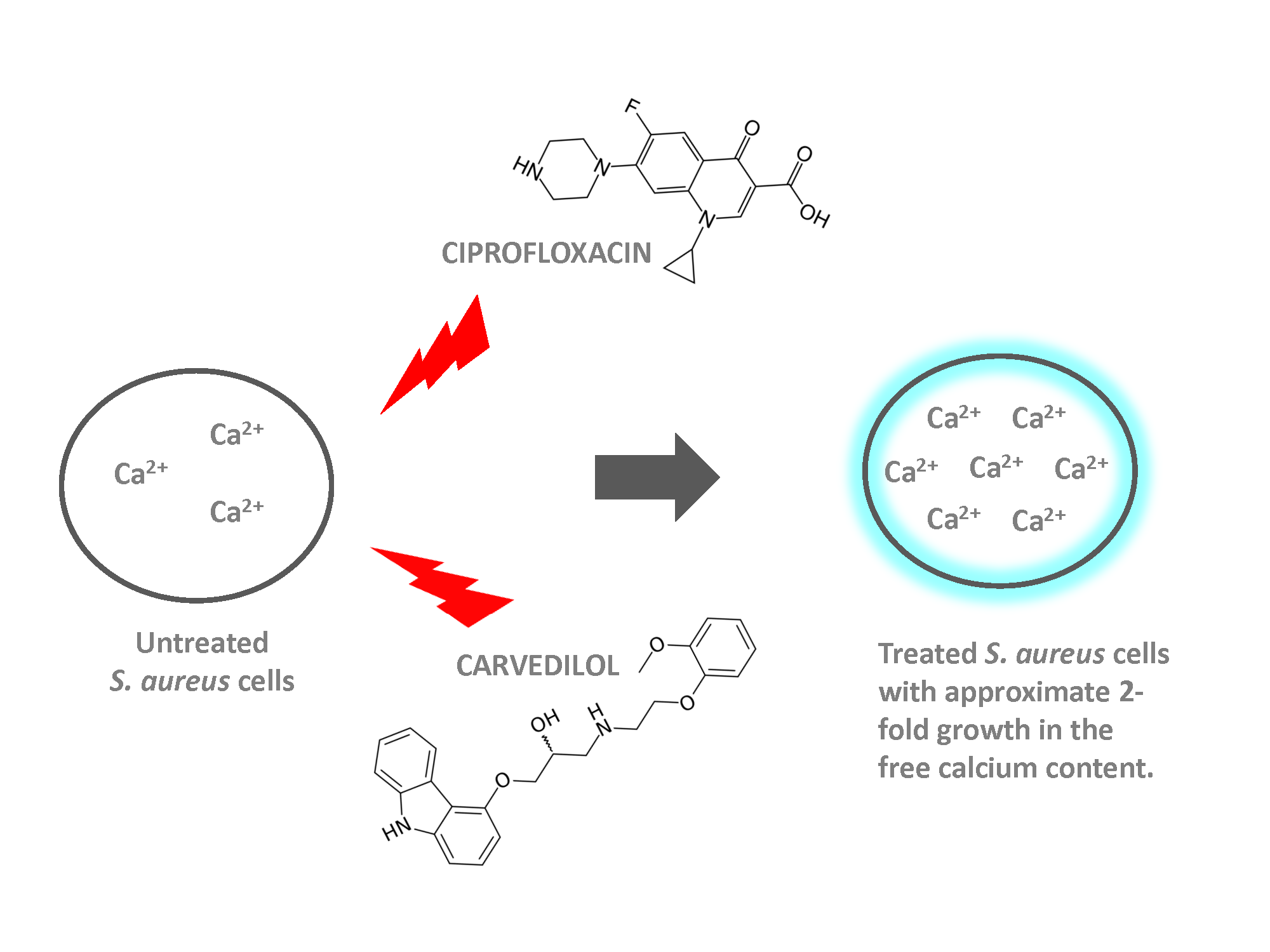
Ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness against Staphylococcus aureus (staph) infections varies significantly. Don’t assume it’s a guaranteed solution; resistance is a growing concern. Laboratory testing to determine staph susceptibility is crucial before treatment.
