.
Remember: Never adjust your medication without consulting your healthcare provider. Incorrect dosing can lead to treatment failure or adverse reactions. Always discuss any concerns regarding medication side effects or the efficacy of the treatment with your physician. Accurate information and adherence to prescribed regimens are key for successful treatment.
- Bactrim Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
- Standard Adult Dosage for Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Alternative Adult Dosages
- Pediatric Dosages
- Important Considerations
- Dosage Forms
- When to Contact Your Doctor
- Standard Bactrim Dosage for Common Infections
- Adjusting Bactrim Dosage Based on Renal Function
- Bactrim Dosage for Specific Patient Populations
- Dosage Adjustments Based on Renal Function
- Dosage Considerations for Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Dosage Adjustments for Liver Disease
- Understanding Bactrim Dosage Forms and Administration
- Oral Dosage Forms
- Important Administration Notes
- Other Forms
- Missed Doses and Potential Side Effects of Incorrect Bactrim Dosage
Bactrim Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions. Dosage depends heavily on the infection being treated, your weight, and your overall health. Self-medicating is dangerous; never adjust your dose without consulting a healthcare professional.
Standard Adult Dosage for Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
A common regimen involves two double-strength tablets (1600mg sulfamethoxazole/800mg trimethoprim) once daily for 5-10 days. Your doctor might prescribe a different schedule.
Alternative Adult Dosages
- For other infections: Dosages vary significantly. Your doctor will determine the correct dose and duration based on your specific condition.
- Kidney problems: If you have kidney disease, your doctor will likely adjust your dose to prevent the buildup of Bactrim in your system.
- Severe infections: Higher doses may be necessary, often administered intravenously in a hospital setting.
Pediatric Dosages
Bactrim is used in children, but the dosage is calculated based on weight. A doctor will provide precise instructions, considering the child’s age and weight. Never administer Bactrim to a child without a doctor’s prescription.
Important Considerations
- Allergic reactions: Stop taking Bactrim and seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms like rash, hives, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Sun sensitivity: Bactrim can increase your sun sensitivity. Use sunscreen and protective clothing when spending time outdoors.
- Interactions: Inform your doctor of all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as Bactrim can interact with other medications.
- Complete the course: Finish the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before the prescription is complete. This helps prevent the infection from returning.
Dosage Forms
Bactrim is available in various forms, including tablets, suspensions, and intravenous solutions. The form your doctor prescribes will depend on your individual needs and the infection being treated.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Contact your doctor if you experience any side effects or if your symptoms don’t improve after a few days of treatment. They can provide guidance and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Standard Bactrim Dosage for Common Infections
Dosage depends on the infection and your individual health. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
For uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), a common regimen is one double-strength tablet twice daily for five to seven days. This equates to 160/800 mg twice daily.
For acute uncomplicated bronchitis, the standard adult dose is usually one double-strength tablet twice daily for 14 days (160/800 mg twice daily). Your physician may adjust duration based on your response.
