For treating bacterial infections, cephalexin stands out as a reliable option. This antibiotic belongs to the cephalosporin class and is commonly prescribed for a variety of infections, including those affecting the skin, lungs, and urinary tract. Its effectiveness against numerous strains of bacteria makes it a go-to choice for healthcare providers.
When taking cephalexin, adhering to the prescribed dosage is crucial. Typically, doctors recommend a dosage of 250 mg to 500 mg every six hours, depending on the severity of the infection. Always ensure to complete the entire course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. This practice helps prevent resistance and ensures the infection is fully eradicated.
Be aware of potential side effects, which can include gastrointestinal discomfort, rash, and allergic reactions. If you experience severe side effects or symptoms such as difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately. Additionally, discussing any current medications with your healthcare provider is essential to avoid interactions.
Cephalexin is generally well-tolerated, but individuals with a history of allergies to penicillin or cephalosporins should use it cautiously. Always consult with your healthcare professional about the best treatment option tailored to your specific health needs.
Prescription Antibiotic Cephalexin
Cephalexin is a commonly prescribed antibiotic for the treatment of various bacterial infections. It belongs to the cephalosporin class of antibiotics, effectively targeting infections such as pneumonia, ear infections, and skin infections. Patients usually take it orally, with or without food, to aid absorption. Adhere to the prescribed dosage to ensure effective treatment.
Monitor for any side effects, which may include nausea, diarrhea, or allergic reactions. If you experience severe symptoms like rash or difficulty breathing, contact your healthcare provider immediately. Staying hydrated can help manage mild side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort.
Complete the full course of medication as directed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the prescription. This practice prevents the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a growing concern in medical treatment.
If you take other medications, inform your doctor to avoid potential interactions. Certain medications may impact how cephalexin works or increase the risk of side effects. Your healthcare provider can adjust dosages to ensure safety and efficacy.
For those with pre-existing kidney issues, dosage adjustments might be necessary. Regular follow-ups will help monitor renal function and overall health while on cephalexin. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should also discuss the use of this antibiotic with their healthcare provider, as risks can vary.
In conclusion, cephalexin is a practical option for treating specific bacterial infections. Always communicate openly with your healthcare provider for the best outcomes during your treatment.
Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Uses of Cephalexin
Cephalexin works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It binds to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, disrupting peptidoglycan cross-linking. This action weakens the cell wall, eventually leading to cell lysis and death. Cephalexin specifically targets gram-positive bacteria and some gram-negative organisms, making it a versatile choice in treating various infections.
Common therapeutic uses of cephalexin include:
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Effective against infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Treats conditions such as pneumonia and bronchitis, often caused by susceptible bacteria.
- Bone Infections: Utilized in treating osteomyelitis, often in conjunction with other antibiotics for comprehensive coverage.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Frequently prescribed for uncomplicated UTIs caused by sensitive organisms.
- Dental Infections: Used pre-emptively or therapeutically for dental bacterial infections.
Cephalexin is taken orally, with dosing adjusted based on the type and severity of the infection. Patients should complete the entire course of therapy, even if symptoms improve, to prevent resistance development. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure the medication’s effectiveness and monitor for potential side effects.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Tips for Cephalexin
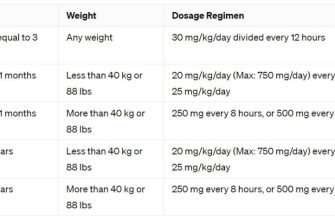
Adults typically receive a cephalexin dosage of 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours. For more severe infections, the dosage can be increased up to 1 gram every 6 hours. Adjustments may be necessary for patients with renal impairment. Consult with a healthcare professional for the appropriate dose based on individual circumstances.
Pediatric Dosage
For children, the recommended dosage is usually 25 to 50 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into several doses. This may vary based on the type of infection being treated. Always verify with a pediatrician before administering cephalexin to children.
Administration Tips
Take cephalexin with a full glass of water to enhance absorption. Administer it at evenly spaced intervals to maintain effective drug levels in the bloodstream. If using the liquid form, shake the bottle well before measuring the dose. Avoid consuming antacids containing magnesium or aluminum within two hours of taking cephalexin, as they can interfere with its absorption.
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications of Cephalexin
Cephalexin may cause side effects that can affect individuals differently. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. If these symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, or swelling, particularly if they have a known allergy to penicillin or other cephalosporins. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat.
Contraindications
Cephalexin is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to cephalosporin antibiotics. Additionally, individuals with specific renal conditions should exercise caution. Always discuss your medical history with your healthcare provider to assess the appropriate use of cephalexin in your case.