For uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), a common Ciprofloxacin dosage is 250mg twice daily for 3-7 days. This is a guideline, and your doctor will determine the best course of treatment based on your individual health status.
Remember, never self-medicate. This dosage information is for educational purposes only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or other qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. They will consider factors like your age, kidney function, and the severity of your infection to prescribe the most appropriate dose and duration.
Important Note: Ciprofloxacin can have side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Less common but more serious side effects also exist. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern; adhering to your prescribed course of medication is vital for successful treatment and preventing future resistance.
Your doctor may also perform tests to confirm the causative bacteria and its susceptibility to Ciprofloxacin before prescribing this antibiotic. This ensures targeted treatment and avoids unnecessary antibiotic use.
- Cipro Dose for Uncomplicated UTI: A Detailed Guide
- Standard Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Uncomplicated UTIs
- Duration of Ciprofloxacin Treatment for Uncomplicated UTIs
- Factors Influencing Treatment Length
- When to Contact Your Doctor
- Possible Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin and What to Do
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Severe Symptoms Requiring Urgent Care
- Other Reasons to Contact Your Doctor
- When to Go to the Emergency Room
- Remember
- Alternative Antibiotics for Uncomplicated UTIs
- Important Disclaimer: Consult Your Doctor
- Factors Influencing Ciprofloxacin Dosage
- Potential Side Effects and Alternatives
- Seeking Immediate Medical Attention
Cipro Dose for Uncomplicated UTI: A Detailed Guide
For most adults with an uncomplicated UTI, the standard Ciprofloxacin dose is 250mg twice daily for 3-7 days. This dosage may vary depending on the severity of your infection and your doctor’s assessment.
Specific duration recommendations:
- 3 days: This shorter course might be considered for some patients with mild infections, but this is at your doctor’s discretion.
- 7 days: This is a more common treatment duration, ensuring complete eradication of the bacteria.
Important factors influencing dosage and duration:
- Bacterial identification: Your doctor will conduct tests to identify the specific bacteria causing your UTI. This helps determine if Ciprofloxacin is the appropriate antibiotic and influences the prescription.
- Severity of symptoms: More severe symptoms may require a longer course of treatment.
- Patient factors: Pre-existing health conditions, kidney function, and allergies play a critical role. Always inform your doctor about your health history.
Possible adjustments:
- Kidney impairment: Reduced kidney function necessitates dose adjustments to prevent drug accumulation. Your doctor will calculate the appropriate dose based on your creatinine clearance.
- Age considerations: Dosage might be adjusted for elderly patients due to potential age-related changes in kidney function. Again, this is determined by your doctor.
Never adjust your Ciprofloxacin dose or duration without consulting your physician. Incorrect use can lead to antibiotic resistance and treatment failure. Always follow the prescribed regimen and complete the full course, even if symptoms improve before the end of the treatment period.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Standard Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Uncomplicated UTIs
For most adults with uncomplicated UTIs, the typical Ciprofloxacin dosage is 250 mg twice daily for 3 to 7 days. Your doctor will determine the precise duration based on your individual needs and response to treatment.
A 500 mg once-daily regimen may be considered in some cases, but this is less common for uncomplicated UTIs. Always follow your physician’s prescription instructions explicitly.
