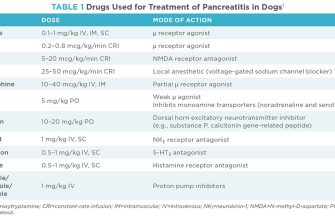
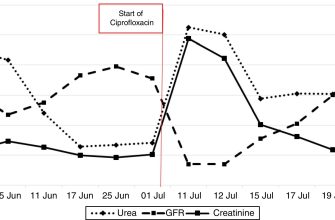
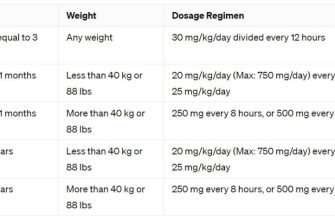
Need Zithromax? Understand its uses first. Zithromax (azithromycin) effectively targets bacterial infections like pneumonia, bronchitis, and certain sexually transmitted infections. Dosage depends on the specific infection; your doctor will determine the correct amount and duration.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Typical courses range from three to five days, but variations exist. Never adjust your dosage or stop treatment early without consulting your physician, even if you feel better. This prevents relapse and the development of antibiotic resistance.
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. More serious but less frequent reactions include allergic reactions (such as rash or difficulty breathing). Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any severe adverse effects. Inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions or medications you are taking to minimize potential interactions.
Remember: Zithromax is a prescription antibiotic. Obtain it only from a licensed healthcare provider. Self-treating bacterial infections can be dangerous and ineffective. Your doctor will perform a proper diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate medication and dosage for your specific situation.
- Zithromax Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Zithromax
- Managing Side Effects
- Important Considerations
- Post-Treatment
- What is Zithromax and What Infections Does it Treat?
- Dosage and Administration of Zithromax: A Practical Overview
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions While Using Zithromax
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common but Serious Side Effects
- Precautions
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Disclaimer:
- Zithromax and Drug Interactions: Understanding Potential Conflicts
- Specific Drug Interactions to Watch For
- Other Potential Interactions
- Seeking Professional Guidance
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Zithromax Treatment
- Signs of Treatment Failure
- Other Reasons to Seek Medical Advice
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Zithromax Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Dosage and treatment duration vary depending on your specific infection.
Understanding Zithromax
Zithromax (azithromycin) is a macrolide antibiotic, effective against a range of bacterial infections. It’s often prescribed for respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia, as well as certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia.
- Common Uses: Respiratory tract infections, skin infections, ear infections, STIs.
- Administration: Typically taken orally as tablets or suspension.
- Treatment Duration: Usually a 3- to 5-day course, depending on the infection.
Managing Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, some may experience side effects. These are usually mild and resolve without intervention. However, report any serious reactions to your doctor immediately.
- Common Side Effects: Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
- Less Common Side Effects: Vomiting, headache, dizziness.
- Serious Side Effects (Seek immediate medical attention): Severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling), irregular heartbeat, liver problems.
Proper hydration is key during treatment. Drink plenty of fluids to help prevent dehydration and support kidney function.
Important Considerations
Certain medications can interact negatively with Zithromax. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking. Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and existing health conditions require careful consideration before starting Zithromax treatment. Always discuss these factors with your physician.
Post-Treatment
Even after symptom improvement, complete the entire prescribed course of Zithromax. Stopping early can lead to treatment failure and the development of antibiotic resistance. Contact your doctor if symptoms worsen or persist after treatment completion.
This information is for general knowledge and should not be considered medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized treatment plans and answers to your specific questions about Zithromax.
What is Zithromax and What Infections Does it Treat?
Zithromax is an antibiotic containing azithromycin, a macrolide. It fights bacterial infections by stopping bacteria from growing. Doctors prescribe it for a variety of infections, depending on their severity and the specific bacteria involved.
Commonly treated infections include:
| Infection Type | Specific Infections |
|---|---|
| Respiratory Infections | Bronchitis, pneumonia (certain types), pharyngitis (strep throat), sinusitis |
| Skin Infections | Cellulitis, erysipelas |
| Ear Infections | Otitis media (middle ear infection) |
| Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) | Chlamydia, gonorrhea (certain types) |
| Other Infections | Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), certain eye infections |
Remember: Zithromax is a prescription medication. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and treatment duration. Do not stop taking the medication early, even if you feel better. Discuss any potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
Dosage and Administration of Zithromax: A Practical Overview
Zithromax (azithromycin) dosage depends heavily on the infection being treated and the patient’s age and weight. Always follow your doctor’s prescription exactly.
