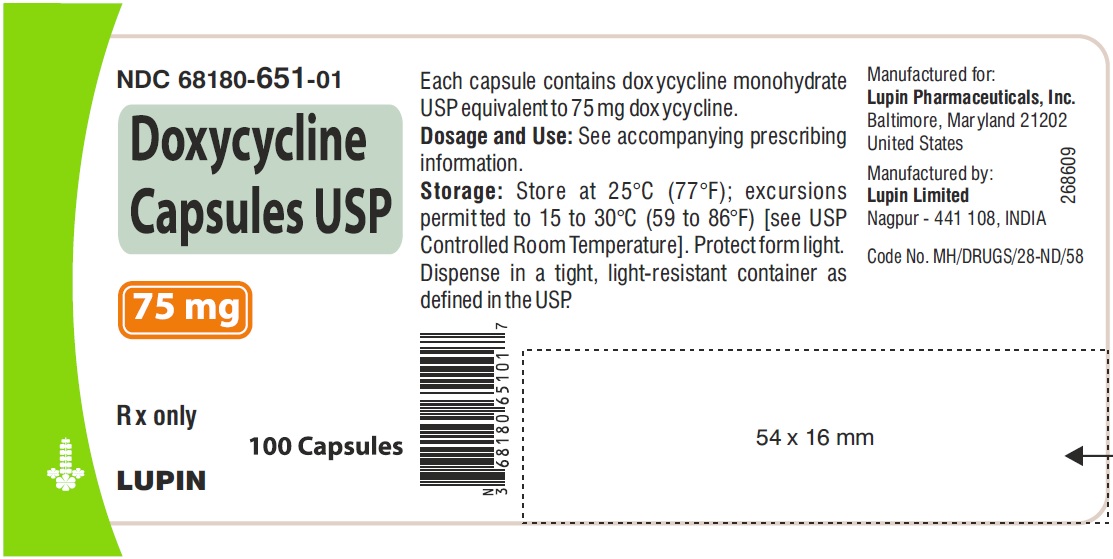
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, often prescribed for bacterial infections like acne, Lyme disease, and respiratory infections. Remember to always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely; dosage varies significantly based on the specific infection and your individual health profile.
Typical adult doses range from 100mg to 200mg daily, administered in one or two divided doses with food to minimize potential stomach upset. Children’s dosages are significantly lower and determined by weight. Never adjust your dosage independently; consult your physician for any modifications.
Potential side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and photosensitivity. Sun exposure should be limited while taking doxycycline. Serious side effects, while rare, include liver damage and esophageal irritation. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe abdominal pain, jaundice, or difficulty swallowing.
Drug interactions are a key concern. Doxycycline interacts with several medications, including antacids, birth control pills, and blood thinners. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are currently taking. This ensures a safe and effective treatment plan.
Before starting doxycycline, disclose any allergies, pregnancy status, and existing medical conditions like kidney or liver disease. These details are critical for your doctor to tailor the prescription appropriately and mitigate any potential risks. Your pharmacist can provide additional information and answer specific questions about your prescription.
- Prescription for Doxycycline: A Detailed Guide
- Common Uses
- Important Considerations
- Taking Doxycycline
- Missed Doses
- Storage
- Follow-up
- Disclaimer:
- What is Doxycycline and What is it Used For?
- Common Dosages and Administration Methods
- Oral Administration
- Other Considerations
- Potential Side Effects and Allergic Reactions
- Drug Interactions: What to Avoid While Taking Doxycycline
- Precautions and Warnings: Who Shouldn’t Take Doxycycline?
- Completing Your Course of Doxycycline: Importance and Considerations
- Where to Get a Prescription and Further Information
- Alternative Options for Prescription Access
- Further Information Resources
- Medication Safety
Prescription for Doxycycline: A Detailed Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Doxycycline dosage varies greatly depending on the infection being treated and your individual health. Typical doses range from 100mg to 200mg daily, sometimes divided into two doses.
Common Uses
- Treatment of bacterial infections like acne, chlamydia, and Lyme disease.
- Prevention of malaria in certain regions.
- Treatment of other infections as directed by a physician.
Duration of treatment also varies, typically ranging from a few days to several weeks. Your doctor will determine the appropriate duration.
Important Considerations
- Allergies: Inform your doctor of any known allergies, especially to tetracyclines.
