If you’re experiencing unusual symptoms after taking Zithromax, prioritize contacting your doctor immediately. Don’t delay seeking medical advice, especially if you notice significant changes in your physical or mental state. This is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Zithromax, or azithromycin, is a powerful antibiotic; however, like all medications, it carries potential side effects. Some common reactions include nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. Less frequent, but more serious, side effects can involve heart problems, such as palpitations or irregular heartbeat. These issues, while uncommon, require prompt medical attention.
Remember, individual responses to medication vary. Factors like dosage, pre-existing conditions, and interactions with other drugs influence how your body reacts. Always discuss your complete medical history with your physician before starting any new medication, including Zithromax, to minimize potential risks and ensure safe and effective treatment.
This information serves as a guide and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, especially concerning any drug’s side effects. Your health is paramount; prioritize seeking professional assistance when necessary.
- Zithromax High: Understanding the Risks and Effects
- Side Effects to Watch For
- Medication Interactions
- Understanding the “High”
- Safe Zithromax Use
- Understanding Zithromax (Azithromycin)
- Common Uses
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Missed Dose
- Disclaimer:
- Common Side Effects of Zithromax
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Zithromax and Alcohol Interaction
- Understanding the Interaction
- Recommendations
- Zithromax and Drug Interactions
- Symptoms of a Zithromax Overdose
- Seeking Medical Attention for Zithromax Related Issues
- Severe Side Effects Requiring Immediate Attention
- Less Severe, But Still Concerning, Symptoms
- Emergency Room Visits
- Managing Zithromax Side Effects
Zithromax High: Understanding the Risks and Effects
Don’t mix Zithromax with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants. This combination significantly increases the risk of serious side effects.
Side Effects to Watch For
Zithromax, while generally safe, can cause side effects. Common reactions include nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. Less common, but more serious, are allergic reactions like rash, swelling, and difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these. Dizziness and vertigo are also possible, potentially impairing coordination and judgment. Driving or operating machinery should be avoided if these symptoms occur.
Medication Interactions
Zithromax interacts with several medications. Always inform your doctor of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Zithromax. This includes blood thinners like warfarin and certain heart medications. Failure to disclose all medications can lead to dangerous interactions.
Understanding the “High”
The term “Zithromax high” is misleading. Zithromax doesn’t cause a euphoric high like recreational drugs. However, the dizziness and disorientation it can cause might be misinterpreted as such. This is dangerous. Never intentionally misuse Zithromax to achieve any altered state of consciousness.
Safe Zithromax Use
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Take the medication as prescribed, and complete the entire course of treatment even if you feel better. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance. If you have any questions or concerns, consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist immediately. They can provide personalized advice and address any specific concerns you have regarding your treatment.
Understanding Zithromax (Azithromycin)
Zithromax, containing azithromycin, is a macrolide antibiotic effectively combating various bacterial infections. It’s available as tablets, capsules, and oral suspension. Remember to always follow your doctor’s prescription exactly.
Common Uses
Zithromax treats a range of infections, including: respiratory tract infections like bronchitis and pneumonia; skin infections such as cellulitis; and sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea. However, its effectiveness varies depending on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
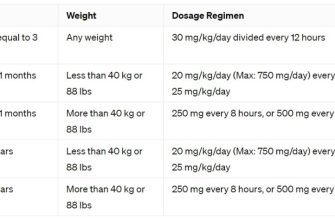
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor determines the appropriate dose based on your weight, the infection’s severity, and your overall health. Typical regimens involve a short course of medication, often just a few days. Take the medication with a full glass of water, and avoid taking antacids concurrently.
Potential Side Effects
Like all medications, Zithromax can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach pain. Less common but more serious effects include allergic reactions (rash, hives, difficulty breathing) and heart rhythm problems. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe side effects.
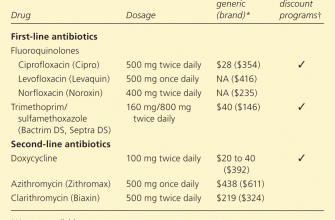
Drug Interactions
| Medication | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Warfarin (blood thinner) | Increased bleeding risk |
| Digoxin (heart medication) | Increased digoxin levels |
| Ergot alkaloids (migraine medication) | Increased risk of ergotism |
This table highlights some potential interactions. Always inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking before starting Zithromax. This ensures safe and effective treatment.
Missed Dose
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double the dose to make up for a missed one. Contact your doctor if you have concerns about missed doses or completing your prescribed course.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any medication or treatment. They can assess your individual needs and provide personalized guidance.
Common Side Effects of Zithromax
Zithromax, like many antibiotics, can cause side effects. The most frequently reported include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. These typically are mild and resolve without treatment. However, severe diarrhea may indicate Clostridium difficile infection, requiring immediate medical attention.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Abdominal pain is another common complaint. Less frequent, but still possible, are indigestion and constipation. Staying hydrated and eating bland foods often helps manage these issues. If symptoms worsen or persist, consult your doctor.
Other Potential Side Effects
Skin reactions, such as rash, are possible. In rare instances, more serious allergic reactions, including swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, can occur, necessitating emergency care. Headache and dizziness are also reported. Unusual fatigue or changes in taste can also happen. Always report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider.
