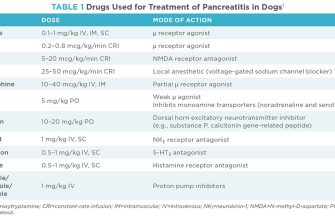
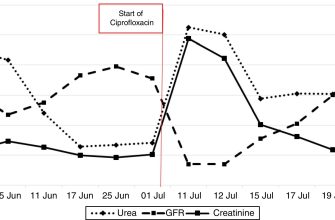
Need information on Cipro 750 mg tablets? Focus on understanding its uses, potential side effects, and proper usage. This guide provides clear, concise details to help you make informed decisions about your health.
Ciprofloxacin, the active ingredient in Cipro 750 mg tablets, is a powerful antibiotic effective against various bacterial infections. Common uses include treating urinary tract infections, respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia, and certain types of skin infections. Remember, antibiotics target bacteria, not viruses; thus, Ciprofloxacin will be ineffective against viral illnesses like the common cold or influenza.
Always consult your doctor before starting Ciprofloxacin. They will assess your specific needs and determine if this antibiotic is the right choice for your condition. Potential side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and headache. Serious, though rare, side effects exist, including tendonitis and allergic reactions. Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Take Ciprofloxacin exactly as prescribed. Do not stop taking it prematurely, even if you feel better, to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria. Proper dosage and duration are critical to treatment success. Following your doctor’s instructions precisely minimizes the risk of complications and ensures optimal treatment outcomes. Store the tablets as instructed on the label to maintain efficacy.
- Cipro 750 mg Tablet: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin
- Common Uses
- Dosage and Administration
- Possible Side Effects
- Precautions and Interactions
- Storage
- Missed Dose
- Disclaimer
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin 750mg Tablets: Uses and Indications
- Specific Infections Treated
- Important Considerations
- Dosage and Administration: A Practical Guide
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions: What to Expect
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Precautions
- Ciprofloxacin 750mg vs. Other Dosages and Alternatives: When to Choose 750mg
Cipro 750 mg Tablet: A Detailed Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. This guide provides supplementary information, not medical advice.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, the active ingredient in Cipro 750 mg tablets, is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It fights bacterial infections by interfering with their DNA replication. This stops bacterial growth and allows your body to heal.
Common Uses
- Respiratory tract infections (e.g., pneumonia, bronchitis)
- Skin and skin structure infections
- Bone and joint infections
- Certain urinary tract infections
- Anthrax (in specific situations)
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor determines the correct dose and duration of treatment based on your specific infection and health. Typical dosages range from 250 mg to 750 mg, taken twice daily. Swallow tablets whole with water; avoid crushing or chewing.
Possible Side Effects
Side effects vary in severity and frequency. Common ones include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Abdominal pain
- Insomnia
Serious, though rare, side effects require immediate medical attention. These can include tendon rupture, allergic reactions, and central nervous system effects.
Precautions and Interactions
- Inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Ciprofloxacin may interact with certain medications.
- Avoid caffeine and other stimulants which may enhance insomnia.
- Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, especially if experiencing diarrhea.
- Avoid sun exposure; use sunscreen if necessary due to increased photosensitivity.
- Report any unusual symptoms promptly to your healthcare provider.
Storage
Store Cipro 750 mg tablets at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep out of reach of children.
Missed Dose
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Do not double the dose.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition. This guide is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin 750mg Tablets: Uses and Indications
Ciprofloxacin 750mg tablets are a powerful antibiotic, effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria. Doctors prescribe them to treat various infections, primarily those caused by susceptible gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria. Common uses include treating urinary tract infections (UTIs), pneumonia, sinusitis, and skin infections. Severe cases of anthrax and plague are also treated with this medication.
Specific Infections Treated
This high dosage is particularly useful in treating severe or complicated infections. For example, a complicated UTI might necessitate a 750mg dose for faster bacterial clearance. Similarly, severe pneumonia requiring hospitalization often benefits from this higher strength. Always consult your doctor to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment. Your individual health status and infection severity will influence treatment decisions.