- Pregnancy & Breastfeeding: Doxycycline is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding due to potential harm to the developing fetus or infant.
- Sun Sensitivity: Doxycycline can increase sun sensitivity. Use sunscreen and protective clothing when exposed to sunlight.
- Interactions: Inform your doctor of all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as some may interact with doxycycline. This includes antacids and dairy products, which can reduce absorption.
- Side Effects: Common side effects may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Less common, but serious side effects are possible. Seek medical attention if you experience severe side effects.
Taking Doxycycline
Take doxycycline with a full glass of water. Avoid taking it with milk or antacids. It’s generally best to take it on an empty stomach, at least one hour before or two hours after meals, to maximize absorption. However, if stomach upset occurs, taking it with food might help. Always consult your physician regarding the best way to take your prescribed dose.
Missed Doses
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it is almost time for your next dose. Do not double the dose.
Storage
Store doxycycline in a cool, dry place, away from moisture and direct sunlight.
Follow-up
Attend all follow-up appointments with your doctor to monitor your progress and ensure the infection is successfully treated.
Disclaimer:
This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your physician or other qualified healthcare professional for any questions about your health or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
What is Doxycycline and What is it Used For?
Doxycycline is a tetracycline antibiotic. Doctors prescribe it to treat various bacterial infections. It combats bacteria by preventing them from producing necessary proteins for their survival.
Common uses include: treating acne, Lyme disease, chlamydia, and other sexually transmitted infections. It’s also effective against infections of the respiratory tract, urinary tract, and skin.
Important Note: Doxycycline is not effective against viral infections like the common cold or flu. Always consult your doctor before using doxycycline or any other medication.
Specific conditions treated: Doxycycline’s broad spectrum allows it to target a wide range of bacteria. For example, it successfully treats infections caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, Rickettsia rickettsii (Rocky Mountain spotted fever), and certain types of pneumonia.
Before taking doxycycline: Inform your doctor about all medications you’re currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible. Also, mention any allergies or existing health conditions, particularly pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Potential side effects: While generally safe, doxycycline can cause nausea, diarrhea, or sun sensitivity. Severe allergic reactions are rare but possible. Stop taking the medication and seek immediate medical help if you experience a serious reaction.
Common Dosages and Administration Methods
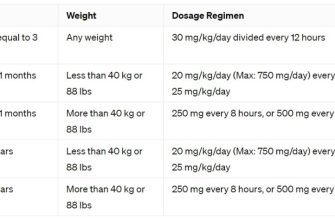
Doxycycline dosage varies significantly depending on the infection being treated. For example, a typical dosage for acne is 50-100 mg once or twice daily. Lyme disease often requires 100 mg twice daily for 14-21 days. Chlamydia treatment usually involves a single 100 mg dose. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions.
Oral Administration
Doxycycline is commonly administered orally, usually with a full glass of water. Avoid taking it with dairy products, antacids, or iron supplements, as these can hinder absorption. Take it on an empty stomach or two hours after a meal for best results.
Other Considerations
Certain factors influence dosage, including age, weight, and kidney function. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should discuss doxycycline use with their physician. Potential side effects can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and photosensitivity. Report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately. Always use your medication as directed and complete the entire course of treatment even if you feel better sooner.
Potential Side Effects and Allergic Reactions
Doxycycline, like all medications, can cause side effects. These are usually mild and temporary, but some can be serious. Always inform your doctor about any new or worsening symptoms.
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and heartburn. These typically subside as your body adjusts to the medication. Drink plenty of water to help alleviate gastrointestinal upset. If symptoms are severe or persistent, contact your doctor immediately.
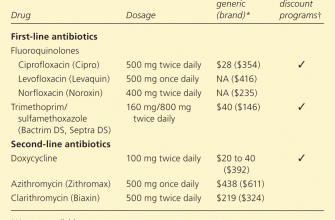
Less common but more serious side effects include:
| Side Effect | Symptoms | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Photosensitivity | Increased sun sensitivity, sunburn | Limit sun exposure, wear protective clothing and sunscreen. |
| Yeast infections (candidiasis) | Vaginal itching, discharge, oral thrush | Contact your doctor for appropriate treatment. |
| Esophageal irritation | Difficulty swallowing, chest pain | Take doxycycline with plenty of water and sit upright for at least 30 minutes after taking it. |
| Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) | Severe, watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, fever | Seek immediate medical attention; this is a serious condition. |
| Allergic reactions | Hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, dizziness | Seek immediate medical attention; this is a medical emergency. |
This information is not exhaustive. Consult the medication leaflet and your doctor for a complete list of potential side effects and interactions. Always report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider.
