Experiencing muscle weakness while taking Ciprofloxacin? Don’t panic. Muscle weakness, or myopathy, is a known, albeit uncommon, side effect. This article provides practical information to help you understand the connection and take appropriate steps.
Report any muscle weakness to your doctor immediately. Early detection is key. Your physician can assess your symptoms, consider alternative antibiotics if necessary, and monitor your condition. Remember, prompt reporting significantly improves management outcomes.
This medication affects the body’s energy production at a cellular level. This can manifest as weakness, particularly in the legs and arms, sometimes accompanied by pain or cramps. The severity varies, ranging from mild discomfort to significant limitations in daily activities. We’ll examine these potential effects in detail throughout this article. Always discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen.
Key takeaway: While muscle weakness is rare, it’s a possible side effect of Ciprofloxacin. Your doctor’s guidance is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. The information provided here aims to increase your awareness and empower you to discuss potential concerns proactively.
- Muscle Weakness with Cipro: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding the Risk
- Recognizing Symptoms
- Seeking Medical Attention
- Alternative Treatments
- Managing Muscle Weakness
- Disclaimer
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin and its Mechanism
- Common Muscle Side Effects Associated with Cipro
- Specific Muscle Issues
- Risk Factors for Cipro-Induced Muscle Weakness
- Specific Medication Interactions
- Recognizing Symptoms of Cipro-Related Muscle Problems
- Seeking Medical Attention and Diagnosis
- Treatment Options for Cipro-Induced Muscle Weakness
- Managing Symptoms
- Addressing Underlying Causes
- Physical Therapy
- Medical Monitoring
- Preventing Cipro-Related Muscle Issues
- Dietary Considerations
- Medication Management
- Additional Tips
Muscle Weakness with Cipro: A Detailed Overview
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) can cause muscle weakness, a side effect reported by some patients. This weakness, sometimes described as myopathy or even tendon rupture, warrants attention.
Understanding the Risk
The risk of muscle problems with Cipro varies. Factors like age, pre-existing conditions (such as kidney disease), and concurrent medications significantly influence individual susceptibility. Older adults appear more vulnerable. Prolonged use of Cipro increases the likelihood of adverse muscle effects.
- Age: Older individuals are at higher risk.
- Kidney function: Impaired kidney function can increase the risk.
- Concurrent medications: Certain drugs may increase the risk when taken alongside Cipro.
- Duration of treatment: Longer treatment courses correlate with higher risk.
Recognizing Symptoms
Muscle weakness associated with Cipro varies in severity. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to significant muscle weakness impacting daily activities.
- Muscle aches and pains: These are common early symptoms.
- Weakness in specific muscle groups: Weakness may be localized or generalized.
- Difficulty with movement: This can range from mild stiffness to severe impairment.
- Muscle cramps: Frequent or severe muscle cramps can be a sign.
- Tendon problems: Pain, swelling, or rupture of tendons, particularly in the Achilles tendon, is a serious potential complication.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you experience any muscle weakness while taking Cipro, contact your doctor immediately. Early intervention is crucial. Your physician will assess your symptoms, review your medical history, and determine the appropriate course of action. This may involve adjusting your medication, conducting tests, or providing supportive care. Never stop taking Cipro without consulting your doctor.
Alternative Treatments
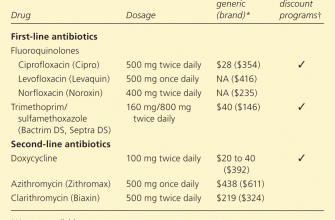
If Cipro-induced muscle weakness is confirmed, alternative antibiotic treatments might be considered. Your doctor will choose the most suitable replacement based on your specific condition and the underlying infection.
Managing Muscle Weakness
Depending on the severity, management strategies can range from rest and supportive measures to physical therapy. Your doctor will guide you on the best approach for your situation.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before making any decisions related to your health or medication.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin and its Mechanism
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, targets bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are vital for bacterial DNA replication, repair, and segregation. Ciprofloxacin inhibits these enzymes, preventing bacteria from properly replicating their DNA, leading to bacterial cell death.
