Need fast, reliable information on ciprofloxacin? Start with dosage: Adults typically take 250-750mg twice daily, adjusted based on infection severity and your physician’s assessment. Remember, this is general advice; always follow your doctor’s prescription instructions precisely.
Ciprofloxacin combats bacterial infections by interfering with their DNA replication. This means it targets the bacteria directly, inhibiting their ability to multiply and spread. Common uses include treating urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and skin infections. However, it’s not effective against viral infections like the common cold.
Important Considerations: Before taking ciprofloxacin, discuss potential side effects with your doctor. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. More serious, though less frequent, reactions might include tendonitis or allergic reactions. Also, inform your doctor about any other medications you’re taking to avoid potential drug interactions. Always keep your doctor informed of your medical history and any new symptoms you experience while using this medication.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance on ciprofloxacin use and treatment. They can accurately assess your needs and provide tailored recommendations to ensure your safety and effective treatment.
- Ciprofloxacin: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin’s Mechanism of Action
- Targeting Bacterial DNA
- Resistance Mechanisms
- Common Uses and Indications for Ciprofloxacin
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions of Ciprofloxacin
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications of Ciprofloxacin
- Medication Interactions Requiring Caution
- Contraindications
- Additional Considerations
- Disclaimer:
- Ciprofloxacin Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Oral Administration
- Intravenous Administration
- Dosage Table (Illustrative – Consult your physician for precise instructions)
- Important Considerations
Ciprofloxacin: A Detailed Overview
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria. It works by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes vital for bacterial DNA replication and cell division. This action leads to bacterial cell death.
Common uses include treating infections of the:
- Respiratory tract (pneumonia, bronchitis)
- Skin and soft tissues
- Bones and joints
- Urinary tract
- Gastrointestinal tract
Ciprofloxacin is available in various forms: oral tablets, extended-release tablets, intravenous infusions, and ophthalmic solutions. Dosage varies depending on the infection’s severity and location, patient’s age and kidney function. Always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely.
Potential side effects include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
More serious, though rare, side effects include:
- Tendinitis and tendon rupture (particularly in older adults or those on corticosteroid medication)
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Photosensitivity
- QT interval prolongation (affecting heart rhythm)
Inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions, allergies, or medications you are taking, especially anticoagulants or medications that prolong the QT interval. Pregnancy and breastfeeding require specific considerations; consult your doctor for advice. Immediate medical attention is needed if you experience severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or severe skin rash.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or stopping any medication.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin’s Mechanism of Action
Ciprofloxacin targets bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are crucial for DNA replication, transcription, and repair in bacteria. Ciprofloxacin inhibits these enzymes by binding to them, preventing DNA supercoiling and relaxation.
Targeting Bacterial DNA
This inhibition halts bacterial DNA replication and transcription, effectively stopping bacterial growth and ultimately leading to bacterial cell death. The drug’s potency stems from its selective action: It preferentially binds to bacterial enzymes over human counterparts, minimizing harm to human cells.
Resistance Mechanisms
Bacterial resistance to ciprofloxacin develops through mutations in the genes encoding DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These mutations alter the enzyme’s structure, reducing ciprofloxacin’s binding affinity. Efflux pumps, which actively remove the antibiotic from the bacterial cell, also contribute to resistance. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for developing strategies to combat antibiotic resistance.
Common Uses and Indications for Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin treats several bacterial infections. Doctors frequently prescribe it for urinary tract infections (UTIs), including complicated and uncomplicated cases. It’s also a go-to treatment for certain types of pneumonia, particularly those caused by susceptible bacteria.
Infections of the skin and soft tissues often respond well to ciprofloxacin, especially those involving wounds or abscesses. This antibiotic proves effective against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis – common culprits in UTIs. It also targets Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a bacterium frequently responsible for hospital-acquired infections.
Ciprofloxacin finds application in treating acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis and some forms of gastroenteritis. Remember, however, it’s vital to confirm the bacterial cause and susceptibility before starting treatment. Your physician will determine the appropriate dosage and duration based on your individual needs and the specifics of your infection.