Drug Interactions: What to Avoid While Taking Doxycycline
Avoid antacids containing calcium, magnesium, aluminum, or iron. These minerals bind to doxycycline, reducing its absorption and effectiveness. Take doxycycline at least two hours before or four hours after taking these antacids.
Dairy products, like milk and yogurt, can also interfere with doxycycline absorption. Space your doxycycline intake away from dairy consumption.
Certain medications, such as warfarin (a blood thinner), can have their effects altered when combined with doxycycline. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are taking.
Doxycycline can increase the risk of sunburn. Use sunscreen with a high SPF and protective clothing when exposed to sunlight.
Combining doxycycline with retinoids (like isotretinoin) may increase the risk of increased pressure within the skull. Discuss this potential interaction with your physician.
Avoid consuming alcohol while on doxycycline; alcohol can worsen any side effects and increase the risk of liver damage.
This list isn’t exhaustive; consult your doctor or pharmacist for a complete overview of potential interactions specific to your health profile and medications.
Precautions and Warnings: Who Shouldn’t Take Doxycycline?
Doxycycline isn’t suitable for everyone. Avoid it if you have specific medical conditions or are taking certain medications.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Doxycycline can harm a developing fetus. Avoid it during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Consult your doctor for alternative treatments.
- Children under 8: Doxycycline can stain developing teeth. It’s generally not prescribed for children under eight.
- Severe Liver or Kidney Problems: Doxycycline is processed by the liver and kidneys. Pre-existing issues with these organs might necessitate an alternative antibiotic.
- Sun Sensitivity: Doxycycline increases sun sensitivity. Use sunscreen and protective clothing while taking it.
- Esophageal Issues: Doxycycline can cause esophageal irritation. Take it with a full glass of water and remain upright for at least 30 minutes after ingestion.
Certain medications interact negatively with doxycycline. These include:
- Antacids: Reduce doxycycline absorption. Separate their intake by at least two hours.
- Warfarin: May increase the risk of bleeding.
- Birth control pills: Doxycycline can decrease their effectiveness.
Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and allergies before starting doxycycline. This allows for a safe and effective treatment plan.
Allergic reactions, such as rash or swelling, are possible. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any.
Completing Your Course of Doxycycline: Importance and Considerations
Finish your entire prescription, even if you feel better sooner. Stopping early allows bacteria to survive and potentially become resistant to the antibiotic. This resistance makes future infections harder to treat.
Take doxycycline at the same time each day. Consistency ensures a steady level of medication in your system for optimal efficacy. A missed dose can reduce effectiveness.
Protect your skin from the sun. Doxycycline can increase your sensitivity to sunlight. Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, wear protective clothing, and limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
Drink plenty of water. Staying hydrated helps your kidneys process the medication. Adequate fluid intake minimizes potential side effects.
Report any side effects to your doctor immediately. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. Severe allergic reactions are rare but require prompt medical attention.
Store doxycycline properly. Keep it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture to maintain its potency.
Do not share your medication. Antibiotics are prescribed for specific infections. Sharing your medication could be harmful and ineffective for others.
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. This includes dosage, duration, and any specific dietary recommendations. Your doctor’s guidance is tailored to your individual needs.
Where to Get a Prescription and Further Information
To obtain a doxycycline prescription, schedule an appointment with your primary care physician or a qualified infectious disease specialist. They will assess your medical history and symptoms to determine if doxycycline is the appropriate treatment.
Alternative Options for Prescription Access
Consider using telehealth services. Many online platforms offer virtual consultations with licensed doctors who can prescribe medication if appropriate. Research reputable telehealth providers and check their licensing and patient reviews before using their services. Remember to always discuss your full medical history with any healthcare provider.
Further Information Resources
The FDA website provides detailed information on doxycycline, including its uses, side effects, and warnings. You can also consult reliable sources such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for up-to-date information on infectious diseases and antibiotic usage. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication.
Medication Safety
Never share your prescription medication. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Report any adverse reactions to your doctor or pharmacist immediately. Store the medication as directed on the label.