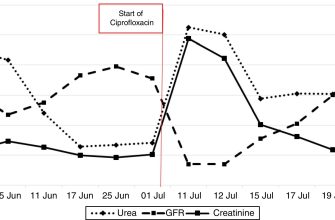
Avoid dairy products for at least two hours before and after taking Ciprofloxacin (Cipro). Calcium in dairy can significantly reduce Cipro’s absorption, hindering its effectiveness in fighting infection.
This interaction isn’t trivial; reduced absorption means a lower concentration of the antibiotic in your bloodstream. Consequently, your body might not receive the necessary medication to combat the bacteria effectively, potentially prolonging your illness or allowing resistant strains to develop.
Specifically, dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese contain calcium, which binds to Cipro. This binding prevents the antibiotic from being properly absorbed into your system. Opt for water as your beverage of choice during this period for optimal medication efficacy.
Remember: This advice pertains to Ciprofloxacin specifically. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance regarding medication interactions and potential side effects. They can provide tailored advice based on your individual health status and prescribed dosage.
- Dairy Products and Cipro: A Detailed Guide
- Timing Your Medication and Dairy Intake
- Alternative Options
- Hydration is Key
- Potential Side Effects
- Ciprofloxacin: Understanding the Antibiotic
- Mechanism of Action
- Potential Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Dosage and Administration
- Important Note:
- Dairy’s Impact on Cipro Absorption
- Calcium’s Role in Ciprofloxacin Interaction
- The Science Behind the Interaction: Chelation
- How Chelation Works
- Impact on Treatment
- Specific Recommendations
- Further Considerations
- Symptoms of Reduced Ciprofloxacin Effectiveness
- Persistent or Worsening Infection Symptoms
- Signs of Bacterial Resistance
- What to Do
- Additional Factors Affecting Ciprofloxacin
- Dietary Interactions
- How to Optimize Ciprofloxacin Treatment: Timing with Dairy
- Calcium’s Impact
- Other Minerals
- Hydration
- Alternatives to Dairy During Cipro Treatment
- Calcium Sources Beyond Milk
- Protein Alternatives
- Addressing Potential Deficiencies
- Consulting Your Doctor: Importance of Communication
- Discussing Dairy Consumption
- Reporting Symptoms
Dairy Products and Cipro: A Detailed Guide
Avoid dairy products while taking Ciprofloxacin (Cipro). Calcium and other minerals in dairy can bind to Cipro, reducing its absorption into your bloodstream. This means the antibiotic may not be as effective at fighting your infection.
Timing Your Medication and Dairy Intake
To maximize Cipro’s effectiveness, take it at least two hours before or six hours after consuming dairy products, including milk, yogurt, cheese, and ice cream. This allows sufficient time for absorption before potential interference occurs.
Alternative Options
If you find it difficult to avoid dairy completely, consider switching to dairy alternatives like almond milk or soy milk during your Cipro treatment. These options are less likely to affect Cipro absorption. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have concerns about dietary changes and medication interactions.
Hydration is Key
Drink plenty of water throughout your Cipro treatment. Adequate hydration promotes the drug’s absorption and helps flush it from your system.
Potential Side Effects
Remember that Cipro can cause gastrointestinal side effects like nausea and diarrhea. While dairy interaction reduces its effectiveness, it does not directly *cause* these side effects. If you experience severe side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Ciprofloxacin: Understanding the Antibiotic
Ciprofloxacin belongs to a group of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones. It works by preventing bacteria from reproducing, thus effectively combating infections. Doctors prescribe it for various bacterial infections, including those of the respiratory tract, urinary tract, skin, bones, and joints.
Mechanism of Action
Ciprofloxacin targets an enzyme vital for bacterial DNA replication, gyrase. By inhibiting this enzyme, the antibiotic stops bacteria from multiplying and repairing their DNA, leading to bacterial cell death. This mechanism distinguishes it from other antibiotic classes, offering efficacy against bacteria resistant to other drugs.
