Avoid Ciprofloxacin if you have a known allergy to fluoroquinolones. This includes medications like levofloxacin and moxifloxacin. A severe allergic reaction can be life-threatening, so this precaution is paramount.
Patients with a history of tendonitis or tendon rupture should also exercise extreme caution. Ciprofloxacin can increase the risk of these conditions, particularly in older adults and those taking corticosteroids. Consult your doctor before using Cipro if you fall into this category.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding present significant considerations. While Cipro’s use during pregnancy isn’t strictly prohibited in all cases, it’s generally avoided due to potential fetal risks. Similarly, the drug’s excretion in breast milk necessitates careful assessment of the benefits versus risks for nursing mothers.
Individuals with epilepsy or a history of seizures should approach Cipro with heightened awareness. The medication may lower the seizure threshold, potentially triggering episodes in susceptible individuals. Your physician will need to carefully weigh the risks and benefits before prescribing.
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Interactions with other drugs can significantly alter Cipro’s effects and increase the likelihood of adverse reactions. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to safe medication use.
- Contraindications for Ciprofloxacin: A Detailed Overview
- Specific Contraindications
- Cautions and Considerations
- Medication Interactions
- Known Allergies and Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Specific Reactions to Watch For
- Tendinitis and Tendon Rupture Risk Factors
- Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, and Pediatric Considerations
- Central Nervous System Effects and Pre-existing Conditions
- Drug Interactions and Concurrent Medications
Contraindications for Ciprofloxacin: A Detailed Overview
Avoid Ciprofloxacin if you have a known allergy to fluoroquinolones. This includes medications like levofloxacin and moxifloxacin. Severe allergic reactions can occur, potentially life-threatening.
Specific Contraindications
- Tendinitis and tendon rupture: Ciprofloxacin increases the risk of tendon problems, particularly in older adults and those taking corticosteroids. Avoid if you have a history of these issues.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Existing nerve damage can worsen with Ciprofloxacin use. Discuss this with your doctor before taking it.
- Myasthenia gravis: This neuromuscular disease can be exacerbated by Ciprofloxacin. It’s contraindicated in this condition.
- Epilepsy or seizure disorders: Ciprofloxacin lowers the seizure threshold, potentially triggering seizures in susceptible individuals.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: While generally avoided during pregnancy, your doctor may prescribe it if the benefits outweigh the risks. Consult your doctor for advice regarding breastfeeding.
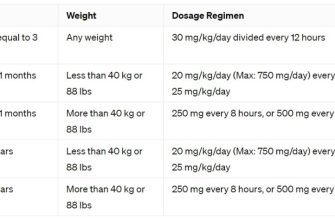
- Patients under 18: Ciprofloxacin is typically not prescribed to children and adolescents due to concerns about cartilage damage.
Cautions and Considerations
Certain conditions require careful monitoring while taking Ciprofloxacin. These include:
- Kidney disease: Dosage adjustments are necessary to prevent drug accumulation.
- Liver disease: Ciprofloxacin metabolism may be affected, requiring close monitoring.
- Heart conditions: Prolonged QT interval can occur, potentially leading to serious heart rhythm problems.
- Mental health conditions: Reports of psychiatric side effects exist; consider the potential risks if you have a history of these issues.
Always inform your doctor of all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to minimize potential interactions.
Medication Interactions
Ciprofloxacin can interact negatively with several medications. Examples include:
- Antacids: Reduce Ciprofloxacin absorption.
- Sucralfate: Binds to Ciprofloxacin, reducing its effectiveness.
- Theophylline: Increased risk of theophylline toxicity.
- Warfarin: May increase bleeding risk.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or stopping any medication.
Known Allergies and Hypersensitivity Reactions
Always inform your doctor about any known allergies, particularly to quinolones or other similar antibiotics. A history of allergic reaction to ciprofloxacin or other fluoroquinolones is a significant contraindication. This means you should absolutely not take ciprofloxacin if you’ve experienced a previous adverse reaction.
Specific Reactions to Watch For
Severe allergic reactions can manifest as hives, swelling (angioedema, particularly of the face, lips, tongue, or throat), difficulty breathing, or a sudden drop in blood pressure (anaphylaxis). Less severe reactions might include itching, rash, or gastrointestinal upset. Any unusual symptom after taking ciprofloxacin warrants immediate medical attention. Report all reactions, even seemingly minor ones, to your physician to help determine the appropriate course of action.
