Suspect epididymitis? Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) is often prescribed, but its effectiveness varies. Bacterial infections are the usual cause, and Cipro targets specific bacteria, making a proper diagnosis crucial.
Accurate identification of the infecting bacteria is paramount. A urine test and physical exam help determine the culprit. If the infection stems from E. coli or other Cipro-susceptible bacteria, it’s likely to be effective. However, increasing antibiotic resistance necessitates a tailored approach based on culture results.
Important: Cipro isn’t a first-line treatment for all cases. Doctors consider several factors, including the severity, patient’s medical history, and potential drug interactions. Alternatives exist, such as other antibiotics or even surgical drainage in severe instances. Always follow a doctor’s prescription and complete the entire course of treatment, regardless of symptom improvement.
Potential side effects range from mild gastrointestinal issues to more serious allergic reactions. Discuss any concerns or pre-existing conditions with your physician. Self-medicating is risky; proper medical guidance is vital for optimal treatment and minimizing potential complications.
- Ciprofloxacin and Epididymitis: A Detailed Look
- What is Epididymitis?
- Causes and Symptoms
- Diagnosis and Treatment
- Seeking Medical Attention
- Cipro and Epididymitis
- Ciprofloxacin: Mechanism of Action Against Epididymitis
- Targeting Common Epididymitis Bacteria
- Considerations for Treatment
- Common Causes of Epididymitis and Ciprofloxacin’s Effectiveness
- When Ciprofloxacin is the Appropriate Treatment
- Factors Influencing Ciprofloxacin Use
- Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
- Alternative Treatment Options for Epididymitis
- Dietary Adjustments
- Herbal Remedies
- Acupuncture
- Comparison Table: Treatment Approaches
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Long-Term Outlook and Prevention Strategies
Ciprofloxacin and Epididymitis: A Detailed Look
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, frequently treats epididymitis caused by bacterial infection. Its effectiveness depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection. Common culprits include E. coli and Chlamydia trachomatis; Ciprofloxacin is generally effective against E. coli but less so against Chlamydia, often necessitating a different antibiotic like doxycycline for co-infection.
A doctor determines the appropriate antibiotic based on a patient’s symptoms, medical history, and test results. Urine and/or semen cultures identify the infectious agent, guiding antibiotic selection. Self-treating epididymitis with Ciprofloxacin is strongly discouraged; misdiagnosis can lead to delayed treatment and complications.
Typical Ciprofloxacin dosage for epididymitis involves a 500mg or 750mg tablet twice daily for 10-14 days, but your doctor will prescribe the precise regimen. Always follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously.
While generally well-tolerated, side effects like nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain are possible. More serious, though less common, side effects include tendonitis and aortic aneurysm risk, particularly in older adults. Report any unusual symptoms immediately to your healthcare provider.
Treatment success depends on several factors, including the severity of the infection, adherence to prescribed medication, and the patient’s overall health. Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve. Failure to finish the prescribed regimen may result in recurring infection or antibiotic resistance.
Epididymitis requires prompt medical attention. Ciprofloxacin plays a significant role in treatment, but its application should be guided by a medical professional. Never self-medicate. Seek professional medical care to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
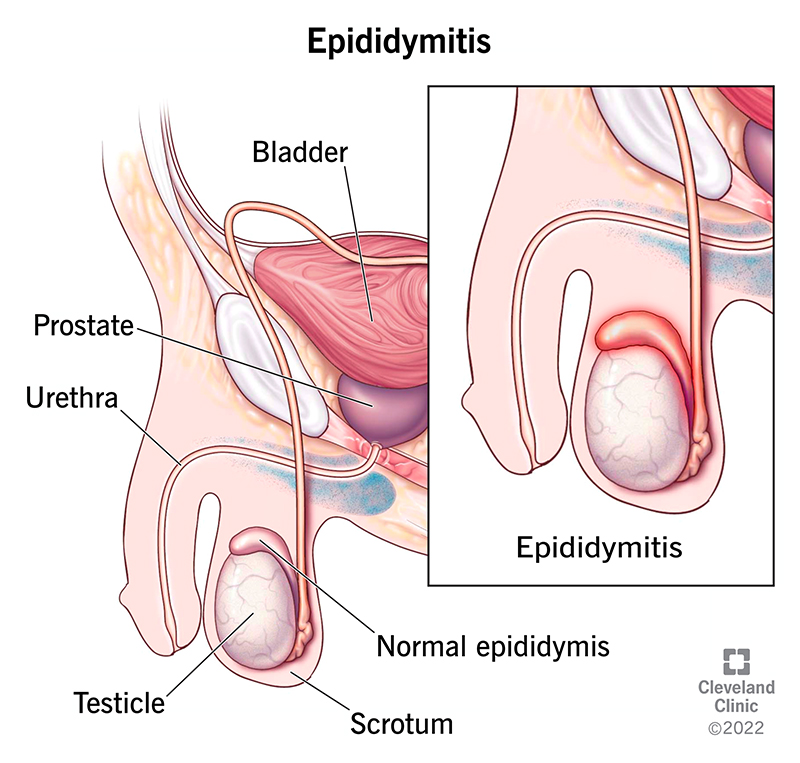
What is Epididymitis?
Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis, a tube-like structure located on the back of each testicle. This tube stores and carries sperm.
Causes and Symptoms
Several factors can cause epididymitis. Common culprits include bacterial infections, often stemming from sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia and gonorrhea, or urinary tract infections. Less frequently, non-infectious causes like injury or blockage of the epididymis may also be responsible.
- Pain: Scrotum swelling and tenderness are common. Pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, sharp pain.
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling of one or both testicles.
- Discomfort during urination or ejaculation: Painful urination or ejaculation can accompany these symptoms.
- Fever and chills: These systemic symptoms often indicate a bacterial infection.
- Discharge from the penis: This is particularly likely if an STI is involved.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Your doctor will diagnose epididymitis through a physical exam and possibly a urine or semen sample analysis to identify the causative agent. Treatment depends on the cause. Bacterial infections often require antibiotics. For non-infectious epididymitis, management focuses on pain relief and supportive measures.
- Medical history: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and sexual history.
- Physical examination: A physical examination of your testicles and scrotum will be performed.
- Diagnostic tests: Urine and semen cultures may be necessary to identify the infection.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is detected, antibiotics will be prescribed.
- Pain management: Pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen will help manage discomfort.
- Rest and elevation: Rest and elevating the scrotum can reduce pain and swelling.
Seeking Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain, high fever, or other concerning symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent complications like infertility or abscess formation.
Cipro and Epididymitis
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic that can be effective against some bacteria that cause epididymitis. However, antibiotic selection depends on the specific infection identified. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate antibiotic based on your individual situation and test results.
Ciprofloxacin: Mechanism of Action Against Epididymitis
Ciprofloxacin combats epididymitis primarily by targeting bacterial DNA replication. It achieves this through inhibition of bacterial topoisomerases, specifically DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are critical for bacterial DNA unwinding and replication, necessary for bacterial growth and survival. By blocking these enzymes, Ciprofloxacin prevents bacterial DNA from replicating, leading to bacterial cell death.
Targeting Common Epididymitis Bacteria
Many cases of epididymitis involve bacteria like Escherichia coli and Chlamydia trachomatis. Ciprofloxacin’s broad-spectrum activity makes it effective against gram-negative bacteria like E. coli. However, its efficacy against C. trachomatis, a gram-negative bacterium but with a unique cell wall structure, is less consistent. Therefore, a targeted antibiotic may be needed depending on the specific causative organism and the results of culture and sensitivity testing.
Considerations for Treatment
Successful treatment hinges on appropriate dosage and duration. Factors influencing choice of regimen include severity of infection, patient’s overall health, and potential drug interactions. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and treatment length to ensure eradication of the infection and prevent complications. Resistance to fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, is an increasing concern. Adherence to prescribed treatment is critical to minimize the risk of developing resistant strains.
Common Causes of Epididymitis and Ciprofloxacin’s Effectiveness
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, often treats epididymitis, but its success depends heavily on the underlying cause. Bacterial infections are the primary culprits.
Common bacterial culprits include: Escherichia coli (E. coli), Chlamydia trachomatis, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. E. coli, a frequent cause of urinary tract infections, can ascend to the epididymis. C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae are sexually transmitted infections (STIs) frequently causing epididymitis.
Ciprofloxacin’s action: It works by inhibiting bacterial DNA replication, effectively halting their growth and killing them. However, increasing antibiotic resistance limits its efficacy. Testing to identify the specific bacteria is crucial before treatment to ensure appropriate antibiotic selection.
Treatment success rates: While Ciprofloxacin generally shows high initial success rates against susceptible bacteria, the emergence of resistant strains means alternative antibiotics, like doxycycline or azithromycin, may be needed. Your doctor will determine the best course of action based on your specific case and test results.
Non-bacterial causes: Remember epididymitis isn’t always bacterial; inflammation can stem from injury, a non-infectious disease process, or blockage. Ciprofloxacin is ineffective against these.
Important note: Self-treating epididymitis is dangerous. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. They will perform a physical exam, order relevant tests (such as urine and semen cultures), and prescribe the most suitable antibiotics, considering your specific situation and the potential for bacterial resistance.
When Ciprofloxacin is the Appropriate Treatment
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, effectively targets many common bacteria responsible for epididymitis. Doctors usually prescribe it when the infection’s suspected cause is E. coli or other gram-negative bacteria. This is because Ciprofloxacin demonstrates strong activity against these organisms.
Factors Influencing Ciprofloxacin Use
However, resistance to Ciprofloxacin is increasing. Therefore, your doctor will consider several factors before prescribing it. A urine test helps identify the causative bacteria and its susceptibility to Ciprofloxacin. Your medical history, including allergies and previous antibiotic use, significantly influences the choice of treatment. Alternatives, like doxycycline or other antibiotics, may be preferred if resistance is suspected or if you have a Ciprofloxacin allergy.