Potential Side Effects
Like all medications, Ciprofloxacin can have side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Less common, but more serious side effects, include tendon inflammation (tendinitis), nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy), and allergic reactions. Always inform your doctor about any existing health conditions or medications you are taking before starting Ciprofloxacin.
Drug Interactions
| Medication Type | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|
| Antacids | Reduces Ciprofloxacin absorption |
| Warfarin | May increase bleeding risk |
| Theophylline | May increase theophylline levels |
This table highlights some significant drug interactions. Consult your physician or pharmacist for a complete list of potential interactions with other medications or supplements you are using.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage varies depending on the type and severity of infection. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose and duration of treatment. Follow their instructions carefully. Typically, Ciprofloxacin is taken orally, but intravenous administration might be necessary in severe cases.
Important Note:
Ciprofloxacin is a powerful antibiotic. Misuse or overuse contributes to antibiotic resistance. Only take it as prescribed by a doctor. Never share your medication. If you experience any unusual side effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Dairy’s Impact on Cipro Absorption
Avoid consuming dairy products within two hours of taking Ciprofloxacin. Calcium and other minerals in dairy bind to ciprofloxacin, reducing its absorption into your bloodstream. This means less of the antibiotic reaches its target, potentially hindering its effectiveness.
Studies show a significant decrease in ciprofloxacin absorption when taken with milk or yogurt. One study demonstrated a 30-40% reduction in bioavailability when consumed concurrently. This decreased absorption can lead to treatment failure or prolonged illness.
Consider water or other non-dairy drinks as the ideal way to take your Ciprofloxacin prescription. Juices are usually fine but may slightly interfere; check with your doctor or pharmacist. Following these guidelines maximizes the antibiotic’s impact.
Remember: Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice regarding medication interactions. They can provide specific guidance based on your health conditions and prescription.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.
Calcium’s Role in Ciprofloxacin Interaction
Avoid taking ciprofloxacin with dairy products immediately before or after. Calcium in dairy can bind to ciprofloxacin, reducing its absorption and potentially hindering its effectiveness.
Here’s what you should know:
- Reduced Absorption: Calcium significantly decreases the amount of ciprofloxacin your body absorbs. Studies show a considerable reduction in bioavailability when taken concurrently.
- Timing Matters: Separate your dairy consumption and ciprofloxacin intake by at least 2 hours. This allows for optimal absorption of the antibiotic.
- Dairy Types: This applies to milk, yogurt, cheese, and other calcium-rich dairy products. Even fortified foods containing high calcium levels should be considered.
- Alternative Medications: If you have concerns about dairy interaction, discuss alternative antibiotic options with your doctor.
- Consult Your Doctor: Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions regarding medication timing and dietary recommendations. This is crucial for optimal treatment.
Proper spacing between ciprofloxacin and calcium intake ensures the medication works as intended. Remember, individual responses vary, so open communication with your physician is key.
- Monitor your symptoms: Pay close attention to your health and report any issues to your doctor.
- Follow dosage instructions carefully: Don’t deviate from the prescribed dosage regimen without medical advice.
The Science Behind the Interaction: Chelation
Calcium and other minerals in dairy products bind to ciprofloxacin, a type of antibiotic. This process is called chelation. Chelation reduces the amount of ciprofloxacin your body absorbs.
How Chelation Works
Ciprofloxacin is a small molecule with a positive charge. Calcium ions in dairy products, also positively charged, repel each other. This repulsion prevents ciprofloxacin from being properly absorbed into your bloodstream. The effect is reduced bioavailability of the antibiotic.
Impact on Treatment
Decreased absorption means lower drug concentrations in your blood. Consequently, the antibiotic may be less effective at fighting off infection. This could prolong your illness or even lead to treatment failure. To ensure optimal drug efficacy, separate dairy consumption and ciprofloxacin intake by at least two hours.
Specific Recommendations
Avoid consuming dairy products within two hours before or after taking ciprofloxacin. This timing recommendation offers a practical approach to mitigate chelation. Remember, individual responses vary, so always consult your doctor for personalized advice.