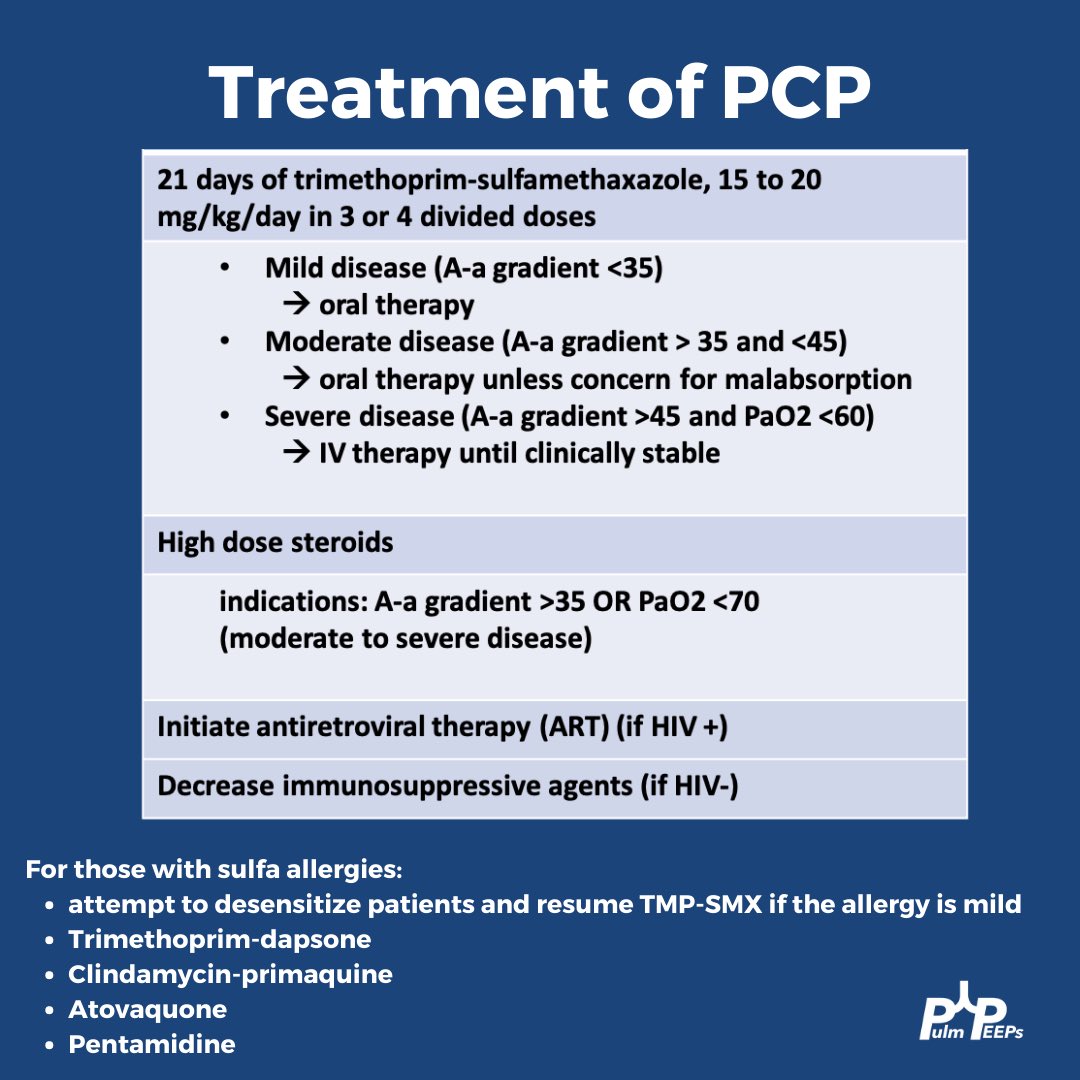
Treatment of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) necessitates a higher dose, often considerably longer treatment periods. This is determined individually by your doctor based on your condition and response to treatment. Self-medicating for PCP is incredibly dangerous.
| Infection | Typical Dosage (Adults) | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Uncomplicated UTI | One double-strength tablet (160/800 mg) twice daily | 5-7 days |
| Acute Uncomplicated Bronchitis | One double-strength tablet (160/800 mg) twice daily | 14 days (may vary) |
| PCP | Varies significantly; consult your physician | Varies significantly; consult your physician |
Children’s dosages are calculated based on weight and the specific infection. Never administer adult Bactrim to children. Consult your pediatrician for appropriate pediatric dosing guidelines.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from your healthcare provider before starting or altering any medication.
Adjusting Bactrim Dosage Based on Renal Function
Patients with impaired kidney function require Bactrim dosage adjustments to prevent drug accumulation and toxicity. Creatinine clearance (CrCl) is the primary determinant. You should use a validated formula, such as the Cockcroft-Gault equation, to calculate CrCl.
For patients with CrCl less than 30 mL/min, reduce the Bactrim dose. A common approach is to administer half the usual dose, or lengthen the dosing interval. Always consult relevant prescribing information for specific recommendations based on the indication and patient’s clinical status.
