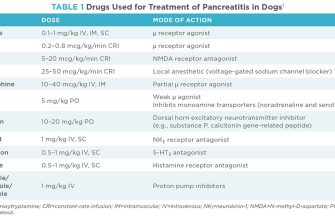
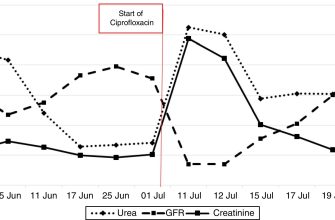
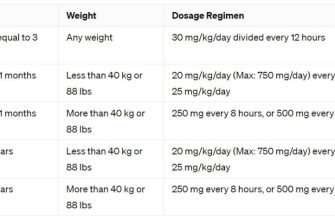
Simultaneous use of Macrobid (nitrofurantoin) and Cipro (ciprofloxacin) is generally considered safe, but requires careful monitoring. However, potential interactions exist, primarily related to renal function. Both drugs are primarily excreted by the kidneys; therefore, concurrent use increases the risk of nephrotoxicity.
Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before combining these medications. They can assess your individual risk factors, such as pre-existing kidney conditions or other medications you are taking, and determine the safest approach. This is particularly crucial for individuals with impaired kidney function.
Closely monitor for signs of kidney problems, including changes in urine output, swelling, fatigue, or unusual bruising. Report any such symptoms immediately to your healthcare provider. Regular blood and urine tests might be recommended to assess your kidney function during concurrent medication.
While rare, some patients may experience gastrointestinal side effects like nausea or diarrhea when taking both drugs. Adequate hydration is recommended to mitigate these side effects and promote proper drug excretion. This personalized approach to medication management ensures optimal health outcomes.
- Macrobid and Cipro Compatibility: A Detailed Overview
- Potential Drug Interactions
- Contraindications and Precautions
- Monitoring and Side Effects
- Alternatives and Treatment Approaches
- Conclusion
- Understanding Macrobid (Nitrofurantoin)
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
- Common Uses
- Important Considerations
- Drug Interactions
- Dosage and Administration
- Contraindications
- Seeking Medical Advice
- Mechanism of Action: How Macrobid and Cipro Work
- Macrobid’s Targeted Approach
- Cipro’s Broader Spectrum
- Key Differences Summarized
- Potential Drug Interactions Between Macrobid and Cipro
- Kidney Function Monitoring
- Gastrointestinal Side Effects
- Reporting Adverse Reactions
- Concurrent Use: When It Might Be Necessary
- Risks and Side Effects of Combined Use
- Consulting a Healthcare Professional: Importance of Medical Advice
- Understanding Your Medications
Macrobid and Cipro Compatibility: A Detailed Overview
Generally, Macrobid (nitrofurantoin) and Cipro (ciprofloxacin) can be taken together, but always consult your doctor or pharmacist before combining them. Both treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), but they target bacteria differently.
Potential Drug Interactions
While not always significant, some interactions are possible. Cipro can slightly reduce the effectiveness of some medications that impact kidney function. Since Macrobid is processed through the kidneys, this is a factor to consider. Your healthcare provider will assess your overall health and medication profile to determine any risk.
Contraindications and Precautions
- Kidney Issues: Both medications are processed through the kidneys. If you have kidney problems, your doctor will carefully weigh the benefits and risks before prescribing either drug, especially together.
- Allergic Reactions: Previous allergic reactions to either medication are absolute contraindications. Report any allergies to your doctor immediately.
- Liver Problems: While less common, liver issues could affect how your body processes these drugs. Discuss any liver conditions with your physician before starting treatment.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Both medications have varying pregnancy safety profiles. Always inform your doctor about your pregnancy or breastfeeding status.
Monitoring and Side Effects
While usually well-tolerated, both drugs have potential side effects. Common side effects of Macrobid include nausea and vomiting. Cipro may cause diarrhea and tendon pain. Your doctor may suggest regular monitoring of your kidney and liver function, especially if you have pre-existing conditions.
Alternatives and Treatment Approaches
- Your doctor might prescribe only one of these medications, depending on the specific bacteria causing the infection and your health status.
- Alternative antibiotics exist for UTIs, so a discussion about appropriate options is important if you have concerns about combining Macrobid and Cipro.