Specifically, ciprofloxacin binds to these enzymes, blocking their activity. This interference halts the crucial processes of DNA unwinding and replication. The drug’s effectiveness stems from its precise interaction with these bacterial-specific enzymes; human cells lack these specific enzymes, minimizing the risk of toxicity to human DNA.
However, individual responses vary. The mechanism’s success relies on the bacteria’s susceptibility to ciprofloxacin. Resistance can develop, making treatment less effective. Factors influencing effectiveness include the bacterial species, the dosage, and the duration of treatment.
Understanding this mechanism is key to appreciating both the therapeutic benefits and potential side effects of ciprofloxacin. While it effectively combats bacterial infections, its interaction with bacterial DNA replication can have unintended consequences on human cells in some instances.
Common Muscle Side Effects Associated with Cipro
Ciprofloxacin, commonly known as Cipro, can cause various muscle problems. Muscle weakness, or myasthenia, is a frequently reported side effect. This can range from mild fatigue to significant difficulty performing everyday tasks. You may experience generalized weakness, affecting multiple muscle groups, or weakness localized to specific areas, such as your legs or arms.
Specific Muscle Issues
Beyond generalized weakness, tendonitis (inflammation of the tendons) is another common concern. This often manifests as pain and inflammation in the tendons of your shoulders, wrists, ankles, or heels. Less frequently, patients report muscle aches and pains, sometimes described as cramps or stiffness.
Rare but serious complications include muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), indicated by muscle pain, weakness, and dark urine. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. Always inform your doctor about any pre-existing muscle conditions before starting Cipro treatment.
Remember, individual reactions vary. While these are common side effects, not everyone taking Cipro will experience them. Open communication with your physician is key to managing potential side effects.
Risk Factors for Cipro-Induced Muscle Weakness
Certain factors increase your risk of experiencing muscle weakness while taking ciprofloxacin. Age significantly influences susceptibility; older adults, particularly those over 65, are at higher risk due to age-related muscle loss and decreased kidney function, impacting drug clearance. Kidney disease itself presents a considerable risk factor, hindering ciprofloxacin elimination and potentially leading to higher drug levels in the body. Concomitant use of certain medications, including corticosteroids and neuromuscular blocking agents, increases the likelihood of muscle weakness. Pre-existing muscle or nerve conditions also heighten vulnerability. Finally, individuals with low magnesium or potassium levels are at increased risk of experiencing adverse muscle effects. Careful monitoring by healthcare professionals is advised for those with these risk factors.
Specific Medication Interactions
Combining ciprofloxacin with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or anticoagulants might raise the risk of muscle problems. Concurrent use of muscle relaxants or other medications affecting muscle function should be discussed with your doctor. Always inform your physician about all medications you’re taking to minimize potential interactions and complications. These interactions can significantly increase the chance of adverse muscle effects.
Recognizing Symptoms of Cipro-Related Muscle Problems
Pay close attention to your body. Muscle weakness associated with Ciprofloxacin can manifest in various ways. Spotting these symptoms early is key.
- Unexplained Muscle Weakness: Notice any unusual fatigue or weakness in your muscles, particularly in your limbs?
- Muscle Pain (Myalgia): Are you experiencing persistent aches or tenderness in your muscles, even without strenuous activity? This can range from mild discomfort to severe pain.
- Muscle Cramps: Frequent, intense muscle spasms or cramps, especially at night, might indicate a problem. Note the frequency and location.
- Difficulty Moving: Do simple tasks, like walking or climbing stairs, feel unusually difficult or strenuous?
- Muscle Atrophy: Has there been a noticeable decrease in muscle size or bulk? This is a more serious sign requiring immediate medical attention.
- Tendon Problems: Ciprofloxacin can also affect tendons, causing pain, inflammation, or even rupture (though rare). Pay attention to pain in your tendons, particularly in the Achilles tendon.
If you experience any of these symptoms while taking Ciprofloxacin, consult your doctor immediately. Provide a detailed account of your symptoms, including their onset and severity. Prompt medical attention can help manage and mitigate potential complications.
