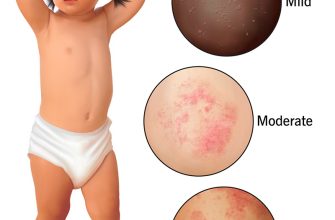
This combination is frequently prescribed for specific bacterial infections, particularly those involving both anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. Think of infections like severe acne or certain periodontal diseases. Doxycycline tackles the aerobic bacteria, while metronidazole targets the anaerobic ones, providing broader coverage.
Remember, this isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Your doctor will consider your individual infection, medical history, and potential drug interactions before recommending this regimen. Always follow their prescribed dosage and duration diligently; premature discontinuation can lead to treatment failure and potential resistance development.
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. More serious, though rare, reactions may involve allergic reactions or issues with your liver. Immediately contact your doctor if you experience severe symptoms or unusual reactions. Regular blood tests might be recommended, particularly for extended treatment courses, to monitor your liver function and overall health.
Before starting this medication, inform your doctor about any other medications you’re currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This is crucial to avoid potential interactions and ensure the safest treatment. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are also significant factors to discuss, as both doxycycline and metronidazole can affect the developing fetus or infant.
- Doxycycline and Metronidazole Combined: A Detailed Overview
- Common Indications
- Important Considerations
- Specific Dosage Recommendations
- Common Infections Treated with Doxycycline and Metronidazole Combination
- Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Combined Therapy
- Considerations and Precautions for Doxycycline and Metronidazole Combination Therapy
- Sun Sensitivity and Photosensitivity
- Gastrointestinal Upsets
- Medication Interactions
- Alcohol Consumption
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Doxycycline and Metronidazole Combined: A Detailed Overview
This combination targets bacterial infections, specifically those caused by both anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. Doxycycline, a broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic, inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. Metronidazole, an antibiotic effective against anaerobic bacteria and some protozoa, disrupts DNA synthesis in susceptible organisms. Their synergistic effect often leads to superior infection control compared to using either drug alone.
Common Indications
This combination frequently treats infections like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), bacterial vaginosis (BV), and intra-abdominal infections. It’s also used for treating skin and soft tissue infections where mixed aerobic and anaerobic bacterial flora are suspected. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Important Considerations
Before starting this regimen, patients should disclose any allergies to tetracyclines or nitroimidazoles. Potential side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and photosensitivity (with doxycycline). Metronidazole can cause metallic taste and dark urine. Alcohol consumption should be avoided during and shortly after treatment with metronidazole due to a potential for disulfiram-like reaction. Pregnant or breastfeeding women need special consideration. Liver and kidney function should be monitored, especially in patients with pre-existing conditions. Regular blood tests are sometimes advised during prolonged treatment. Accurate dosage and duration are crucial for successful treatment and minimizing side effects. Always follow your physician’s instructions precisely.
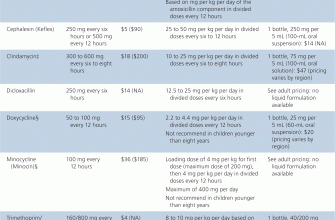
Specific Dosage Recommendations
Dosage varies depending on the specific infection and patient factors. A doctor will determine the appropriate dose of each medication and the overall duration of therapy. Self-medication is strongly discouraged.
Common Infections Treated with Doxycycline and Metronidazole Combination
This combination targets infections caused by bacteria sensitive to both antibiotics. It’s frequently used to treat specific conditions where both anaerobic and aerobic bacteria are suspected.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Doxycycline addresses Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, while metronidazole combats anaerobic bacteria like Bacteroides species, often involved in PID.
- Intra-abdominal Infections: This combination effectively tackles polymicrobial infections involving both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, common in intra-abdominal abscesses or peritonitis. Surgical drainage is usually needed alongside antibiotic therapy.
- Gynecological Infections: Beyond PID, this combination may be used for other gynecological infections with mixed bacterial flora. A doctor will determine the precise diagnosis and suitability of this combination.
- Infections Following Dental Procedures: Post-operative infections following dental extractions or other procedures can be treated with this combination, particularly if anaerobic bacteria are suspected.
Note: This combination isn’t suitable for all infections. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment recommendations. They will assess your specific infection and determine the most appropriate antibiotics.
- Proper diagnosis is paramount.
- Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern; appropriate use is critical.
- Always follow the prescribed dosage and duration.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Combined Therapy
Doxycycline and metronidazole, when used together, can increase the risk of certain side effects. Gastrointestinal upset, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, is common. You might also experience a metallic taste in your mouth. Less frequently, but still possible, are headaches, dizziness, and vaginal yeast infections.
This combination can interact with several medications. Warfarin, a blood thinner, may have its effect amplified, potentially leading to increased bleeding risk. It’s crucial to inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Alcohol consumption should be minimized or avoided entirely, as it can worsen side effects and increase the risk of liver damage. Certain antacids can reduce doxycycline absorption, so maintain a sufficient time gap between taking these medications.
Monitor for signs of allergic reactions such as rash, itching, or swelling. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing or any severe allergic reactions. Regular blood tests might be necessary to monitor for potential drug interactions and side effects, especially if you have pre-existing conditions like liver or kidney disease.
Remember, this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any medication, especially a combination therapy like this. They can assess your individual risk and provide personalized guidance.
Considerations and Precautions for Doxycycline and Metronidazole Combination Therapy
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting this combination therapy. This prevents potential drug interactions.
Monitor for signs of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI), such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. This antibiotic combination can disrupt gut flora, increasing CDI risk. Report these symptoms immediately to your healthcare provider. Treatment for CDI may be necessary.
Sun Sensitivity and Photosensitivity
Doxycycline increases sun sensitivity. Avoid prolonged sun exposure and use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Wear protective clothing when outdoors, especially during peak sun hours.
Gastrointestinal Upsets
Both doxycycline and metronidazole can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own. However, severe or persistent gastrointestinal issues require medical attention.
Medication Interactions
This combination may interact with anticoagulants (blood thinners), oral contraceptives, and certain seizure medications. Your doctor should carefully manage these interactions. Discuss your complete medical history to minimize risks.
Alcohol Consumption
Avoid alcohol consumption while taking metronidazole. Combining metronidazole with alcohol can cause a disulfiram-like reaction, leading to unpleasant symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, flushing, and headache.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Discuss the risks and benefits of this therapy with your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant. Alternative treatments may be considered.