Avoid using Zithromax (azithromycin) on rats without explicit veterinary guidance. Incorrect dosage can lead to serious health complications, including gastrointestinal upset and liver damage.
Zithromax is designed for specific bacterial infections in mammals, and its use in rats requires careful consideration of their unique physiology and metabolism. Always consult a veterinarian experienced in rodent care before administering any medication, including antibiotics.
Veterinary professionals can accurately diagnose the underlying issue, determine the appropriate antibiotic and dosage, and monitor your rat’s response to treatment. They can also advise on safe handling and administration techniques to minimize stress for your pet.
Remember, incorrect medication can delay effective treatment and potentially worsen your rat’s condition. A proper diagnosis and treatment plan from a vet is the safest approach for your rat’s health.
Seeking professional veterinary care ensures your rat receives the best possible treatment and minimizes potential risks associated with medication. Prioritize your rat’s well-being by consulting a veterinarian before using any human medications.
- Zithromax and Rats: Understanding the Risks
- Zithromax Use in Rodent Control: Efficacy and Safety Concerns
- Efficacy Limitations
- Safety Concerns
- Alternative Rodent Control Methods
- Accidental Ingestion of Zithromax by Rats: Potential Effects and Treatment
- Preventing Rat Exposure to Zithromax: Safe Storage and Disposal Practices
Zithromax and Rats: Understanding the Risks
Never administer Zithromax (azithromycin) to rats without veterinary guidance. Doing so can be dangerous.
Azithromycin is designed for specific mammalian species and dosages. Incorrect administration to rats can lead to:
- Gastrointestinal upset: Vomiting and diarrhea are common side effects.
- Liver damage: Azithromycin can stress the liver, potentially causing irreversible harm in rats.
- Cardiac complications: In some cases, azithromycin can interfere with heart function in rats.
- Allergic reactions: Rats, like other mammals, can exhibit allergic reactions to the medication, ranging from mild skin irritation to severe respiratory distress.
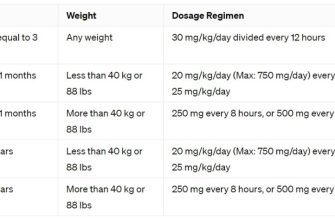
The proper treatment for a sick rat involves a veterinarian’s expertise. They can diagnose the underlying illness and prescribe the correct medication and dosage, considering the rat’s weight, age, and overall health. Incorrect dosage can be deadly.
Here’s what to do if you suspect your rat is ill:
- Observe your rat for symptoms like lethargy, loss of appetite, or unusual behavior.
- Contact an exotic animal veterinarian immediately. Do not attempt self-medication.
- Provide accurate information about your rat’s history, diet, and observed symptoms.
- Follow your vet’s instructions precisely for administering any medication or treatment.
Remember, responsible pet ownership includes seeking professional veterinary care for your pets. Never rely on human medications for treating rat illnesses.
Zithromax Use in Rodent Control: Efficacy and Safety Concerns
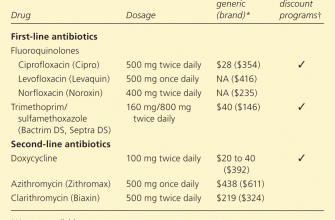
Using Zithromax (azithromycin) for rodent control requires careful consideration. While some studies suggest potential efficacy against certain rodent-borne diseases, direct use as a rodenticide is not recommended. Azithromycin targets bacterial infections, not the rodents themselves.
Efficacy Limitations
Research on azithromycin’s impact on rodent populations is limited. Existing studies primarily focus on its role in treating diseases carried by rodents, not on its ability to directly kill or control their numbers. Therefore, relying on azithromycin for rodent population reduction is unreliable.
Safety Concerns
Improper use of azithromycin poses risks. Accidental ingestion by humans or pets is a significant concern. Moreover, developing antibiotic resistance in rodent populations could have long-term implications for public health. Environmental contamination from discarded medication is another potential problem.
Alternative Rodent Control Methods
Proven and safe methods for rodent control include trapping, exclusion (preventing access), and using rodenticides registered for this purpose. Always follow product instructions carefully and consult pest control professionals for effective and safe strategies.
Accidental Ingestion of Zithromax by Rats: Potential Effects and Treatment
If a rat accidentally ingests Zithromax, immediate veterinary attention is crucial. The drug’s effects on rats aren’t fully understood, but potential consequences include gastrointestinal upset, like vomiting and diarrhea. More serious reactions, though less common, might involve neurological symptoms such as tremors or seizures.
Treatment focuses on supportive care. Your vet will likely induce vomiting or administer activated charcoal to absorb the medication. Intravenous fluids may be necessary to combat dehydration. Close monitoring is required to watch for complications. The prognosis depends on the amount ingested and the rat’s overall health. Early intervention significantly improves the chances of a positive outcome.
Prevention is key. Store Zithromax securely, away from rodents, to minimize accidental exposure. Consider using rodent-proof containers and practicing good sanitation to deter rats from entering your home.
Note: This information is for educational purposes only and shouldn’t replace professional veterinary advice. Contact your vet immediately if you suspect your rat has ingested Zithromax.
Preventing Rat Exposure to Zithromax: Safe Storage and Disposal Practices
Keep Zithromax in its original, tightly sealed container. Store it in a locked cabinet or high shelf, out of reach of children and pets, including rats.
Dispose of expired or unwanted Zithromax according to your local regulations. Many pharmacies offer drug take-back programs. Check their website or call ahead to confirm participation.
Never flush medications down the toilet or drain. This contaminates water sources and can harm wildlife.
Clean up any spills immediately using absorbent materials like paper towels. Place the contaminated material in a sealed bag before disposal.
Regularly inspect areas where rats might be present for signs of medication. If you find signs of rat infestation, contact a pest control professional.
Secure all food sources to prevent attracting rats to your home. This includes proper storage of pet food and sealing garbage tightly.
Keep your home clean and free of clutter to reduce potential rat harborage areas.