Standard treatment for chlamydia involves a single 500mg dose of Ciprofloxacin. This is generally sufficient to eradicate the infection. However, remember that this information is for general knowledge only and shouldn’t replace consultation with a healthcare professional.
Your doctor might adjust this dosage based on your specific health condition and medical history. Factors such as liver or kidney function can influence the prescribed amount. Always discuss potential drug interactions with your physician before beginning any treatment.
Never self-medicate. Incorrect dosage can lead to treatment failure and potential antibiotic resistance. A proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan from a qualified healthcare provider are crucial for successful chlamydia treatment and preventing complications.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any adverse reactions after taking Ciprofloxacin. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting, but more serious reactions are possible. Your doctor can provide guidance and manage any issues that arise.
- Ciprofloxacin Chlamydia Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin’s Role in Chlamydia Treatment
- Standard Dosage Regimen for Ciprofloxacin against Chlamydia
- Duration of Ciprofloxacin Treatment for Chlamydia Infection
- Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin and What to Watch For
- Serious Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Monitoring Your Health
- Interactions with Other Medications: Important Considerations
- Alternatives to Ciprofloxacin for Chlamydia Treatment
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention During Treatment
- Signs of Treatment Failure
- Importance of Completing the Full Course of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin Chlamydia Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide
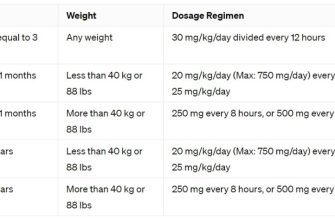
The typical Ciprofloxacin dosage for Chlamydia trachomatis infection is a single 500mg oral dose. However, your doctor might prescribe a different regimen depending on your individual needs and the severity of your infection.
For uncomplicated urogenital Chlamydia infections, a single dose is often sufficient. However, some doctors may opt for a 7-day course of 500mg twice daily. This approach is often taken for rectal or pharyngeal infections, or in cases where a single-dose treatment has been unsuccessful.
It’s critical to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you feel better before finishing. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance and treatment failure.
Here’s a table summarizing potential dosage regimens:
| Infection Site | Dosage Regimen |
|---|---|
| Uncomplicated urogenital | Single 500mg dose OR 500mg twice daily for 7 days |
| Rectal or pharyngeal | 500mg twice daily for 7 days |
Remember, this information is for guidance only. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. They will consider your medical history, current health status, and the specific type of Chlamydia infection you have before determining the appropriate dosage and treatment plan. Never self-medicate. Seeking professional medical advice is paramount for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of Chlamydia.
Potential side effects of Ciprofloxacin include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience severe or persistent side effects.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin’s Role in Chlamydia Treatment
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, directly targets and kills the Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria responsible for chlamydia infections. It works by interfering with the bacteria’s DNA replication, preventing their growth and spread.
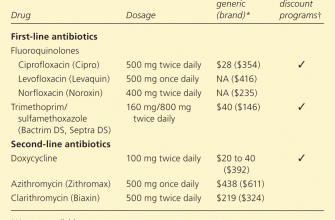
However, increasing antibiotic resistance makes ciprofloxacin a less preferred choice for chlamydia treatment now. The CDC and other health organizations generally recommend azithromycin or doxycycline as first-line treatments due to their higher effectiveness and lower risk of contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Doctors may consider ciprofloxacin only if alternative antibiotics are unsuitable, such as in cases of allergy or intolerance. They will carefully assess individual patient needs and potential risks before prescribing it.
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and duration of treatment precisely. Incomplete treatment can lead to persistent infection, complications, and increased resistance. Never self-medicate; a proper diagnosis is crucial before starting any antibiotic treatment.
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are necessary to ensure the infection has cleared completely and to monitor for any adverse reactions to the medication. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing long-term health issues associated with chlamydia.
Standard Dosage Regimen for Ciprofloxacin against Chlamydia
Ciprofloxacin is generally prescribed as a single oral dose of 500mg for chlamydia treatment. This is usually sufficient to eradicate the infection.
However, it’s crucial to remember that this is a general guideline. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate dosage based on your specific health condition and other factors. Let’s look at some important considerations:
- Severity of Infection: In some cases, a longer course of treatment might be recommended, perhaps a 500mg dose for a few days.
- Individual Health: Pre-existing conditions, allergies, and other medications you’re taking might influence the dosage and treatment plan.
- Type of Infection: The specific strain of Chlamydia and the site of infection may be relevant factors your doctor needs to consider.
Never self-medicate. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. They will perform necessary tests and provide personalized recommendations tailored to your needs. Failure to follow medical advice can lead to complications.
Following your doctor’s instructions carefully is vital for successful treatment and preventing reinfection or the development of antibiotic resistance. They will provide clear directions on how and when to take the medication, along with any necessary follow-up appointments. This ensures a more positive health outcome.
- Obtain a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional.
- Strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage and schedule.
- Complete the full course of medication, even if symptoms improve.
- Inform your doctor about any side effects you experience.
- Refrain from sexual activity until the infection is cleared.