Cross-reactivity with other quinolones is possible. If you’re allergic to one quinolone, there’s a chance you might react to others, including ciprofloxacin. Discuss your allergy history thoroughly with your doctor to ensure they prescribe an alternative antibiotic.
Tendinitis and Tendon Rupture Risk Factors
Ciprofloxacin use increases your risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture. Several factors amplify this risk.
| Risk Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Age (over 60) | Older adults experience decreased collagen production, making tendons more vulnerable to damage. |
| Kidney or liver impairment | These conditions affect drug metabolism, potentially leading to higher drug concentrations and increased risk. |
| Concurrent corticosteroid use | Steroids weaken tendons, synergistically increasing the risk with Cipro. |
| Prior tendon injury | Previously injured tendons are more susceptible to further damage. |
| High-intensity physical activity | Strenuous exercise puts added stress on tendons, exacerbating the risk. |
| Organ transplant | Immunosuppressant medications often used post-transplant increase tendon vulnerability. |
If you experience tendon pain, stop taking Cipro and consult a doctor immediately. Early detection and rest are key to preventing serious complications.
Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, and Pediatric Considerations
Ciprofloxacin use during pregnancy carries potential risks to the developing fetus, including cartilage damage. Therefore, avoid Cipro during pregnancy unless the potential benefit clearly outweighs the risk. Discuss alternatives with your doctor.
Ciprofloxacin enters breast milk. While the exact risk to infants is unclear, consider breastfeeding alternatives if Cipro is necessary. Your physician can help weigh the risks and benefits.
For pediatric patients, Ciprofloxacin is generally not recommended for children under 18 due to the potential for cartilage damage. Alternative antibiotics are usually safer and more appropriate for this age group. Always consult your child’s pediatrician before administering any medication.
Note: This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before using Ciprofloxacin or any medication.
Central Nervous System Effects and Pre-existing Conditions
Ciprofloxacin can affect the central nervous system, causing headaches, dizziness, and even seizures in susceptible individuals. Therefore, use caution if you have a history of seizures or epilepsy. Your doctor should carefully weigh the benefits against these risks.
Pre-existing neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, may worsen with Ciprofloxacin use. Report any new or worsening neurological symptoms to your physician immediately. This includes tremors, difficulty coordinating movement, or changes in vision or cognitive function.
Patients with a history of psychiatric disorders, including depression or anxiety, should also be monitored closely. Ciprofloxacin may exacerbate these conditions, potentially leading to worsening symptoms or new onset mental health issues. Open communication with your healthcare provider is vital.
Individuals with brain damage or head injuries should discuss the use of Ciprofloxacin with their doctor. The drug’s potential CNS effects may be amplified in patients with compromised neurological function.
Always inform your doctor about all pre-existing conditions, including neurological and psychiatric diagnoses, before starting Ciprofloxacin treatment. This allows for a proper risk assessment and facilitates informed decision-making regarding your treatment plan.
Drug Interactions and Concurrent Medications
Ciprofloxacin interacts with several medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins.
Antacids: Concurrent use with antacids containing magnesium or aluminum hydroxide can reduce ciprofloxacin absorption. Separate administration by at least 2 hours is recommended.
Sucralfate: This medication binds to ciprofloxacin, significantly decreasing its absorption. Administer ciprofloxacin at least two hours before or after taking sucralfate.
Iron supplements: Iron supplements can also interfere with ciprofloxacin absorption. Maintain a two-hour gap between taking ciprofloxacin and iron supplements.
Theophylline: Ciprofloxacin can increase theophylline levels, potentially leading to toxicity. Careful monitoring of theophylline levels is necessary during concurrent use.
Warfarin: Ciprofloxacin may enhance the anticoagulant effect of warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding. Regular blood tests to monitor INR are crucial.
Probenecid: This medication inhibits the renal excretion of ciprofloxacin, potentially leading to higher blood levels and increased risk of side effects. Dosage adjustments may be needed.
Caffeine: Ciprofloxacin can increase caffeine levels, resulting in potential side effects like jitteriness or insomnia. Monitor your caffeine intake.
This information is not exhaustive. Consult your physician or pharmacist for personalized advice regarding potential drug interactions with ciprofloxacin, especially if you have multiple underlying health conditions or are taking other prescription medications.