Note: Ciprofloxacin is not suitable for all bacterial infections. Viral infections, like the common cold or influenza, will not respond to this antibiotic. Always consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, while effective, can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. These usually are mild and resolve without treatment. However, report persistent or severe digestive issues to your doctor.
More serious, though less common, side effects involve tendon problems, particularly in older adults and those taking corticosteroids. Pain, swelling, or inflammation in a tendon requires immediate medical attention. Avoid strenuous activity if you experience any tendon discomfort.
Ciprofloxacin can also affect your nervous system. Dizziness, headaches, and confusion are possible. If you experience these, avoid driving or operating machinery until symptoms subside. Report any significant neurological changes to your doctor.
Photosensitivity is another potential concern. Limit sun exposure and use sunscreen with a high SPF while taking Ciprofloxacin. This precaution minimizes the risk of sunburn.
Before starting Ciprofloxacin, inform your doctor about all your medications, including supplements and herbal remedies. Interactions with certain drugs can occur. Also, mention any pre-existing medical conditions, especially kidney or liver problems.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding should be discussed with your physician before commencing Ciprofloxacin treatment. The drug’s effects on pregnancy and nursing infants require careful evaluation.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking Ciprofloxacin prematurely, even if you feel better, unless advised by your doctor.
If you experience an allergic reaction, such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical help. This is a serious side effect requiring prompt intervention.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications of Ciprofloxacin
Avoid ciprofloxacin with antacids containing magnesium or aluminum. These can significantly reduce ciprofloxacin absorption.
Ciprofloxacin interacts negatively with theophylline, increasing the risk of theophylline toxicity. Monitor theophylline levels carefully if you’re using both medications.
Concurrent use of ciprofloxacin and warfarin may increase bleeding risk. Closely monitor your INR if you’re taking both medications.
Medication Interactions Requiring Caution
Probenecid reduces ciprofloxacin excretion, potentially increasing ciprofloxacin levels and side effects. Your doctor should carefully monitor your condition.
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs) like ibuprofen or naproxen may increase the risk of central nervous system effects, such as seizures, when combined with ciprofloxacin. Be aware of this increased risk.
Caffeine metabolism might be affected, leading to higher caffeine levels. Consider reducing caffeine intake.
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin or other fluoroquinolones is an absolute contraindication.
Ciprofloxacin is contraindicated in patients with a history of tendonitis or tendon rupture associated with fluoroquinolone use.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding require careful evaluation of risk versus benefit, as data on these conditions is limited. Consult your healthcare provider.
Additional Considerations
Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking before starting ciprofloxacin. This will help avoid potential drug interactions.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking ciprofloxacin abruptly.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or stopping any medication.
Ciprofloxacin Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. Dosage depends heavily on the infection being treated and your individual health. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Oral Administration
Ciprofloxacin tablets or capsules should be swallowed whole with a full glass of water. Avoid taking them with dairy products or antacids, as these can reduce absorption. Take them on an empty stomach or two hours after a meal for optimal effectiveness.
Intravenous Administration
Intravenous ciprofloxacin is administered by a healthcare professional. The infusion rate and duration vary depending on the infection’s severity and the patient’s response to treatment. Close monitoring is necessary during IV administration.
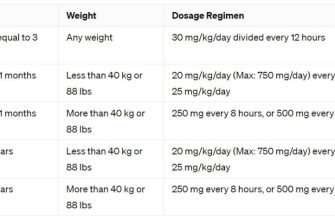
Dosage Table (Illustrative – Consult your physician for precise instructions)
| Infection Type | Usual Adult Dosage | Administration Route |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) | 250-750 mg twice daily | Oral or IV |
| Pneumonia | 750 mg twice daily | Oral or IV |
| Skin Infections | 500-750 mg twice daily | Oral or IV |
Note: This table provides general examples. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration based on your specific needs. Children’s dosage differs significantly and requires careful calculation by a healthcare professional.
Important Considerations
Inform your doctor about any allergies, existing medical conditions (especially kidney or liver problems), and other medications you are taking. Report any unusual side effects immediately. Complete the full course of treatment, even if you feel better, to prevent relapse. Regular monitoring of kidney function may be needed, particularly with prolonged or high-dose treatment.