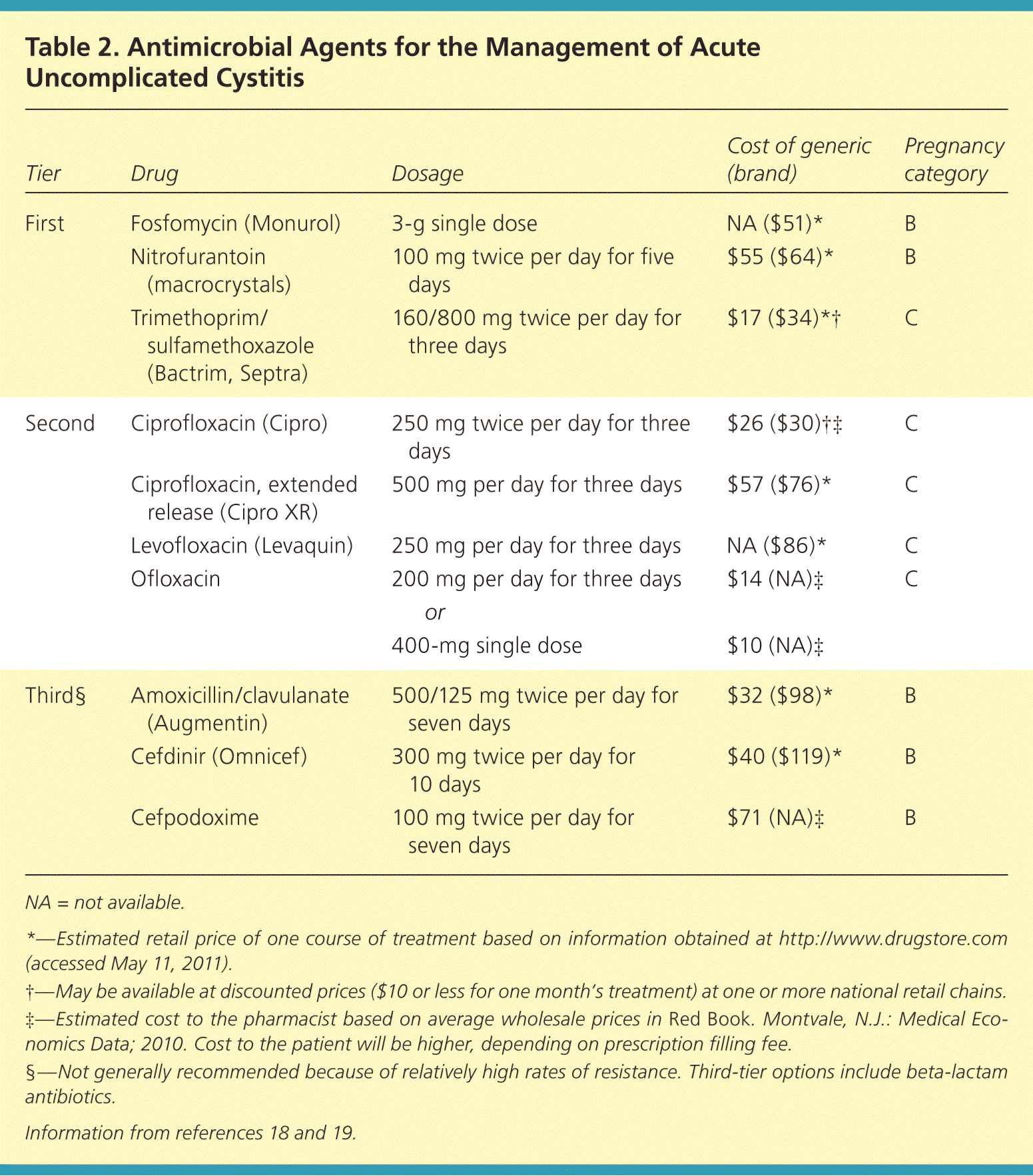
Children’s dosing is different and should always be determined by a pediatrician. Never administer adult dosages to children.
Factors like kidney function and other medical conditions can affect the appropriate Ciprofloxacin dosage. Open communication with your doctor is key to ensuring safe and effective treatment.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and should not substitute advice from a healthcare professional. Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication.
Duration of Ciprofloxacin Treatment for Uncomplicated UTIs
The typical course of Ciprofloxacin for an uncomplicated UTI is 3 to 7 days. Doctors often prescribe a 3-day course for patients with mild symptoms and a good response to treatment. However, a 7-day course might be necessary for more severe infections or if symptoms persist after the initial 3 days.
Factors Influencing Treatment Length
Several factors influence the prescribed duration. These include the severity of your symptoms, the results of any urine culture (identifying the bacteria and its susceptibility to Ciprofloxacin), your overall health, and your physician’s clinical judgment. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never shorten or lengthen your course of antibiotics without their explicit approval. Failing to complete the prescribed treatment can lead to recurrent infections or antibiotic resistance.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if symptoms worsen, new symptoms develop, or your symptoms haven’t improved after the initial 3 days of treatment. This proactive approach ensures timely management of your infection and minimizes the risk of complications.
Possible Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin and What to Do
Ciprofloxacin, while effective, can cause side effects. Most are mild and temporary, but some require medical attention. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. If you experience these, drink plenty of fluids and consider over-the-counter medications for relief. However, persistent or severe diarrhea could indicate Clostridium difficile infection; contact your doctor immediately if this occurs.