Conclusion
Taking Macrobid and Cipro together is sometimes possible, but a physician’s guidance is crucial. This detailed overview highlights potential interactions, precautions, and alternatives. Remember to fully disclose your medical history and any current medications to your healthcare provider for safe and effective treatment.
Understanding Macrobid (Nitrofurantoin)
Macrobid, containing nitrofurantoin, targets specific urinary tract bacteria. It’s a commonly prescribed antibiotic for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Key Considerations:
- Mechanism of Action: Nitrofurantoin interferes with bacterial metabolic processes, preventing their growth and reproduction within the urinary tract.
- Spectrum of Activity: It effectively combats Escherichia coli (E. coli), a frequent UTI culprit, along with other gram-negative bacteria. However, it’s less effective against many gram-positive bacteria and some resistant strains.
- Dosage and Administration: Your doctor determines the appropriate dosage based on your specific condition. It’s typically taken orally, often with food to minimize stomach upset. Adhere strictly to your prescribed regimen, even if symptoms subside.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Less frequent, but more serious, reactions can include lung problems (pulmonary fibrosis), especially with long-term use. Report any unusual symptoms promptly to your physician.
- Contraindications: Pregnant women in their third trimester, individuals with severe kidney impairment, and those with a history of nitrofurantoin-related lung issues should generally avoid it.
- Drug Interactions: Nitrofurantoin can interact with certain medications. Discuss all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, with your doctor before starting treatment.
- Allergic Reactions: Like any medication, allergic reactions are possible. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
Monitoring Treatment: Your doctor may order tests to monitor your kidney function and the effectiveness of the treatment.
Important Note: This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
Ciprofloxacin, commonly known as Cipro, is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It targets a wide range of bacterial infections by inhibiting bacterial DNA replication. This means it stops bacteria from reproducing, allowing your body’s immune system to fight off the infection.
Common Uses
Doctors prescribe Cipro for various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections (UTIs), respiratory tract infections like bronchitis and pneumonia, skin infections, and certain types of sexually transmitted infections. It’s also used to treat anthrax exposure and some types of food poisoning.
Important Considerations
Cipro is a powerful antibiotic, so understanding potential side effects is vital. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Less common, but more serious, side effects can include tendonitis, tendon rupture, and nerve damage. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any unusual symptoms.
Drug Interactions
Cipro can interact with other medications, so always provide your doctor with a complete list of current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Certain medications may increase the risk of side effects when taken with Cipro.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage varies depending on the infection and individual factors. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose and duration of treatment. Always follow prescribed instructions carefully. Do not stop taking Cipro prematurely, even if you feel better, unless directed by your doctor. This can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Contraindications
| Condition | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Known allergy to fluoroquinolones | Avoid Cipro if you have a history of allergic reactions to fluoroquinolone antibiotics. |
| Pregnancy or breastfeeding | Consult your doctor regarding the risks and benefits before using Cipro during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. |
| Certain neurological conditions | Pre-existing neurological conditions may increase the risk of nerve-related side effects. |
Seeking Medical Advice
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting any new medication, including Cipro. They can assess your individual needs and determine the appropriate course of treatment. Never self-medicate.
Mechanism of Action: How Macrobid and Cipro Work
Macrobid (nitrofurantoin) and Cipro (ciprofloxacin) both fight bacterial infections, but they do so in different ways. Macrobid disrupts bacterial cell production of energy and other crucial processes, effectively killing the bacteria. It achieves this by interfering with bacterial DNA. This mechanism is particularly effective against certain types of Gram-negative bacteria that commonly cause urinary tract infections.
Macrobid’s Targeted Approach
Nitrofurantoin’s impact is primarily focused on the urinary tract. This targeted action minimizes side effects in other parts of the body. This makes it a favored choice for treating uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
Cipro’s Broader Spectrum
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, works differently. It inhibits an enzyme, DNA gyrase, that bacteria need to unwind and replicate their DNA. Without this enzyme’s function, bacterial DNA replication stops, leading to bacterial death. Cipro’s broader spectrum of activity targets a wider range of bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative species. This makes it useful for treating a variety of infections.