Important Considerations
Remember, Ciprofloxacin is a prescription medication; never self-medicate. Before starting treatment, discuss any potential drug interactions with your physician or pharmacist. Common side effects can include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. More serious, though rare, side effects include tendon rupture and allergic reactions. Report any adverse effects immediately to your healthcare provider. Appropriate antibiotic stewardship is crucial; Ciprofloxacin should only be used when necessary to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Dosage and Administration: A Practical Guide
Ciprofloxacin 750 mg tablets are typically administered once or twice daily, depending on your specific infection and your doctor’s prescription. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Swallow the tablet whole with a full glass of water. Do not crush, chew, or break the tablet. Taking it with food may reduce stomach upset, but this should be discussed with your prescribing physician.
The duration of treatment varies greatly depending on the type of infection. You should complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before the medication is finished. Stopping early can lead to the infection returning, and potentially becoming resistant to treatment.
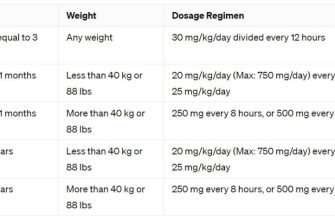
| Possible Infection Types | Typical Dosage | Treatment Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) | Once or twice daily | 7-14 days |
| Respiratory Infections (Pneumonia, Bronchitis) | Twice daily | 7-14 days (or longer, depending on severity) |
| Skin Infections | Twice daily | 7-14 days |
Missed Dose: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Do not double the dose to make up for a missed one. Contact your doctor if you miss multiple doses.
Side Effects: Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. More serious side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you experience any concerning symptoms.
This information is for guidance only and does not replace the advice of a healthcare professional. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking Ciprofloxacin or any medication.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions: What to Expect
Ciprofloxacin, the active ingredient in Cipro 750 mg tablets, can cause various side effects. Common ones include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These usually are mild and resolve without treatment. However, severe diarrhea, particularly if bloody or watery, requires immediate medical attention as it may indicate Clostridium difficile infection.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Beyond diarrhea, you might experience abdominal pain, indigestion, or constipation. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can often mitigate these issues. If symptoms persist or worsen, contact your doctor.
Other Potential Side Effects
Less common but potentially serious side effects include tendonitis (inflammation of tendons), particularly in the Achilles tendon. This risk is increased in older adults and those taking corticosteroids. Report any tendon pain or swelling immediately. Allergic reactions, ranging from mild skin rash to severe anaphylaxis, are also possible. Stop taking Cipro and seek immediate medical care if you experience symptoms like hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Headaches, dizziness, and insomnia are other reported side effects.
Precautions
Before taking Cipro, inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions, especially liver or kidney problems, myasthenia gravis (a neuromuscular disorder), or epilepsy. Also disclose all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, as interactions can occur. Cipro can increase sensitivity to sunlight, so use sunscreen and protective clothing during sun exposure. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should discuss the risks and benefits with their doctor before using Cipro. Regularly monitor your health and don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you have concerns.
Ciprofloxacin 750mg vs. Other Dosages and Alternatives: When to Choose 750mg
Select the 750mg Ciprofloxacin tablet for treating serious infections like complicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), complicated intra-abdominal infections, or pneumonia. This higher dose provides a stronger, faster antibacterial effect compared to lower dosages.
For uncomplicated UTIs, a lower dosage, such as 250mg or 500mg, might suffice. Your doctor will assess the severity of your infection and tailor the dose accordingly.
Alternatives exist, such as levofloxacin or moxifloxacin. However, Ciprofloxacin remains a reliable choice, especially for infections resistant to other antibiotics. Your doctor will consider factors like antibiotic resistance patterns and your individual health when choosing the right antibiotic.
Important Note: Always consult your physician before starting or changing your antibiotic treatment. They’ll evaluate your specific situation and determine the most appropriate dosage and medication to effectively combat your infection. Self-medication can be dangerous.
The 750mg dose isn’t universally superior; it’s a powerful option for specific severe infections where a higher concentration is needed for optimal treatment. Lower doses are suitable for less severe cases, and alternatives offer additional treatment options depending on the infection and your individual health.