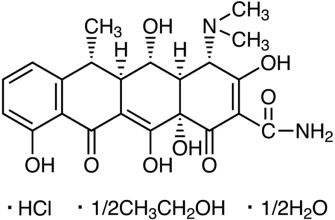
Need information on Zithromax? WebMD offers a wealth of data, but let’s cut to the chase. This antibiotic, azithromycin, treats various bacterial infections, from pneumonia to ear infections. However, understanding its uses, potential side effects, and interactions is crucial.
WebMD highlights common Zithromax side effects like diarrhea and nausea. Less frequent but more serious reactions, such as allergic reactions (potentially life-threatening), are also documented. Always check for drug interactions with other medications you are currently taking; Zithromax can interact negatively with some heart medications, for instance.
Before starting Zithromax, talk to your doctor. They can assess your specific health situation, determine if Zithromax is right for you, and tailor a treatment plan that minimizes risks. Don’t self-medicate; proper diagnosis and prescription are paramount for safe and effective treatment. WebMD’s information serves as a resource, but professional medical advice remains invaluable.
- Zithromax: A WebMD Overview
- Common Uses
- Potential Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Important Note
- Understanding Zithromax’s Uses and Dosage
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Medication Interactions
- Contraindications
- Finding Reliable Information and Seeking Medical Advice
Zithromax: A WebMD Overview
WebMD lists Zithromax (azithromycin) as a macrolide antibiotic, treating various bacterial infections. Remember to always consult your doctor before starting any medication.
Common Uses
This antibiotic effectively targets infections like pneumonia, bronchitis, sinusitis, and certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia. It also treats skin infections and ear infections in children and adults. Dosage varies depending on the infection and patient factors; follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Potential Side Effects
Possible side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. More serious, though rare, reactions may include allergic reactions (such as difficulty breathing or swelling) and liver problems. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any severe side effects.
Drug Interactions
Zithromax can interact with other medications, particularly those metabolized by the liver. Inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are currently taking to minimize potential interactions. This is crucial for your safety and treatment efficacy.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Discuss Zithromax use with your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning a pregnancy. The medication may not be suitable for everyone in these circumstances.
Important Note
This information is for general knowledge and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance on Zithromax usage, dosage, and potential risks. Self-treating can be dangerous; proper diagnosis and treatment are vital.
Understanding Zithromax’s Uses and Dosage
Zithromax, or azithromycin, treats various bacterial infections. Doctors prescribe it for common illnesses like bronchitis, pneumonia, and some sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Dosage depends on the specific infection and your individual health. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Do not adjust the dosage without consulting them.
| Infection Type | Typical Dosage | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Community-acquired pneumonia | 500 mg on day 1, then 250 mg daily for four days | 5 days |
| Acute bacterial sinusitis | 500 mg on day 1, then 250 mg daily for four days | 5 days |
| Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis (strep throat) | 500 mg once daily for three days | 3 days |
| Chlamydia | 1 gram as a single dose | 1 day |
Note: This table provides examples only. Your doctor will determine the correct dosage based on your condition and medical history. They may adjust the dose or duration of treatment based on your response to the medication.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and stomach pain. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience severe or persistent side effects. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking before starting a new course of antibiotics.
Zithromax is a prescription antibiotic; never take it without a doctor’s prescription. Self-medicating can be dangerous and can lead to antibiotic resistance. Always discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Zithromax, like all medications, can cause side effects. These are usually mild, but you should be aware of them.
Common side effects include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
Less common, but more serious, side effects require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat)
- Signs of liver damage (yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, abdominal pain)
- Severe skin reactions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis)
- Tendonitis or tendon rupture
- Prolonged QT interval (a heart rhythm problem)
Before taking Zithromax, inform your doctor about:
- Any allergies you have, particularly to azithromycin or other antibiotics.
- Current medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding status.
- Liver or kidney problems.
- History of heart rhythm problems.
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking the medication prematurely, even if you feel better. This could lead to recurrence of infection and antibiotic resistance.
Drink plenty of fluids while taking Zithromax to help prevent dehydration, a common side effect of this medication.
If you experience any concerning side effects, contact your doctor immediately. This information does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist with any questions or concerns about Zithromax or any other medication.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, before starting Zithromax. This includes prescription drugs, even if you’re only taking them occasionally.
Medication Interactions
Zithromax can interact with certain medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. For example, concurrent use with drugs that prolong the QT interval (like some antiarrhythmics or certain antidepressants) may increase the risk of heart rhythm problems. Combining Zithromax with warfarin (a blood thinner) might necessitate closer monitoring of your blood clotting time. Ergot derivatives should be avoided during Zithromax treatment due to the potential for ergotism.
Contraindications
Zithromax is contraindicated for individuals with known hypersensitivity to azithromycin or any of its components. Patients with a history of liver problems should discuss potential risks with their physician before starting treatment, as Zithromax can cause liver damage in rare cases. Pregnancy and breastfeeding also require careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional.
This information is not exhaustive; consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance on potential drug interactions and contraindications specific to your health status and medication regimen. They can provide tailored advice and monitor you for any adverse effects.
Finding Reliable Information and Seeking Medical Advice
Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any medication, including Zithromax. They can assess your specific health needs and potential drug interactions.
For reliable information on Zithromax, check the official prescribing information from the manufacturer. You can usually find this on the FDA website or the manufacturer’s website.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) websites offer trustworthy information about medications and health conditions. Use their search functions to find relevant data.
Reputable medical websites, such as MedlinePlus (run by the NIH), often provide accurate drug information, but always verify information with your doctor. Be wary of health information found on unverified blogs or social media.
When researching online, look for information from government agencies, medical journals, or large, established healthcare organizations. Consider the source’s credibility before accepting any information as fact.
If you experience any side effects while taking Zithromax, contact your doctor immediately. Don’t rely solely on online forums for diagnosis or treatment guidance; professional medical evaluation is critical.
Remember, self-treating can be dangerous. Always seek professional medical advice for any health concerns or before making changes to your medication regimen.