Key Differences Summarized
In short: Macrobid directly damages bacterial DNA and is primarily used for urinary tract infections; Cipro inhibits an enzyme crucial for DNA replication, offering a broader spectrum of activity against various bacterial infections.
Potential Drug Interactions Between Macrobid and Cipro
While Macrobid (nitrofurantoin) and Cipro (ciprofloxacin) are both antibiotics, taking them together might increase your risk of certain side effects. Both medications can affect your kidneys; therefore, combining them requires careful monitoring, especially if you have pre-existing kidney problems. This combination isn’t inherently dangerous for everyone, but it necessitates closer medical supervision.
Kidney Function Monitoring
Your doctor should regularly assess your kidney function with blood tests while you are on this dual antibiotic regimen. This is to detect any potential adverse effects early on and make necessary adjustments to dosage or treatment plan. Increased fluid intake is advisable to support healthy kidney function.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Both Macrobid and Cipro can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Taking them concurrently may intensify these gastrointestinal side effects. If you experience severe or persistent digestive issues, contact your doctor immediately. Smaller, more frequent meals may help manage these symptoms.
Reporting Adverse Reactions
It’s vital to promptly report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider. This includes but isn’t limited to: skin rashes, unusual bleeding, severe abdominal pain, or changes in urination. Open communication with your doctor ensures the safest possible outcome while taking both medications.
Concurrent Use: When It Might Be Necessary
Doctors sometimes prescribe Macrobid (nitrofurantoin) and Cipro (ciprofloxacin) concurrently to treat complex urinary tract infections (UTIs). This happens when a UTI involves multiple bacteria, some susceptible to Macrobid and others to Cipro. A physician might choose this approach if initial tests suggest mixed bacterial infection, or if the patient hasn’t responded to Macrobid alone. This dual approach aims to broaden antimicrobial coverage.
However, this combined therapy isn’t routine. Before prescribing both, your doctor will assess your individual medical history, considering potential drug interactions and your overall health. Factors such as kidney function play a significant role in this decision. Always discuss potential side effects and alternative treatments.
The decision to use Macrobid and Cipro together is based on a thorough evaluation of the infection’s characteristics and your specific needs. Your physician will weigh the benefits of broader coverage against potential risks associated with combined antibiotic use. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to ensuring the safest and most effective treatment plan.
Remember: Never self-medicate or alter your prescribed antibiotic regimen without consulting your doctor. This information is for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice.
Risks and Side Effects of Combined Use
Avoid combining Macrobid (nitrofurantoin) and Cipro (ciprofloxacin) unless explicitly directed by your doctor. Concurrent use increases the risk of several side effects.
Gastrointestinal issues are common with both drugs independently; combining them significantly raises the probability of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. You might experience more severe symptoms than with either medication alone.
Kidney problems can worsen with this combination. Both Macrobid and Cipro can affect kidney function, and taking them together elevates the risk of kidney damage, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney disease. Regular monitoring of kidney function is advised.
The risk of tendonitis and tendon rupture, while relatively low with either drug alone, increases when taken together. This risk is heightened in older adults or those on corticosteroid medication.
Central nervous system side effects such as dizziness, headache, and confusion can be amplified with concurrent use. These side effects can impair daily functioning and potentially lead to accidents.
Allergic reactions, though uncommon, are possible with both drugs. Combining them doesn’t inherently increase the allergy risk but could lead to a more severe reaction if an allergy exists.
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting a new prescription. Open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional: Importance of Medical Advice
Always discuss your medication regimen with your doctor or pharmacist. They can assess potential drug interactions, like those between Macrobid and Cipro, and tailor a treatment plan to your specific health needs. This includes considering your medical history, current medications, and any allergies.
Understanding Your Medications
Never adjust your medication doses or stop taking prescribed medications without consulting your healthcare provider. Incorrect dosage or abrupt cessation can negatively impact your health. Your doctor can explain the purpose, potential side effects, and proper use of each medication in your prescription. Open communication is key to successful treatment.
Your doctor or pharmacist possesses the expertise to evaluate your unique situation and provide personalized advice. They’ll help you understand the risks and benefits of different treatment options and guide you toward the best approach for your condition. This ensures optimal treatment and minimizes potential adverse effects.