Doxycycline is a common antibiotic frequently prescribed for certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, it’s not a cure-all; its effectiveness varies depending on the specific STI. Specifically, it’s often used to treat chlamydia and non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU), caused by bacteria like Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma genitalium. Remember, always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
For chlamydia, a single 1-gram dose of doxycycline is often sufficient, although a 7-day course may be recommended depending on the severity and location of the infection. Treating chlamydia promptly is critical to prevent potential long-term complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women. Self-treating is risky; proper diagnosis guarantees appropriate treatment.
Mycoplasma genitalium infections are more challenging to treat and may require a longer course of doxycycline, often combined with another antibiotic like azithromycin. Your doctor will determine the best course of action based on your individual circumstances and test results. This highlights the importance of comprehensive testing before starting any treatment.
Important Note: Doxycycline is not effective against syphilis, gonorrhea, or HIV. These STIs require different treatments. Ignoring proper medical guidance can lead to serious health consequences. Seek professional medical advice immediately if you suspect you have an STI.
- Doxycycline for STIs: A Detailed Guide
- What STIs Does Doxycycline Treat?
- Dosage and Administration of Doxycycline for STIs
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Lyme Disease
- Other STIs
- Administration Guidelines
- Potential Side Effects of Doxycycline
- Drug Interactions with Doxycycline
- When to Seek Alternative Treatment Options
- Important Considerations and Precautions
Doxycycline for STIs: A Detailed Guide
Doxycycline treats several sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
It’s crucial to remember that self-treating STIs is dangerous. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Chlamydia: Doxycycline is a common treatment for chlamydia infection. The standard course typically involves taking 100mg twice daily for seven days. Your doctor may adjust this based on your individual needs and test results.
- Gonorrhea: While it’s less frequently used as a *sole* treatment for gonorrhea due to increasing antibiotic resistance, doxycycline might be part of a combination therapy prescribed by your physician.
- Lyme disease: Though not strictly an STI, Lyme disease can be transmitted sexually, and doxycycline is often used in its early stages. Dosage and duration depend on the severity and stage of infection.
- Other STIs: Doxycycline might be included in the treatment plan for other bacterial infections sometimes associated with STIs, like syphilis (though usually not the primary treatment).
Possible Side Effects: Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and sun sensitivity. Rare but serious reactions can occur. Report any unexpected symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Medication Interactions: Doxycycline can interact with various medications, including antacids, blood thinners, and some birth control pills. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are currently taking.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Doxycycline isn’t generally recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding, due to potential risks to the developing fetus or nursing infant. Alternatives exist, and your doctor will make the best recommendation for your situation.
- Allergic Reactions: If you have a known allergy to tetracyclines (the family of antibiotics that includes doxycycline), inform your doctor. Severe allergic reactions are possible.
After Treatment: Even after successful treatment, it’s vital to get retested to confirm the infection is cleared. Practice safe sex to prevent future infections. Your doctor will provide guidance on post-treatment care and follow-up testing.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider for any questions about your health or treatment.
What STIs Does Doxycycline Treat?
Doxycycline treats chlamydia and gonorrhea infections. It’s often prescribed for these bacterial STIs, usually in combination with other antibiotics for gonorrhea to combat antibiotic resistance.
However, doxycycline is not a treatment for all STIs. It’s ineffective against viral STIs like HIV, herpes, and HPV. Similarly, it won’t treat syphilis.
Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Self-treating STIs can lead to serious complications, including infertility and increased risk of transmission. Proper diagnosis ensures you receive the correct medication and appropriate care.
Remember, early detection and treatment are key to managing STIs effectively. If you suspect an STI, seek medical attention immediately.
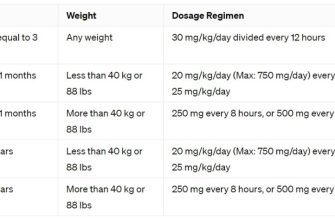
Dosage and Administration of Doxycycline for STIs
Doxycycline dosage for STIs varies depending on the specific infection. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Chlamydia
- Adult Dosage: A single 100mg dose is often prescribed, but some regimens call for 100mg twice a day for seven days.
- Important Note: Pregnant women should not take doxycycline. Alternative antibiotics are used for chlamydia in pregnancy.
Gonorrhea
- Adult Dosage: Generally, a single 200mg dose of doxycycline is combined with another antibiotic (like ceftriaxone) for optimal treatment. A seven-day course might also be prescribed.
- Important Note: Doxycycline alone is not sufficient to treat gonorrhea.
Lyme Disease
- Adult Dosage: A typical treatment involves 100mg twice a day for 10-21 days. The duration is determined by the severity of the infection and physician’s assessment.
- Important Note: Lyme disease requires careful monitoring. Follow your doctor’s guidance meticulously throughout and after treatment.
Other STIs
Doxycycline may be used to treat other STIs such as syphilis in some situations, often in conjunction with other medications. Your doctor will determine the best course of action based on individual circumstances and test results.