Common Adult Dosages: For many common infections, a typical regimen involves 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg daily for four days. Some infections may require a different dosage.
Pediatric Dosages: Pediatric dosages are calculated based on weight, usually 10 mg/kg on day one, followed by 5 mg/kg daily for four days. A doctor will determine the precise amount.
Administration: Zithromax is available as tablets, capsules, and oral suspension (liquid). Take it with a full glass of water, typically once a day. Avoid taking antacids within one hour of taking Zithromax, as this can interfere with absorption.
Important Considerations: Always inform your doctor of any other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, as interactions are possible. If you experience allergic reactions such as rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention. Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before the medication is finished to prevent antibiotic resistance.
This information is for general knowledge only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your physician or pharmacist for specific guidance on Zithromax dosage and administration.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions While Using Zithromax
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, before starting Zithromax. This helps prevent potential drug interactions.
Common Side Effects
- Diarrhea: Drink plenty of fluids and contact your doctor if it becomes severe or persistent.
- Nausea and vomiting: Take Zithromax with food to minimize these effects. Small, frequent meals might help.
- Abdominal pain: Try taking the medication with food. If pain persists, seek medical advice.
- Headache: Over-the-counter pain relievers might offer relief. If severe, consult your doctor.
- Vaginal yeast infection: This is more common in women. Your doctor can recommend treatment.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
These require immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, hives, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat).
- Signs of liver problems (dark urine, yellowing of the skin or eyes, abdominal pain).
- Signs of tendonitis or tendon rupture (pain, swelling, or inflammation in a tendon).
- Hearing problems (ringing in the ears, dizziness, hearing loss).
- Changes in heart rhythm.
Precautions
- Avoid alcohol while taking Zithromax, as it can increase the risk of side effects.
- Inform your doctor if you have a history of liver or kidney problems.
- Use sun protection, as Zithromax can increase sun sensitivity.
- Zithromax may interact with other medications. Discuss all medications with your physician.
- Complete the entire course of treatment, even if you start feeling better. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance.
When to Seek Medical Help
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any concerning side effects or if your symptoms worsen.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your physician or other qualified healthcare provider for any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen.
Zithromax and Drug Interactions: Understanding Potential Conflicts
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, before starting Zithromax. This includes prescription medications, even if you haven’t used them recently.
Specific Drug Interactions to Watch For
Digoxin: Zithromax can increase digoxin levels, potentially leading to heart rhythm problems. Close monitoring of your digoxin levels is necessary while taking Zithromax.
Warfarin: Combining Zithromax with warfarin may increase bleeding risk. Your doctor will likely monitor your INR (International Normalized Ratio) more frequently to manage this.
Ergot alkaloids (e.g., ergotamine, dihydroergotamine): Concurrent use with Zithromax can cause severe vasoconstriction, potentially leading to serious complications.
Theophylline: Zithromax may increase theophylline levels, which can result in side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and heart palpitations. Careful monitoring of your theophylline levels is recommended.
Other Potential Interactions
Antacids: Taking antacids near the time you take Zithromax can reduce its absorption. Separate administration by at least two hours is usually recommended.
Certain antibiotics: Interactions with other antibiotics are possible, although not always clinically significant. Your doctor can advise on compatibility with other prescription antibiotics.
Seeking Professional Guidance
This information is not exhaustive. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before mixing Zithromax with other medications. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific health conditions and medications. Never self-medicate.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Zithromax Treatment
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience a severe allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, or tongue, or hives. These symptoms require immediate medical attention.
Signs of Treatment Failure
Persistent or worsening symptoms after completing the prescribed course indicate potential treatment failure. Don’t delay; schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss alternative treatment options.
Other Reasons to Seek Medical Advice
New or worsening symptoms unrelated to your initial condition should also be reported to your doctor. For example, significant stomach pain, severe diarrhea, or unusual vaginal discharge require prompt medical evaluation. Also, inform your doctor about any other medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions can occur.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
If you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning a pregnancy, discuss Zithromax use with your doctor. They will help assess the potential risks and benefits. They can advise on the safest course of action for you and your baby.