Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) is not typically used to treat strep throat or other streptococcal infections. Streptococcus bacteria are susceptible to penicillin and its derivatives, which are usually the first-line treatment options.
While Cipro is a broad-spectrum antibiotic effective against various bacterial infections, its mechanism doesn’t target the specific types of bacteria that commonly cause strep infections as effectively. Using Cipro for strep could lead to ineffective treatment, potentially allowing the infection to worsen or develop into a more serious condition.
Always consult your doctor before starting any antibiotic treatment. They will diagnose your specific infection and prescribe the most appropriate antibiotic based on the identified bacteria and your medical history. Incorrect antibiotic use contributes to antibiotic resistance, a significant public health concern. Your doctor will guide you to the best course of action for a speedy recovery.
Penicillin or amoxicillin are generally preferred for strep infections due to their high efficacy and lower risk of side effects compared to fluoroquinolones like Cipro. These medications directly target the streptococcal bacteria and are well-established in treating strep infections. Discuss treatment options with your physician to make an informed decision about your healthcare.
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and Strep Throat: Understanding the Mismatch
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) is not effective against strep throat.
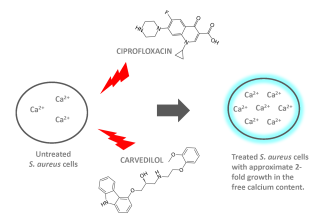
Strep throat, caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, responds to antibiotics like penicillin or amoxicillin. These antibiotics target the bacteria’s cell wall, leading to bacterial death. Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, works differently. It inhibits an enzyme necessary for bacterial DNA replication and repair. Streptococcus pyogenes is resistant to the mechanism of action of ciprofloxacin.
Using Cipro for strep throat won’t treat the infection. This can delay proper treatment, potentially leading to complications like rheumatic fever. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate antibiotic selection. A rapid strep test can quickly determine if you have strep throat. Your doctor will prescribe the correct antibiotic based on your test results and medical history. Accurate diagnosis ensures effective treatment and prevents complications.
In short: Never use Cipro for strep throat. Seek medical attention for appropriate treatment.
When Ciprofloxacin *Might* Be Relevant in Treating Complications of Strep Infections
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, isn’t a first-line treatment for uncomplicated strep throat or skin infections. However, it may play a role in managing specific, serious complications.
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN): While Ciprofloxacin doesn’t directly treat PSGN, which is an immune response to strep infection, it can address any secondary bacterial infections that might complicate this condition. Your doctor will likely focus on managing blood pressure and other symptoms but might prescribe Ciprofloxacin if a new bacterial infection arises.
Necrotizing fasciitis: This severe, flesh-eating infection, although rare, can sometimes follow a streptococcal infection. Ciprofloxacin, in combination with other antibiotics, might be part of a broad-spectrum approach to combat this life-threatening condition. The choice of antibiotics depends on the specific strain of bacteria identified.
Rheumatic fever: This autoimmune complication is less common now due to effective strep throat treatment, but if a bacterial infection coexists with rheumatic fever, Ciprofloxacin might be considered. The priority remains managing the inflammation and preventing heart damage.
Sepsis: If a strep infection progresses to sepsis (a life-threatening response to infection), Ciprofloxacin might be included in the antibiotic regimen, particularly if the bacteria shows resistance to other antibiotics. The specific choice of antibiotics depends entirely on the severity and the infecting organism’s susceptibility.
Important Note: Ciprofloxacin use should be guided by a physician. They will consider factors such as the specific infection, antibiotic susceptibility testing, your medical history, and potential side effects. Self-treating strep infections or their complications can be harmful.