Stop Cipro-induced tendon pain with these steps: First, immediately discontinue Ciprofloxacin. This antibiotic is a known culprit in tendon damage. Ignoring this crucial first step prolongs healing time and increases the risk of serious complications.
Next, focus on rest. Avoid activities that stress the affected tendon. This means modifying your exercise routine or taking time off work, if necessary. Listen to your body; pushing through the pain only exacerbates the injury.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in recovery. A physical therapist can guide you through specific exercises to strengthen the tendon and restore its function. They’ll also teach you proper posture and movement techniques to prevent future issues. Expect a personalized plan; your therapist will tailor the exercises to your specific needs and progress.
Consider over-the-counter pain relief. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen or naproxen, can reduce pain and inflammation. Always follow the dosage instructions on the packaging. If pain persists or worsens, consult your doctor; they may suggest stronger pain management options.
Finally, maintain open communication with your doctor. Regular checkups monitor your progress and allow for adjustments to your treatment plan. Early intervention and consistent care lead to the best outcomes. Remember, proper healing takes time and patience.
- How to Treat Cipro Tendonitis
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin-Induced Tendonitis
- Rest and Physical Therapy for Cipro Tendonitis
- Physical Therapy: A Gradual Return to Activity
- Beyond Physical Therapy
- Medication and Pain Management for Cipro Tendonitis
- Long-Term Management and Prevention of Recurrence
- Physical Therapy and Exercise
- Medication and Supplements
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Preventing Future Episodes
- Alternative Therapies
How to Treat Cipro Tendonitis
First, stop taking Ciprofloxacin immediately if you suspect tendonitis. This is crucial for preventing further damage.
Rest is paramount. Avoid activities that stress the affected tendon. This includes strenuous exercise and repetitive movements.
Ice the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. This reduces inflammation.
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation. Follow dosage instructions carefully.
Your doctor might recommend physical therapy to strengthen the tendon and improve its flexibility once the inflammation subsides. This often involves targeted exercises.
In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medication or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. They might also recommend tendon surgery as a last resort.
Maintain a healthy diet, including plenty of protein, to support tendon healing. Proper nutrition aids recovery.
Monitor your progress closely and report any worsening symptoms to your physician promptly. Early intervention is key.
Complete rest and careful adherence to your doctor’s advice are vital for a successful recovery. Follow their guidance closely.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin-Induced Tendonitis
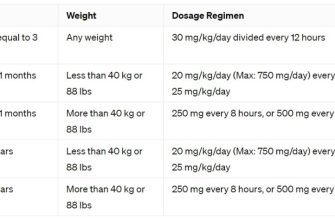
Ciprofloxacin, a common antibiotic, can unfortunately cause tendonitis, inflammation of a tendon. This risk increases with age and in people already taking corticosteroids. The Achilles tendon is most frequently affected.
Symptoms often include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected tendon. You might experience tenderness to the touch, and potentially limited range of motion. Early diagnosis is key.
Risk factors beyond age and corticosteroid use include kidney problems, a history of tendon injuries, and high doses of Ciprofloxacin. Proper hydration may help, but discuss this with your doctor.
Treatment focuses on rest, ice, and pain relief. Your doctor might prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Physical therapy may be necessary to regain strength and flexibility post-recovery. Avoid strenuous activity during treatment and consider using supportive devices, such as braces or splints.
Surgery is rarely required but may be considered for severe cases that don’t respond to conservative treatment. This decision requires careful consideration with your physician.
Prevention involves careful consideration of Ciprofloxacin use. Always discuss alternatives with your doctor before taking this antibiotic if you have risk factors. Monitor for symptoms and promptly report any concerns.
Rest and Physical Therapy for Cipro Tendonitis
Immediately reduce strenuous activities on the affected tendon. Complete rest isn’t always necessary, but avoid movements that cause pain. Listen to your body; pain is a signal to stop.
Physical Therapy: A Gradual Return to Activity
Your physical therapist will create a customized program. This typically involves range-of-motion exercises to maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness. Expect gentle strengthening exercises to rebuild tendon strength gradually, avoiding overexertion. They might also use modalities like ultrasound or ice to manage pain and inflammation. Progress slowly; setbacks are possible, and patience is key. Regular sessions are vital for optimal recovery. Expect your therapist to monitor your progress and adjust the program as needed. Consistent adherence to your home exercise program is also crucial for success.
Beyond Physical Therapy
Your doctor might recommend other supportive therapies, such as bracing or splinting, to reduce stress on the affected tendon during recovery. Discuss these options with your physician to determine what’s right for you.
Medication and Pain Management for Cipro Tendonitis
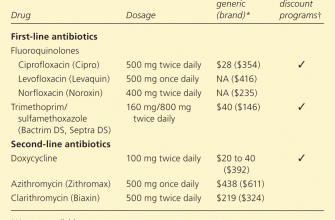
Your doctor might prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen or naproxen, to reduce pain and inflammation. Always follow prescribed dosages carefully.
In cases of severe pain, stronger pain relievers, such as opioids, may be considered; however, these are usually short-term solutions due to potential side effects. Discuss this option thoroughly with your physician.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role. Your therapist will design a program of targeted exercises to strengthen tendons and improve flexibility. Consistent participation is key to successful recovery.
Corticosteroid injections can provide temporary pain relief, but they’re not a long-term solution and carry the risk of tendon rupture. This should be discussed carefully with your doctor, weighing the benefits against the risks.
Rest is critical. Avoid activities that aggravate your pain. Gradually increase activity levels as your tendon heals, guided by your physician or physical therapist. Listen to your body and avoid pushing it too hard.
Bracing or splinting the affected area can provide support and reduce strain on the tendon, promoting healing. Your doctor or physical therapist will advise on the appropriate bracing technique.
Surgery is rarely necessary for Cipro tendonitis. It’s generally considered only as a last resort if conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
Remember to consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment tailored to your specific situation.
Long-Term Management and Prevention of Recurrence
Prioritize rest. Avoid strenuous activities that aggravate your tendon until pain subsides. Gradual return to activity is key; don’t rush it.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Engage in a targeted physical therapy program. This often includes exercises to strengthen the affected tendon and improve flexibility. A physiotherapist will guide you through appropriate stretches and strengthening routines.
- Eccentric exercises, which involve lengthening the muscle against resistance, are particularly helpful.
- Low-impact cardiovascular activities like swimming or cycling can maintain fitness without stressing tendons.
Medication and Supplements
Your doctor might recommend over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen. In some cases, they may prescribe stronger medications to manage pain and inflammation. Some studies suggest that certain supplements, such as glucosamine and chondroitin, might support tendon health, but more research is needed. Discuss this with your doctor before taking any supplements.
Lifestyle Modifications
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on your joints. Ensure adequate hydration; dehydration can negatively impact tendon health. A balanced diet rich in protein and nutrients is supportive.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor or physical therapist are crucial. This allows for monitoring of your progress, adjustments to treatment plans, and early detection of any potential setbacks. Listen to your body and don’t hesitate to communicate any concerns.
Preventing Future Episodes
- Warm up thoroughly before any exercise or physical activity.
- Cool down afterwards to reduce muscle stiffness.
- Use proper form during exercise to prevent strain.
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activities to avoid overexertion.
- Wear appropriate supportive footwear.
- Consider using protective gear during activities that place stress on tendons.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals find relief with alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage. However, evidence supporting their effectiveness in treating tendonitis is limited. Discuss these options with your healthcare provider before pursuing them.