Severe symptoms, such as high fever or significant pain, may also prompt your doctor to select a different, broader-spectrum antibiotic initially. They might start with intravenous antibiotics and then transition to oral Ciprofloxacin once your condition improves. The severity of your case dictates the treatment approach.
Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, while effective, can cause various side effects. Common reactions include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These usually are mild and resolve without intervention. However, some individuals experience more severe reactions.
Gastrointestinal Issues: Beyond nausea and diarrhea, you might experience vomiting, constipation, or indigestion. Severe cases may involve colitis, a potentially serious inflammation of the colon. Report persistent or severe gastrointestinal distress to your doctor immediately.
Nervous System Effects: Dizziness, headache, and insomnia are possible. Rarely, more serious neurological problems like seizures or peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage) can occur. Seek medical attention if you experience unusual neurological symptoms.
Allergic Reactions: Skin rashes, itching, and hives are common allergic reactions. In rare but serious instances, anaphylaxis (a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction) can develop. If you experience symptoms of anaphylaxis–like difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue–seek immediate emergency medical care.
Other Potential Side Effects: Ciprofloxacin can affect your tendons, increasing the risk of tendon rupture, particularly in older adults and those taking steroid medications. Joint pain is also possible. Sunlight sensitivity can lead to sunburn more easily, so use sunscreen. Changes in blood sugar levels have been reported.
Note: This is not an exhaustive list. Always consult your physician about any concerns regarding side effects. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual health history and circumstances.
Alternative Treatment Options for Epididymitis
Consider home remedies to manage pain and inflammation. Applying ice packs for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, can reduce swelling. Rest is crucial; avoid strenuous activity. Elevating your scrotum also promotes drainage and reduces discomfort.
Dietary Adjustments
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods may help your body heal. Focus on fruits, vegetables, and lean protein sources. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats.
Herbal Remedies
Some individuals find relief with herbal remedies like turmeric (known for its anti-inflammatory properties) or bromelain (a pineapple enzyme with anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects). Always consult a healthcare professional before using herbal supplements, especially if you’re on other medications.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine technique involving thin needles inserted into specific points on the body, may offer pain relief for some. Its effectiveness for epididymitis requires further research, but some find it beneficial.
Comparison Table: Treatment Approaches
| Treatment | Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ice Packs | Reduces inflammation | Easy, readily available, inexpensive | Temporary relief, doesn’t address underlying cause |
| Dietary Changes | Supports body’s healing process | Promotes overall health | Requires consistent effort, may not provide immediate relief |
| Herbal Remedies (e.g., Turmeric) | Anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving effects | May reduce pain and inflammation | Potential drug interactions, effectiveness varies |
| Acupuncture | Stimulates body’s healing response | May provide pain relief | Effectiveness varies, not a substitute for medical care |
Remember: These alternative options are supplemental and should not replace prescribed antibiotics or medical care for epididymitis. Always seek professional medical advice for diagnosis and treatment. Ignoring a serious infection can lead to complications.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Go to the emergency room immediately if you experience severe pain, especially if it’s accompanied by:
- High fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C).
- Chills.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Abdominal pain.
- Swollen scrotum.
- Inability to urinate.
Seek medical attention within 24 hours if you notice:
- Increasing pain despite taking prescribed antibiotics.
- Persistent scrotal swelling.
- Pus or discharge from the penis.
Prompt treatment is key to preventing complications. Don’t delay seeking help if you are concerned about your symptoms.
- Contact your doctor or urologist as soon as possible to discuss your symptoms and arrange an appointment.
- Follow their advice diligently regarding medication and rest.
- Keep a record of your symptoms and their severity to help your doctor monitor your progress.
Early intervention leads to better outcomes. Your health is your priority.
Long-Term Outlook and Prevention Strategies
Most men recover fully from Cipro-treated epididymitis within a few weeks. Complete resolution of symptoms usually occurs within 1-3 months. However, some men may experience lingering discomfort or tenderness. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to a better outcome.
To prevent future epididymitis, practice safe sex. Use condoms consistently and correctly. This significantly reduces the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), a common cause of epididymitis. Maintain good hygiene, including regular showering and clean underwear.
Adequate hydration supports overall health and can aid recovery. Avoid activities that strain the testicles, such as heavy lifting or prolonged bicycle riding, especially during the acute phase of infection. If symptoms persist or worsen after completing the antibiotic course, consult your doctor. Regular check-ups, particularly if you have a history of STIs, can help identify and address potential issues early.
Prompt treatment with antibiotics like Ciprofloxacin is usually successful. However, antibiotic resistance is a growing concern. Therefore, adhering strictly to your prescribed course of antibiotics is vital to preventing complications and recurrence. Complete the entire prescription even if you feel better before finishing it.