Further Considerations
Other minerals in dairy, like magnesium and phosphate, can also chelate with ciprofloxacin, though to a lesser extent than calcium. This highlights the importance of considering the entire nutritional profile of dairy when taking this antibiotic.
Symptoms of Reduced Ciprofloxacin Effectiveness
If you’re taking Ciprofloxacin and suspect its effectiveness is waning, watch for these warning signs. Early detection is key!
Persistent or Worsening Infection Symptoms
- Persistent Fever: A fever that doesn’t subside or recurs after initial improvement.
- Increased Pain or Swelling: Noticeable worsening of pain or inflammation at the infection site.
- Unresolved Discharge: Pus, mucus, or other discharge continues despite treatment.
- New or worsening symptoms: The appearance of new symptoms or an intensification of existing symptoms.
Signs of Bacterial Resistance
These signs may indicate the bacteria causing your infection are developing resistance to Ciprofloxacin:
- Slow or No Improvement: You experience minimal improvement or no improvement in your symptoms after several days of taking Ciprofloxacin.
- Relapse: Your symptoms improve, then return even stronger after a period of seeming recovery.
- Spread of Infection: The infection spreads to other parts of your body.
What to Do
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. Do not adjust your dosage or discontinue the medication without medical advice. Your doctor may need to perform additional tests or switch you to a different antibiotic.
Additional Factors Affecting Ciprofloxacin
Dietary Interactions
- Dairy products can interfere with the absorption of Ciprofloxacin, potentially reducing its efficacy. Avoid consuming dairy products within two hours of taking your medication.
- Antacids and certain minerals can also affect absorption. Consult your doctor or pharmacist about potential interactions with other medications or supplements.
Remember, prompt medical attention is vital for successful treatment. Your doctor can provide personalized advice based on your individual circumstances.
How to Optimize Ciprofloxacin Treatment: Timing with Dairy
Avoid consuming dairy products within two hours before and two hours after taking Ciprofloxacin. This minimizes the potential for decreased absorption of the antibiotic.
Calcium’s Impact
Dairy products are rich in calcium, which can bind to ciprofloxacin, reducing its absorption into your bloodstream. A lower drug concentration means it may be less effective at fighting the infection. Aim for a minimum two-hour gap to allow for optimal absorption.
Other Minerals
Besides calcium, other minerals in dairy like magnesium and iron can also interact with ciprofloxacin. Maintaining the two-hour spacing helps reduce the influence of these minerals on the antibiotic’s efficacy.
Hydration
Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially while taking Ciprofloxacin. This supports proper absorption and helps flush the drug through your system.
Alternatives to Dairy During Cipro Treatment
Consider plant-based milk alternatives like soy, almond, oat, or rice milk. These options provide calcium and other nutrients without the potential interaction with Cipro.
Calcium Sources Beyond Milk
For calcium, explore fortified plant milks, tofu, leafy green vegetables (like kale and spinach), and canned sardines (with bones). These sources offer a diverse range of nutrients alongside calcium.
Protein Alternatives
Replace dairy protein with legumes (lentils, beans, chickpeas), nuts, seeds, and meat. These options are rich in protein and support a balanced diet during your treatment.
Addressing Potential Deficiencies
Monitor your intake of calcium, vitamin D, and probiotics. If you’re concerned about meeting your daily requirements, discuss supplementation with your doctor.
Consulting Your Doctor: Importance of Communication
Tell your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This includes antibiotics like Cipro. Accurate information ensures they can assess potential interactions.
Discussing Dairy Consumption
Openly discuss your dairy intake with your physician. Explain the quantity and types of dairy products you consume daily. This allows them to advise on potential modifications during your Cipro treatment.
Reporting Symptoms
Describe any side effects you experience while taking Cipro, including digestive issues. Note the timing of symptoms relative to medication and dairy consumption. This detailed information aids in diagnosis and treatment.
Don’t hesitate to ask questions! Clarify any uncertainties about medication, interactions, or dietary adjustments. Your doctor’s guidance ensures safe and effective treatment.