Duration of Ciprofloxacin Treatment for Chlamydia Infection
The standard Ciprofloxacin dosage for chlamydia is a single 500mg dose. However, this is becoming less common due to increasing antibiotic resistance.
While a single dose was once sufficient, current guidelines often recommend a longer course of treatment.
- Alternative Regimens: If a single dose isn’t prescribed, expect a treatment course lasting 7-10 days.
- Doxycycline: Doxycycline is now the preferred treatment option for chlamydia infections and is usually prescribed for 7 days. It’s crucial to complete the entire course regardless of symptom improvement.
Remember to always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. They will tailor the treatment plan to your specific needs and medical history. Failing to complete the prescribed course can lead to treatment failure and potential complications.
- Follow-up Testing: Your doctor will likely schedule a follow-up test to confirm the infection has cleared after treatment. This is crucial for ensuring the treatment’s success.
- Partners: If you have sexual partners, informing and treating them is critical to prevent re-infection. Your doctor can advise on the best approach.
These recommendations represent current best practices. However, medical advice should always come from a qualified healthcare professional who can assess your individual circumstances.
Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin and What to Watch For
Ciprofloxacin, while effective against chlamydia, can cause side effects. Monitor yourself for common reactions like nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. These are usually mild and resolve quickly. However, report any persistent or worsening gastrointestinal issues to your doctor.
Serious Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical help if you experience: Severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat), tendon pain or rupture (especially in the Achilles tendon), seizures, or unusual bleeding or bruising. These are less common but serious complications.
Other Potential Side Effects
Less frequent but still possible side effects include headache, dizziness, insomnia, and sun sensitivity. If you notice any unusual skin reactions after sun exposure while taking Ciprofloxacin, protect your skin diligently and contact your doctor.
Remember to fully inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Ciprofloxacin. This helps to minimize potential drug interactions and side effects.
Monitoring Your Health
Stay hydrated while taking Ciprofloxacin to help prevent side effects. Report any unexpected or concerning symptoms to your physician. Regular follow-up appointments can aid in early detection and management of any potential problems.
Interactions with Other Medications: Important Considerations
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal remedies, and supplements. This includes antacids containing magnesium or aluminum, which can reduce Ciprofloxacin absorption. Theophylline levels may increase when taken concurrently with Ciprofloxacin; monitor for signs of theophylline toxicity like nausea, vomiting, or tremors. Concurrent use with caffeine may also increase its effects.
Ciprofloxacin can interact with blood thinners like warfarin, potentially increasing bleeding risk. Close monitoring of your INR (International Normalized Ratio) is necessary if you’re on warfarin. Avoid taking Ciprofloxacin with drugs that prolong the QT interval, such as certain antiarrhythmics or antidepressants, as this increases the risk of heart rhythm problems. Metformin interactions are possible, requiring careful monitoring of blood sugar levels.
Specific interactions vary depending on individual medications and dosages. Your healthcare provider can assess your unique situation and provide personalized guidance regarding potential drug interactions. Open communication with your doctor ensures safe and effective treatment.
Alternatives to Ciprofloxacin for Chlamydia Treatment
Doxycycline is the preferred alternative. A 7-day course of 100mg twice daily is generally prescribed. This antibiotic is well-tolerated by most patients.
Azithromycin offers a single-dose option of 1 gram, making it convenient. However, it’s important to note that some strains of chlamydia may be resistant to azithromycin, making it less reliable than doxycycline.
Both doxycycline and azithromycin are generally safe and effective, but individual responses can vary. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and complete the entire course of medication, even if symptoms improve.
If you have allergies or other health concerns, discuss alternative treatment options with your healthcare provider. They can assess your individual needs and recommend the best course of action.
Remember, untreated chlamydia can lead to serious health complications. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing long-term consequences.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention During Treatment
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe allergic reactions like difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, or hives. These are serious symptoms requiring urgent medical care.
Signs of Treatment Failure
Seek immediate medical attention if your symptoms worsen or don’t improve after a week of treatment. This might indicate the infection isn’t responding to the Ciprofloxacin, and alternative treatment may be necessary. Persistent pain, fever, or unusual discharge are also warning signs.
Also, contact your doctor if you develop new symptoms such as severe stomach pain, bloody diarrhea, or signs of tendonitis (pain or swelling in a tendon). These could signify serious side effects.
Importance of Completing the Full Course of Ciprofloxacin
Finish all your Ciprofloxacin, even if you feel better before the prescription ends. Stopping early allows surviving bacteria to multiply, potentially leading to a recurrence of the infection and the development of antibiotic resistance. This resistance makes future treatment more challenging and less effective.
A typical Ciprofloxacin course for chlamydia is seven days. Failing to complete this regimen increases your risk of re-infection by approximately 50%, necessitating another round of antibiotics. This also increases the risk of complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women.
Consistently taking your medication as prescribed is paramount. This simple step significantly enhances the chances of successful treatment and reduces long-term health risks. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any adverse reactions to the medication.
Remember: Your doctor’s guidance is key. Always follow their specific instructions for dosage and duration.