- Keep a detailed symptom journal: Note the date, time, location, and severity of any muscle-related issues.
- Report all symptoms to your doctor: Do not hesitate to seek medical advice if you’re concerned.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions: Adhere to any treatment plan recommended by your healthcare provider.
Remember, early detection and appropriate medical intervention are critical for managing Ciprofloxacin-related muscle problems.
Seeking Medical Attention and Diagnosis
If you experience muscle weakness while taking ciprofloxacin, contact your doctor immediately. Don’t delay; prompt medical attention is key.
Your doctor will likely conduct a thorough physical examination, focusing on your muscle strength and reflexes. They’ll review your medical history, including current medications and any previous health issues.
Blood tests may be ordered to check for electrolyte imbalances or other underlying conditions that could contribute to your weakness. Further tests, such as electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies, might be necessary to assess nerve and muscle function.
Openly discuss all symptoms with your physician. Detailed descriptions of when the weakness began, its severity, and any associated symptoms are helpful for accurate diagnosis.
Based on the assessment, your doctor will determine the cause of your muscle weakness. If ciprofloxacin is suspected as a contributing factor, they’ll discuss treatment options, which might include medication adjustments or alternative antibiotics.
Remember, accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of your condition depend on clear communication with your healthcare provider. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and express your concerns.
Treatment Options for Cipro-Induced Muscle Weakness
First, discontinue Ciprofloxacin immediately unless specifically instructed otherwise by your physician. This is the most crucial step in alleviating muscle weakness. Your doctor will assess your specific situation and guide you on the best course of action.
Managing Symptoms
Symptom management focuses on improving comfort and function. Rest is paramount; avoid strenuous activities. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage muscle aches. Gentle stretching and range-of-motion exercises, as recommended by a physical therapist, can aid in improving muscle function and preventing further stiffness. Hydration is also key; drink plenty of water.
Addressing Underlying Causes
Cipro-induced myopathy is sometimes associated with other factors, such as electrolyte imbalances. Your doctor may order blood tests to check for these imbalances and prescribe corrective measures, such as electrolyte supplements. In rare cases, your physician may prescribe medications to address specific complications.
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can create a personalized exercise program designed to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. They’ll guide you through specific exercises and stretches that are safe and beneficial given your condition. Regular physical therapy sessions are often a cornerstone of recovery.
Medical Monitoring
Regular checkups with your physician are necessary to monitor your progress and adjust treatment as needed. Open communication with your doctor about your symptoms is crucial for effective management of Cipro-induced muscle weakness.
Preventing Cipro-Related Muscle Issues
Maintain adequate hydration. Drink plenty of water throughout your Ciprofloxacin treatment. Dehydration can exacerbate muscle problems.
Prioritize regular, gentle exercise. Consult your doctor before starting any new exercise routine, but light activity like walking can help maintain muscle health. Avoid strenuous workouts during treatment.
Include magnesium-rich foods in your diet. Foods like spinach, almonds, and avocados contain magnesium, a mineral potentially helpful in preventing muscle weakness. Discuss supplementation with your doctor before taking any magnesium supplements.
Dietary Considerations
Consume a balanced diet. Focus on nutrient-rich foods to support overall health and muscle function during your antibiotic course. This includes lean protein, fruits, and vegetables.
Limit alcohol consumption. Alcohol can interfere with muscle function and deplete nutrients, potentially worsening side effects.
Medication Management
Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Take Ciprofloxacin exactly as prescribed. Do not stop taking it prematurely, even if you feel better.
Report any muscle pain or weakness immediately. Contact your physician if you experience unusual muscle aches, cramps, or weakness. Early intervention can often prevent more serious issues.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Muscle weakness | Report to your doctor immediately |
| Severe muscle pain | Seek medical attention urgently |
| Muscle cramps | Increase hydration and consider reporting to your doctor |
Additional Tips
Get sufficient rest. Adequate sleep is crucial for muscle recovery and overall health.
Consider alternative antibiotics. If you have a history of Ciprofloxacin-related muscle problems, discuss alternative antibiotic options with your doctor.