Remember, this information is not exhaustive. Always consult your physician or pharmacist for complete details and personalized advice concerning Zithromax side effects and potential interactions with other medications.
Zithromax and Alcohol Interaction
Avoid alcohol while taking Zithromax (azithromycin). Zithromax can interact with alcohol, potentially increasing the risk of side effects like nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. This interaction isn’t always severe, but it’s best to err on the side of caution.
Understanding the Interaction
While the exact mechanism isn’t fully understood, alcohol can add stress to your liver, which is already working to process the Zithromax. This increased workload may lead to more pronounced side effects. The combination can also exacerbate existing liver conditions.
Recommendations
For optimal results and to minimize potential adverse reactions, abstain from alcohol throughout your entire course of Zithromax treatment. This includes beer, wine, and spirits. If you experience any concerning side effects, contact your doctor immediately. Remember, responsible medication use means being fully informed about potential interactions.
Zithromax and Drug Interactions
Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, before starting Zithromax. This includes prescription medications, even those you infrequently use.
Zithromax can interact negatively with certain medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. For example, concurrent use with warfarin (a blood thinner) may increase bleeding risk. Similarly, it can affect the metabolism of some drugs, altering their blood levels.
Specific examples of drugs that may interact include: digoxin (for heart conditions), theophylline (for lung conditions), ergot alkaloids (for migraines), and certain antacids. Your doctor can provide a more comprehensive list tailored to your individual health profile.
Never self-medicate or adjust dosages without consulting your physician. They can assess potential interactions and adjust your treatment plan accordingly, ensuring your safety and the efficacy of your medications.
If you experience any unusual symptoms while taking Zithromax, such as unusual bleeding, rapid heartbeat, or dizziness, contact your doctor immediately.
Proactive communication with your healthcare provider is key to minimizing the risks of drug interactions while on Zithromax. Openly discussing all your medications is vital for your well-being.
Symptoms of a Zithromax Overdose
If you suspect a Zithromax overdose, seek immediate medical attention. Don’t delay.
Overdosing on Zithromax can manifest in several ways. These symptoms vary in severity depending on the amount ingested and individual factors.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Expect nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These are often the most common early signs.
- Hearing Problems: Ringing in the ears (tinnitus) or temporary hearing loss are possible.
- Cardiac Effects: In severe cases, irregular heartbeat or QT prolongation (a change in heart rhythm) can occur. This is serious and requires urgent medical intervention.
- Neurological Symptoms: Dizziness, headache, and confusion are potential symptoms.
- Allergic Reactions: While less frequent with an overdose itself, a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) is possible. Watch for swelling, rash, difficulty breathing, or chest tightness.
The severity of symptoms determines the urgency of treatment. Mild symptoms might warrant observation, while serious symptoms necessitate immediate hospitalization.
- Call emergency services (911 or your local equivalent) immediately. Do not attempt self-treatment.
- Provide details to medical professionals: Tell them the amount of Zithromax ingested, when it happened, and any symptoms experienced.
- Follow their instructions carefully: They may recommend inducing vomiting (only if instructed!), administering activated charcoal, or other treatments.
Remember, quick action is key. Early intervention increases the chance of a positive outcome.
Seeking Medical Attention for Zithromax Related Issues
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe allergic reactions like difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, or hives. These are serious and require immediate medical intervention.
Severe Side Effects Requiring Immediate Attention
Seek immediate medical help for signs of serious side effects, including severe abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes), dark urine, or unusual bleeding or bruising. These could indicate liver problems or other serious complications. Report these symptoms to your physician without delay.
Less Severe, But Still Concerning, Symptoms
Contact your doctor if you experience less severe side effects that persist or worsen. This includes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, or vaginal yeast infections. Your doctor can assess your symptoms and recommend appropriate management strategies, potentially including adjustments to your medication or treatment for the side effects.
Remember to always inform your physician about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential drug interactions. Accurate reporting assists your doctor in providing the best care.
Emergency Room Visits
Go to the nearest emergency room if you experience a severe allergic reaction or other life-threatening side effect. This is critical for prompt treatment and potential life-saving intervention. Do not hesitate to seek emergency care in these urgent situations.
Managing Zithromax Side Effects
Feeling unwell after taking Zithromax? Many experience mild side effects. Let’s address them proactively.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Take Zithromax with food to minimize stomach upset. Small, frequent meals can help. If nausea persists, contact your doctor.
- Diarrhea: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated. Severe or persistent diarrhea requires immediate medical attention; it could indicate a serious complication called Clostridium difficile infection.
- Headache: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) can provide relief. Avoid aspirin unless directed by your doctor.
- Abdominal Pain: Mild pain often subsides. However, severe or persistent abdominal pain needs medical evaluation.
- Allergic Reactions: Watch for signs like rash, hives, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical help if you experience an allergic reaction.
Remember:
- Follow your doctor’s prescription instructions carefully.
- Complete the entire course of medication, even if you start feeling better.
- Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor or pharmacist.
- Avoid alcohol while taking Zithromax, as it can worsen side effects.
This information is for guidance only. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice regarding Zithromax and its potential side effects. They can accurately assess your specific situation and provide tailored recommendations.