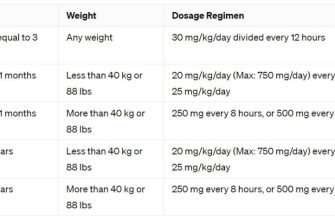
Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for precise dosage instructions. The correct amount of Zithromax suspension depends heavily on your child’s weight and the specific infection being treated. Don’t guess – accurate dosing is crucial for effective treatment.
Typical dosages for children range from 10 mg/kg to 12 mg/kg once daily for three days, or 10 mg/kg once daily for five days, depending on the infection. Remember, the doctor will determine the best treatment plan based on your child’s individual needs.
Carefully measure the suspension using the provided measuring device. Never use a household spoon as this can lead to inaccurate dosing and affect treatment outcome. Follow the instructions on the prescription label meticulously.
Important Note: This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s prescription and instructions, and contact them if you have any questions or concerns about your child’s medication. Never adjust the dosage on your own.
- Zithromax Suspension Dose: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Zithromax (Azithromycin) Suspension
- Dosage and Administration
- Possible Side Effects
- Storage and Disposal
- Dosage for Children Based on Weight
- Dosage for Adults: Common Infections
- Dosage Adjustments for Specific Infections
- Administering Zithromax Suspension: Tips and Techniques
- Refrigeration and Storage
- Administering the Dose
- Troubleshooting
- Additional Notes
- Possible Side Effects and Precautions
- Missed Dose: What to Do
- When to Seek Medical Advice
Zithromax Suspension Dose: A Comprehensive Guide
Always follow your doctor’s prescription. Dosage depends on the infection being treated and the patient’s weight.
For children weighing 44 pounds or less, the typical dose is 10 mg/kg given once daily for three days. For instance, a 22-pound child would receive 100 mg once daily for three days.
Children weighing over 44 pounds usually receive a dose based on the adult regimen: 500 mg once daily for three days. Always confirm the exact dose with your doctor or pharmacist.
Shake the suspension well before each dose to ensure even distribution of the medication. Use a calibrated measuring device, like the one provided with the medication, for accurate dosing. Never use household spoons.
Complete the full course of medication, even if you feel better before the prescribed period ends. Stopping early may allow bacteria to survive and cause the infection to return.
Side effects are possible. Common ones include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Store Zithromax suspension at room temperature, away from direct heat and sunlight. Check the expiration date and dispose of any expired medication properly.
This guide provides general information. It does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance.
Understanding Zithromax (Azithromycin) Suspension
Zithromax suspension is an antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. It’s vital to follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. The medication comes in different strengths, so the correct dose depends on your weight, age, and the specific infection being treated. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor will specify the correct amount of Zithromax suspension to take each day. Typical dosages often involve a higher dose on the first day, followed by lower daily doses for several days. Always measure the suspension using the provided measuring device, ensuring accuracy. Shake the bottle well before each dose to ensure even distribution of the medication. Follow instructions carefully regarding when to take it – with or without food. Complete the entire course of treatment, even if you start feeling better before the prescribed duration has ended. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Possible Side Effects
Common side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. More serious but rarer side effects are possible, including allergic reactions (like rash, hives, or difficulty breathing). Seek immediate medical attention should you experience these. Report any significant side effects to your doctor or pharmacist. Always review the medication guide included with your prescription for a complete list of potential side effects.
Storage and Disposal
Store Zithromax suspension in the refrigerator, ensuring it remains at the temperature specified on the label. Discard any unused medication after the expiration date. Follow your local guidelines for proper disposal of medications. Never flush medications down the toilet unless specifically instructed.
Dosage for Children Based on Weight
Zithromax suspension dosage for children is determined by their weight. Always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. This information is for guidance only and should not replace professional medical advice.
| Weight Range (kg) | Dosage (mg/kg) | Total Daily Dose (mg) – typically given as a single daily dose |
|---|---|---|
| 10-14 | 10 | 100-140 |
| >14 | 8-10 | 112-140+ |
The table above provides general guidelines. Your pediatrician will adjust the dosage based on your child’s specific needs and health condition. They may prescribe a different dosage or duration of treatment.
Always administer the medication as directed. Carefully measure the correct dose using the provided measuring device. Never use a household spoon. If you have any questions or concerns, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
Side effects are possible, and you should monitor your child closely. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor. This includes vomiting, diarrhea, or allergic reactions. Accurate weight measurement is crucial for proper dosage.
Dosage for Adults: Common Infections
For most common bacterial infections, the standard Zithromax (azithromycin) suspension dosage for adults is 500 mg once daily for three days. This regimen is often prescribed for infections like pharyngitis (strep throat), bronchitis, and some types of pneumonia.
However, dosage adjustments may be necessary depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s individual characteristics. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose. Some infections may require a longer course of treatment, perhaps 500 mg once daily for five days.
For certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia, a single 1 gram dose is often sufficient. Always follow your physician’s instructions precisely, as variations in dosage are common depending on the specific infection being treated.
