Need information on Ciprofloxacin? Start with understanding its primary use: treating bacterial infections. This antibiotic targets a broad spectrum of bacteria, making it effective against various ailments. Remember, however, it’s a prescription medication; always consult a doctor before use.
Ciprofloxacin works by inhibiting bacterial DNA replication, effectively stopping their growth and allowing your immune system to handle the infection. Common applications include urinary tract infections (UTIs), respiratory infections like pneumonia, and certain skin infections. Dosage varies significantly depending on the infection and your overall health; follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Important Note: Ciprofloxacin can cause side effects. These range from mild gastrointestinal issues like nausea and diarrhea to more serious reactions such as tendon rupture or allergic responses. Report any unusual symptoms immediately to your healthcare provider. Proper hydration is also crucial during treatment. Do not stop taking Ciprofloxacin without consulting your physician.
Before starting treatment, inform your doctor of any existing health conditions, particularly those involving your heart, kidneys, or nervous system, as well as any current medications you’re taking. This helps avoid potential drug interactions and ensures safer administration. This antibiotic is not effective against viral infections, like the common cold or influenza.
- Ciprofloxacin: A Detailed Overview
- Administration and Dosage
- Side Effects and Precautions
- Drug Interactions
- Resistance and Alternatives
- Ciprofloxacin’s Mechanism of Action and Spectrum of Activity
- Gram-Negative Bacteria
- Gram-Positive Bacteria
- Other Organisms
- Common Uses and Indications for Ciprofloxacin
- Gastrointestinal and Skin Infections
- Other Indications
- Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Ciprofloxacin
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Drug Interactions
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Precautions and Contraindications for Ciprofloxacin Use
Ciprofloxacin: A Detailed Overview
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic targeting a wide range of bacterial infections. It works by inhibiting bacterial DNA replication, effectively stopping their growth and reproduction. This makes it a powerful tool against many common culprits, including E. coli, Salmonella, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Administration and Dosage
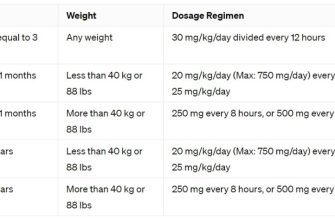
Ciprofloxacin comes in various forms: oral tablets, intravenous infusions, and ophthalmic solutions. Your doctor determines the appropriate dosage based on your infection’s severity, your body weight, and kidney function. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Missed doses should be taken as soon as possible, unless approaching the time for your next dose.
Side Effects and Precautions
Like all medications, ciprofloxacin can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. More serious, though rare, side effects include tendonitis, peripheral neuropathy, and allergic reactions. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any unusual symptoms. Ciprofloxacin is generally not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, or children under 18 due to potential risks. Individuals with known allergies to fluoroquinolones should avoid it. Avoid prolonged sun exposure while taking ciprofloxacin, as it can increase sun sensitivity.
Drug Interactions
Ciprofloxacin can interact with certain medications, including antacids, caffeine, and some blood thinners. Always disclose all medications and supplements you are taking to your doctor or pharmacist to minimize potential adverse effects. This proactive approach ensures medication safety and efficacy.
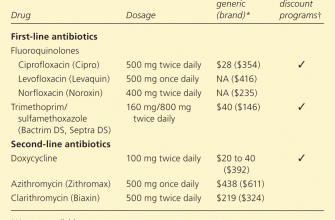
Resistance and Alternatives
Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern. Overuse of ciprofloxacin contributes to this problem. Doctors carefully consider the necessity of ciprofloxacin, exploring alternative antibiotics when feasible. Proper antibiotic stewardship helps maintain ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness for future use. This responsible approach is crucial for public health.
Ciprofloxacin’s Mechanism of Action and Spectrum of Activity
Ciprofloxacin targets bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are crucial for DNA replication, transcription, and repair. By inhibiting these enzymes, ciprofloxacin prevents bacterial cell division and ultimately leads to bacterial cell death.