Administration Guidelines
- Take doxycycline with a full glass of water.
- Avoid taking it with dairy products, antacids, or iron supplements, as they can reduce absorption.
- Take the medication at the same time each day, preferably with food to minimize stomach upset.
- Complete the entire course of medication, even if you feel better before finishing all the pills. This ensures complete eradication of the infection.
- Report any side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or sun sensitivity, to your doctor immediately.
This information is for guidance only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Consult your doctor or healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of any sexually transmitted infection.
Potential Side Effects of Doxycycline
Doxycycline, while effective against many STIs, can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. These are usually mild and resolve without treatment. However, more serious reactions are possible, though less frequent.
Sun sensitivity is a common side effect. Avoid prolonged sun exposure and use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. If you experience a sunburn, contact your doctor.
Yeast infections are another potential side effect, particularly in women. Symptoms include vaginal itching and discharge. Your doctor can prescribe medication to treat this.
Doxycycline can affect your gut flora, potentially leading to oral thrush (a fungal infection of the mouth). Look for white patches in your mouth and consult your doctor if this occurs.
In rare cases, doxycycline can cause more serious reactions like esophageal irritation. Avoid lying down for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication to reduce this risk. Drink plenty of water with each dose.
Allergic reactions, while uncommon, can range from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling, or hives.
This information is not exhaustive. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for a complete list of potential side effects and to discuss any concerns.
Drug Interactions with Doxycycline
Doxycycline can interact with several medications, potentially affecting their effectiveness or causing adverse reactions. Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking before starting doxycycline.
Antacids: Avoid taking doxycycline with antacids containing calcium, magnesium, aluminum, or iron. These substances reduce doxycycline absorption. Separate your doses by at least two hours.
Dairy Products: Dairy products, such as milk and yogurt, can also impair doxycycline absorption. Consume them at least two hours before or after taking the medication.
Warfarin (Coumadin): Doxycycline can increase the effects of warfarin, a blood thinner. Close monitoring of your INR (International Normalized Ratio) is necessary if you take both medications.
Oral contraceptives: Doxycycline can reduce the effectiveness of certain oral contraceptives. Use additional contraceptive methods while taking doxycycline and for a month after you stop taking it.
Methotrexate: Combining doxycycline and methotrexate increases the risk of methotrexate toxicity. Your doctor may need to adjust your methotrexate dosage or monitor you closely.
Note: This information is not exhaustive. Consult a pharmacist or doctor for a complete list of potential interactions and for personalized advice.
When to Seek Alternative Treatment Options
Doxycycline works well for many STIs, but sometimes it’s not the best choice. Consider alternatives if you experience severe allergic reactions like difficulty breathing or swelling. A serious allergic reaction requires immediate medical attention.
If your symptoms don’t improve after a full course of doxycycline, see your doctor. This suggests the infection may be resistant to the medication, or it may be a different infection entirely. Retesting is needed to confirm the diagnosis and inform treatment.
Certain STIs, like gonorrhea, are increasingly resistant to doxycycline. Your doctor will conduct tests to determine the best treatment. They might prescribe a different antibiotic, potentially a combination therapy for best results.
Pregnancy or breastfeeding significantly impacts medication choices. Doxycycline is often avoided during pregnancy and breastfeeding, so alternative antibiotics, safer for the mother and child, are preferred. Discuss this with your doctor to select a safe and effective treatment.
Pre-existing medical conditions can affect antibiotic choices. Kidney or liver problems may limit which antibiotics you can safely use. Always inform your doctor of any health conditions before starting treatment.
| Situation | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe allergic reaction | Seek immediate medical attention. |
| Symptoms persist after treatment | Return to your doctor for retesting and alternative treatment. |
| Gonorrhea infection | Discuss alternative antibiotics with your doctor. |
| Pregnancy or breastfeeding | Consult your doctor for safe antibiotic alternatives. |
| Pre-existing medical conditions | Inform your doctor before starting treatment. |
Important Considerations and Precautions
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Some medications interact negatively with doxycycline.
Doxycycline can increase your sun sensitivity. Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
Report any signs of allergic reaction immediately. These include rash, hives, itching, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical attention.
Stomach upset is a common side effect. Take doxycycline with food or milk to minimize this. If nausea or vomiting persists, contact your doctor.
Doxycycline can affect the effectiveness of birth control pills. Discuss alternative birth control methods with your doctor while taking this medication and for at least a month after completing the course.
Avoid consuming dairy products or antacids within two hours of taking doxycycline, as they can impair absorption.
Complete the entire course of doxycycline, even if you feel better. Stopping early can lead to treatment failure and antibiotic resistance.
This medication can cause yeast infections in women. If you experience vaginal itching or discharge, consult your doctor.
Doxycycline may affect your liver function. Your doctor may order blood tests to monitor your liver health. Report any signs of liver problems, such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, or unusual fatigue.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting any medication.