Remember, this information is for general guidance only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized dosage recommendations and potential drug interactions.
Dosage Adjustments for Specific Infections
For mild to moderate community-acquired pneumonia in adults, a typical Zithromax suspension dose is 500 mg on day one, followed by 250 mg daily for four days. However, severe cases may require a higher dose or a longer duration of treatment. Always follow your doctor’s prescription.
In children with otitis media, the dosage depends on weight. The typical regimen involves a 10 mg/kg dose on the first day, followed by 5 mg/kg daily for four days. Always consult your pediatrician for precise dosing based on your child’s weight and medical history.
Treatment of pharyngitis and tonsillitis in adults usually involves 500 mg on day one, followed by 250 mg daily for four days. Adjustments may be necessary depending on the severity of the infection and the causative organism.
For uncomplicated skin infections like impetigo, a 500 mg daily dose for three days is often prescribed for adults. Children require weight-based dosing as determined by their physician.
Remember: This information is for guidance only. Your doctor will determine the appropriate Zithromax suspension dose for your specific infection and health condition. Never alter the prescribed dosage without consulting your physician. Always adhere to your doctor’s instructions.
Administering Zithromax Suspension: Tips and Techniques
Always use the provided oral syringe for accurate dosing. This ensures you give your child the correct amount of medication. Avoid using household spoons as they lack the precision needed.
Gently shake the bottle well before each dose to ensure the medication is evenly mixed. This prevents uneven distribution of the antibiotic.
Refrigeration and Storage
Refrigerate the suspension after reconstitution. Keep it at a temperature between 36°F and 46°F (2°C and 8°C). Discard any unused medication after 10 days.
Administering the Dose
Administer the medication at roughly the same time each day, following your doctor’s instructions. Consistency helps maintain therapeutic levels of the antibiotic in the body.
If your child vomits within 30 minutes of taking the medication, give them the missed dose as soon as they can tolerate it. If vomiting persists, contact your doctor for advice.
Mix the suspension with a small amount of food or drink, like applesauce or juice, if your child has difficulty swallowing it directly. But only follow this if specifically permitted by your doctor. Never mix it with milk or other dairy products.
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Child refuses to take the medication | Offer a small reward after medication (such as stickers), try mixing with an acceptable food, or involve your child in the administration. |
| Medication tastes bad | Chill the suspension before administering. Check with your pharmacist or doctor about available flavorings or alternatives. |
| Difficulty measuring the dose | Practice using the oral syringe before administration. Ensure you read the measurement line carefully. |
Additional Notes
Monitor your child for any allergic reactions, such as rash, hives, swelling or breathing difficulties. Contact your doctor or seek immediate medical attention if you notice any adverse reactions.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Always talk to your doctor or pharmacist before starting Zithromax, especially if you have pre-existing conditions. They can help determine the correct dosage and monitor for potential problems.
Common side effects include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
Less common but more serious side effects require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Severe allergic reactions (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- Signs of liver damage (e.g., dark urine, pale stools)
- Severe skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
- Prolonged QT interval (heart rhythm abnormality)
Specific precautions to consider:
- Allergies: Inform your doctor about any known drug allergies, particularly to antibiotics.
- Liver problems: Zithromax should be used cautiously in individuals with liver disease. Regular liver function tests might be necessary.
- Kidney problems: Dosage adjustments may be needed for those with kidney impairment. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose.
- Myasthenia gravis: This neuromuscular disease may worsen with Zithromax use.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor before using Zithromax during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
- Interactions: Zithromax can interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners (warfarin) and antacids. Tell your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
This information is not exhaustive. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and to address any concerns you may have.
Missed Dose: What to Do
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. If it’s close to the next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule.
Don’t double the dose to make up for a missed one. This can lead to side effects.
- Always follow your doctor’s instructions or the pharmacist’s guidance regarding the dosage and timing.
- Check the label on your Zithromax suspension for specific instructions.
- Contact your doctor or pharmacist if you have questions or concerns about missed doses.
Consistent medication is key for effective treatment. If you frequently miss doses, discuss strategies with your healthcare provider to improve adherence to your medication schedule. They may offer suggestions to help you remember to take your medicine on time.
- Consider using a pill organizer.
- Set medication reminders on your phone or computer.
- Ask a friend or family member to remind you.
Remember, your health is important. Following your doctor’s instructions and taking your medication as prescribed will help ensure the best outcome for your treatment.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Contact your doctor immediately if your child experiences a severe allergic reaction, including difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, or hives.
Seek immediate medical attention if your child develops severe diarrhea or vomiting, leading to dehydration indicated by decreased urination, dry mouth, or excessive thirst.
Call your doctor if your child shows signs of new or worsening infection, such as a high fever, persistent cough, or increased pain.
Report any unusual side effects, like yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), dark urine, or persistent abdominal pain, to your physician at once.
If you have any concerns about your child’s response to Zithromax, don’t hesitate to call your doctor for clarification. Regular monitoring ensures the medication’s efficacy and addresses potential issues proactively.