For example, if the standard dose is 160/800 mg twice daily, a patient with CrCl less than 30 mL/min might receive 80/400 mg twice daily, or 160/800 mg once daily. Closely monitor patients for adverse effects, particularly hematological changes and hyperkalemia. Regular serum creatinine and complete blood counts are vital.
Patients on hemodialysis require specific dosage adjustments. Administer the medication after dialysis. Consult the drug’s prescribing information for the recommended regimen in this population. The dose and frequency may vary depending on the dialysis schedule.
Always individualize the dosage based on the patient’s specific CrCl, overall health status, and the severity of the infection. Regularly monitor kidney function during Bactrim therapy, especially in patients at risk of renal impairment.
Remember, this information is for guidance only. Always refer to the most current product labeling and consult with a healthcare professional for accurate and individualized dosage recommendations.
Bactrim Dosage for Specific Patient Populations
Adjusting Bactrim dosage is crucial for certain patient groups. For infants under two months, Bactrim is generally avoided due to potential kernicterus risk. For those two months to five years old, the dosage is often calculated based on weight, typically 6-8 mg/kg of sulfamethoxazole every 12 hours. Always confirm this with a pediatrician.
Dosage Adjustments Based on Renal Function
Patients with impaired kidney function require lower doses. Creatinine clearance (CrCl) guides this adjustment. Consult a physician or pharmacist to determine the correct dosage based on the patient’s specific CrCl. They’ll use established formulas to calculate the adjusted dose, ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Dosage Considerations for Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Bactrim use during pregnancy should be carefully considered and is usually reserved for serious infections where the benefits outweigh potential risks. A physician will guide this decision. Similar caution is advised for breastfeeding mothers, balancing the maternal need with potential effects on the infant. Discuss options with your doctor.
Dosage Adjustments for Liver Disease
While Bactrim is mostly metabolized by the kidneys, liver disease might still impact drug levels. Consult a physician for dosage adjustments in these cases. Close monitoring might be necessary.
Understanding Bactrim Dosage Forms and Administration
Bactrim, a combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, comes in several forms. Choose the form best suited to your needs and always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Oral Dosage Forms
- Tablets: Available in various strengths, usually swallowed with water. Dosage depends on infection severity and patient factors.
- Suspension (Liquid): Convenient for children or individuals who have difficulty swallowing pills. Shake well before each dose. Dosage is measured using a marked measuring spoon or syringe.
Important Administration Notes
- Take with Food: Taking Bactrim with food can minimize stomach upset.
- Full Course of Treatment: Complete the entire prescribed course, even if you feel better before finishing. This prevents resistance development.
- Fluid Intake: Drink plenty of fluids while taking Bactrim to help prevent kidney problems. This is especially important with higher doses.
- Missed Dose: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Don’t double the dose.
- Allergies: Inform your doctor about any allergies, particularly to sulfa drugs, before starting Bactrim.
- Drug Interactions: Bactrim can interact with other medications. Discuss all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, with your doctor or pharmacist.
Other Forms
While less common, Bactrim may be available in intravenous (IV) form for severe infections, administered in a hospital setting by healthcare professionals. Dosage and administration for IV forms differ significantly from oral forms. Always follow a physician’s guidance.
This information is for guidance only. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice and the most up-to-date information on Bactrim dosage and administration.
Missed Doses and Potential Side Effects of Incorrect Bactrim Dosage
If you miss a Bactrim dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses to make up for a missed one. Contact your doctor for advice if you frequently miss doses or are unsure how to proceed.
Incorrect Bactrim dosage can lead to treatment failure, meaning your infection may not clear up completely. This increases the risk of antibiotic resistance, making future infections harder to treat. You may also experience a resurgence of your symptoms.
Side effects from incorrect dosing vary, but may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, skin rashes, and abdominal pain. More serious side effects, while rare, can involve severe allergic reactions, blood disorders, and kidney problems. These require immediate medical attention. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist of any side effects you experience.
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and duration of treatment precisely. Proper adherence significantly reduces the risk of complications and ensures optimal treatment outcome. If you have questions about your medication, don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider for clarification.