Less common but serious side effects need prompt medical evaluation. These include:
| Side Effect | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe allergic reaction (rash, hives, swelling, difficulty breathing) | Seek immediate medical help. This is a medical emergency. |
| Tendinitis or tendon rupture (pain, swelling, or inability to use a joint) | Stop taking Ciprofloxacin and consult your doctor. Avoid strenuous activity. |
| Seizures | Stop taking Ciprofloxacin and seek immediate medical attention. |
| Peripheral neuropathy (numbness, tingling, or pain in the extremities) | Contact your doctor; they may adjust your treatment. |
| Photosensitivity (increased sun sensitivity) | Use sunscreen with a high SPF and wear protective clothing when outdoors. |
This list isn’t exhaustive, and individual reactions vary. Always report any unusual symptoms to your doctor. They can assess your situation and advise on appropriate management.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Contact your doctor or seek immediate medical care if your UTI symptoms worsen or don’t improve after 72 hours of taking Cipro, even with some improvement.
Severe Symptoms Requiring Urgent Care
- High fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C)
- Severe abdominal pain or back pain
- Chills
- Vomiting
- Blood in your urine
- Inability to urinate
These symptoms could indicate a more serious kidney infection or other complication requiring prompt treatment.
Other Reasons to Contact Your Doctor
- You experience new or worsening symptoms while taking Cipro.
- You have a history of kidney problems or other medical conditions that might affect how you react to Cipro.
- You are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- You are allergic to Cipro or other fluoroquinolone antibiotics.
- Your symptoms don’t improve after three days of taking the medication as prescribed.
Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor if you have any concerns about your UTI or your treatment.
When to Go to the Emergency Room
Go to the nearest emergency room if you experience any of these severe symptoms. Delaying treatment could have serious consequences.
Remember
This information is for general knowledge and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or stopping any medication.
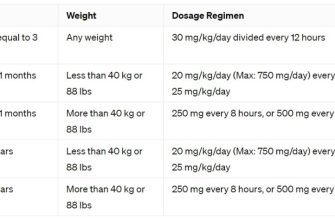
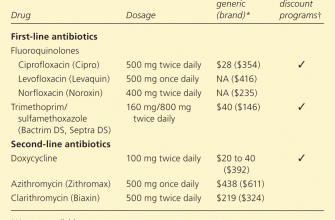
Alternative Antibiotics for Uncomplicated UTIs
For uncomplicated UTIs, Nitrofurantoin is a common alternative to Ciprofloxacin. It’s generally well-tolerated and effective against many common UTI bacteria. The typical dosage is 100mg four times daily for five to seven days.
Another option is Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX), often prescribed as Bactrim or Septra. This combination targets a broad range of UTI-causing bacteria. A typical regimen involves two tablets twice daily for three days. However, increasing bacterial resistance necessitates careful consideration of local resistance patterns before prescribing.
Fosfomycin is a single-dose antibiotic, making it convenient for patients. Its efficacy is comparable to other options for uncomplicated UTIs. Consult prescribing information for specific dosage instructions.
Cephalexin is another broad-spectrum antibiotic sometimes used. It is usually administered orally. A common dosage is 250-500mg four times daily for seven to ten days. Resistance is a concern, so check local susceptibility data.
Remember, antibiotic choice depends on several factors, including patient allergies, bacterial resistance patterns in your area, and individual patient circumstances. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Important Disclaimer: Consult Your Doctor
This information is for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Self-treating a UTI can be risky. A proper diagnosis requires a doctor’s evaluation. They will perform tests to confirm the infection and identify the specific bacteria causing it. This ensures you receive the correct antibiotic and dosage, minimizing the risk of complications and antibiotic resistance.
Factors Influencing Ciprofloxacin Dosage
Several factors influence the appropriate Ciprofloxacin dosage for a UTI, including your age, weight, kidney function, and the severity of your infection. Your doctor will consider these factors before prescribing any medication.
Potential Side Effects and Alternatives
Ciprofloxacin, like all antibiotics, can cause side effects. These range from mild (nausea, diarrhea) to more serious (tendonitis, allergic reactions). Your doctor will discuss these potential side effects and explore alternative antibiotics if necessary, especially if you have allergies or pre-existing conditions. Ignoring these considerations could harm your health.
Seeking Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe abdominal pain, high fever, or signs of a serious infection. Delaying treatment can lead to complications like kidney infection or sepsis.