Experiencing Cipro-related side effects? You’re not alone. Many individuals report debilitating symptoms after taking this antibiotic, a condition often referred to as “Floxing.” This article offers practical advice and resources to help you manage your experience.
First, connect with a support group. Sharing your story with others who understand the unique challenges of Floxing can significantly improve your emotional well-being. Online communities provide a safe space for peer-to-peer support and information exchange. Many groups offer direct access to medical professionals specialized in post-antibiotic side effects.
Secondly, meticulously document your symptoms. Maintain a detailed record, including dates, times, symptom severity, and any associated triggers. This comprehensive log provides valuable data for consultations with your healthcare provider and specialists. Precise records can aid in diagnosis and treatment planning. Consider using a dedicated symptom tracking app or a simple journal.
Finally, actively seek medical attention. Don’t hesitate to consult multiple specialists until you find the right fit. A multidisciplinary approach, involving specialists in infectious disease, neurology, and other relevant fields may be necessary. Advocate for yourself; your experience matters, and a proactive approach is crucial for your recovery.
Floxed by Cipro: Understanding the Risks
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) carries a risk of tendon rupture, particularly in older adults and those taking corticosteroids. This serious side effect, known as “Floxing,” can affect Achilles tendons most commonly, but other tendons can also be involved. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience tendon pain or inflammation while taking Cipro.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Symptoms of tendon damage include sudden, sharp pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected joint. Don’t ignore these signals. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical for preventing permanent damage. Early intervention significantly improves recovery chances.
Minimizing Your Risk
Inform your doctor about your complete medical history, including existing conditions and medications, before starting Cipro. Older adults and those with kidney problems have a heightened susceptibility. Avoid strenuous activity while on Cipro, and carefully consider the risks and benefits with your doctor before taking it. Alternatives may exist depending on your specific condition.
Long-Term Effects
While many recover fully, some experience persistent tendon issues. These can include chronic pain, reduced flexibility, and limited mobility. Regular follow-up appointments with your physician are vital to monitor any lingering complications and manage ongoing pain. Physical therapy can aid in rehabilitation.
Reporting Adverse Reactions
Report any suspected adverse reaction to Cipro or other medications to your doctor immediately and consider reporting it to the relevant regulatory agencies, such as the FDA (in the US) or the MHRA (in the UK). This information aids in tracking medication safety and may help prevent similar incidents.
Recognizing Ciprofloxacin-Induced Tendinitis and Tendon Rupture
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience new or worsening pain, swelling, or stiffness in a tendon, especially in your Achilles, shoulder, hand, or wrist, after taking ciprofloxacin.
Pay close attention to these key symptoms:
- Sudden, sharp pain in a tendon
- Swelling around the affected tendon
- Limited range of motion or difficulty using the affected joint
- A popping or snapping sensation in the tendon
- Bruising around the affected area
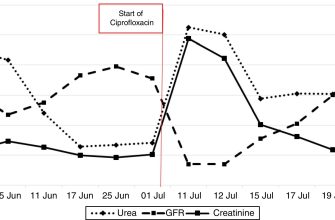
These symptoms can appear within days to weeks of starting ciprofloxacin, even after you stop the medication. The risk increases with higher doses and longer treatment durations.
Certain factors increase your susceptibility:
- Age over 60
- History of tendon problems
- Concurrent use of corticosteroids
- Kidney disease
Diagnosis usually involves a physical exam and possibly imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent tendon rupture. Treatment often involves rest, physical therapy, and pain management. In some cases, surgery may be necessary.
If you suspect ciprofloxacin-induced tendinitis or tendon rupture, promptly discontinue ciprofloxacin and contact your doctor. Open communication with your healthcare provider about your symptoms and medication history is vital for your health.
Managing and Treating Ciprofloxacin-Induced Tendon Damage
Stop taking ciprofloxacin immediately if you experience tendon pain or inflammation. Consult your doctor; early intervention is key.
Rest is paramount. Avoid activities that stress the affected tendon. This includes weight-bearing exercises and strenuous movements. Modify your daily routine to minimize strain.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in recovery. A therapist will design a program of gentle exercises to strengthen and rehabilitate the tendon. Follow their instructions carefully and be patient; healing takes time.
Your doctor might prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation. Always adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration.
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair a ruptured tendon. This is a last resort, typically reserved for complete tendon tears.
Pain management is a priority. Besides NSAIDs, your doctor might suggest other pain relief options, including topical creams or other analgesics. Discuss all your options.
Monitor your progress closely. Report any worsening symptoms or new concerns to your healthcare provider immediately. Regular check-ups aid in tracking recovery.
Full recovery varies depending on the severity of the damage and individual response to treatment. Complete healing can take weeks, or even months. Patience and diligent adherence to the treatment plan are crucial.
Preventing Ciprofloxacin-Related Tendon Problems
Maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight puts extra stress on your joints, increasing tendon vulnerability.
Prioritize regular, low-impact exercise. Activities like swimming or walking strengthen tendons without excessive strain.
Listen to your body. Rest immediately if you experience any tendon pain or stiffness. Ignoring early symptoms can worsen the condition.
Consume a balanced diet. Ensure sufficient intake of protein, calcium, and vitamin D, all vital for tendon health.
Stay hydrated. Proper hydration supports overall bodily function, including tendon health.
Avoid strenuous activity while taking Ciprofloxacin. This includes heavy lifting and intense workouts.
Inform your doctor about any existing tendon conditions or family history of tendon problems before starting Ciprofloxacin.
Report any tendon pain or discomfort to your doctor immediately, even if it appears minor. Early intervention is key.
Consider alternative antibiotics if feasible. Discuss other treatment options with your physician if Ciprofloxacin poses a significant risk.
After completing your Ciprofloxacin course, gradually resume normal activities. Avoid sudden increases in physical exertion.