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Ciprofloxacin demonstrates potent activity against many Gram-negative bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Haemophilus influenzae. Its effectiveness stems from its ability to readily penetrate the outer membrane of these bacteria and reach its intracellular targets.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
While generally less effective against Gram-positive bacteria than against Gram-negatives, ciprofloxacin remains active against some strains, such as Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-sensitive strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (some strains), and Listeria monocytogenes. Note that resistance is a growing concern, so susceptibility testing is vital before treatment.
Other Organisms
Ciprofloxacin also exhibits activity against atypical bacteria like Legionella pneumophila and Mycoplasma pneumoniae, along with some intracellular pathogens. However, the spectrum of activity varies, depending on the specific bacterial strain and its susceptibility profile.
Remember: Antibiotic use should always be guided by culture and susceptibility testing to ensure optimal treatment and minimize the development of resistance.
Common Uses and Indications for Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin treats various bacterial infections. Doctors frequently prescribe it for urinary tract infections (UTIs), including complicated and uncomplicated cases. It’s also a common choice for treating infections of the respiratory tract, such as bronchitis and pneumonia, particularly those caused by susceptible bacteria.
Gastrointestinal and Skin Infections
Ciprofloxacin effectively targets infections in the gastrointestinal system, such as diarrhea caused by specific bacteria (like Salmonella and Campylobacter). It also finds use in treating skin and soft tissue infections, particularly those caused by susceptible strains of bacteria. Always consult a physician for diagnosis and treatment.
Other Indications
Beyond these common uses, ciprofloxacin plays a role in treating certain types of bone and joint infections and certain sexually transmitted infections. However, antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, so its usage should always align with current guidelines and susceptibility testing results. Remember to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, while effective, carries potential side effects. Common reactions include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Less frequent, but more serious, adverse events involve tendon rupture, particularly in older adults and those on corticosteroid medications. Always inform your doctor about any existing health conditions, especially tendon issues or a history of seizures. This information aids in safe prescription and monitoring.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Upset stomach and diarrhea are frequently reported. Severe cases may require medical attention. Staying hydrated and consuming bland foods can often alleviate milder symptoms. Your physician can recommend appropriate management strategies for more severe digestive problems.
Drug Interactions
Ciprofloxacin interacts negatively with certain medications. Concurrent use with antacids containing magnesium or aluminum can reduce Ciprofloxacin’s absorption. Simultaneous administration with theophylline, caffeine, or warfarin may alter their effects. Always provide your doctor with a complete list of your current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to prevent harmful interactions.
Other Potential Side Effects
Less common side effects include dizziness, lightheadedness, and allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling). In rare instances, serious conditions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis can occur. Seek immediate medical help if you experience these severe reactions. Remember to report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider.
Precautions and Contraindications for Ciprofloxacin Use
Before starting Ciprofloxacin, inform your doctor about all your medical conditions, including allergies. This is particularly important for those with a history of tendon problems.
- Avoid Ciprofloxacin if you’re allergic to it or other quinolones. Severe allergic reactions can occur.
- Discuss your medication history with your doctor. Some medications interact negatively with Ciprofloxacin.
- Inform your doctor if you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy. Ciprofloxacin may not be suitable during these periods.
- Report any signs of tendonitis or tendon rupture. Ciprofloxacin can increase the risk of these conditions, especially in older adults and those taking corticosteroids.
Ciprofloxacin can cause side effects, some serious:
- Nervous system effects: Headache, dizziness, confusion, seizures (rare but possible).
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain. Severe diarrhea may indicate Clostridium difficile infection.
- Photosensitivity: Increased sensitivity to sunlight. Use sunscreen and protective clothing.
Certain conditions contraindicate Ciprofloxacin use:
- Myasthenia gravis: Ciprofloxacin can worsen this muscle disorder.
- Epilepsy or seizure disorder: Ciprofloxacin can lower the seizure threshold.
- Severe renal impairment: Dose adjustments are necessary; your doctor will guide you.
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency: This can lead to hemolytic anemia.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking Ciprofloxacin prematurely, even if you feel better. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any concerning side effects.