Specific staph strains, like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), often exhibit resistance to Ciprofloxacin. This means Ciprofloxacin might not be the right choice for these infections, leading to treatment failure and potentially worse outcomes. Always consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
If Ciprofloxacin is prescribed for a staph infection, strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration. Premature discontinuation can allow surviving bacteria to multiply, potentially increasing resistance and prolonging the infection. Monitor for any adverse reactions and report them immediately to your healthcare provider.
Alternative antibiotics exist for treating staph infections, including vancomycin and linezolid. Your doctor will select the most appropriate antibiotic based on your specific infection, your medical history, and the results of susceptibility testing. Remember, responsible antibiotic use is key to fighting antimicrobial resistance.
- Ciprofloxacin and Staph Infections: A Detailed Overview
- What is Ciprofloxacin and How Does it Work?
- Staphylococcus aureus (Staph) Infections: Types and Severity
- Skin Infections
- Serious Infections
- Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
- Factors Influencing Severity
- Ciprofloxacin’s Effectiveness Against Different Staph Strains
- MSSA Susceptibility
- MRSA Resistance
- Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CoNS)
- Susceptibility Testing: A Critical Step
- Alternative Antibiotics
- When Ciprofloxacin is Prescribed for Staph Infections
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Ciprofloxacin
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Nervous System Effects
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Important Considerations
- Alternative Treatments for Staph Infections Resistant to Ciprofloxacin
- Surgical Drainage
- Antibiotic Combinations
- Bacteriophage Therapy
- Immunomodulatory Therapies
- Important Considerations Before Taking Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin and Staph Infections: A Detailed Overview
Ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness against staph infections depends heavily on the specific strain of Staphylococcus involved. It’s crucial to remember that many Staphylococcus aureus strains, including MRSA (methicillin-resistant S. aureus), are resistant to ciprofloxacin. Therefore, ciprofloxacin is generally not the first-line treatment for staph infections.
Ciprofloxacin primarily targets susceptible strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis and some S. aureus strains. However, susceptibility testing is vital before prescribing ciprofloxacin to ensure its efficacy. This involves laboratory analysis to determine the antibiotic’s effect on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Treatment success hinges on accurate diagnosis and appropriate antibiotic selection. A physician will consider factors like infection severity, patient’s medical history, and the results of susceptibility testing. They will prescribe the most effective antibiotic for the individual case.
Potential side effects of ciprofloxacin include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. More serious side effects are less common but possible. Always discuss potential side effects with your doctor.
Alternative antibiotics, such as vancomycin or linezolid, often prove more effective against MRSA and other ciprofloxacin-resistant staph strains. Your doctor will determine the best treatment course based on your specific needs.
Self-treating staph infections with ciprofloxacin or any antibiotic is dangerous. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Delaying proper treatment can lead to complications and spread of infection.
What is Ciprofloxacin and How Does it Work?
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It fights bacterial infections by targeting an enzyme called DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.
These enzymes are crucial for bacterial DNA replication and repair. By inhibiting these enzymes, Ciprofloxacin prevents bacteria from reproducing and ultimately causes their death.
- DNA Gyrase: This enzyme unwinds and supercoils bacterial DNA, allowing replication and transcription.
- Topoisomerase IV: This enzyme separates newly replicated bacterial DNA strands during cell division.
Ciprofloxacin’s mechanism works differently than many other antibiotics. This makes it effective against various bacteria, including some resistant to other antibiotics.
- The drug binds to DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.
- This binding blocks the enzymes’ function.
- Bacterial DNA replication and repair are disrupted.
- Bacterial cell death follows.
Remember, Ciprofloxacin is a prescription drug; always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Misuse can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Staphylococcus aureus (Staph) Infections: Types and Severity
Staphylococcus aureus (Staph) bacteria cause a range of infections, varying significantly in severity. Mild infections often clear up without treatment, while others require prompt medical attention.
Skin Infections
Common skin infections include folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles), impetigo (highly contagious sores), and cellulitis (infection of deeper skin layers). These typically present as red, swollen, painful areas. Treatment often involves topical antibiotics. Severe cases might necessitate oral antibiotics.
Serious Infections
More serious Staph infections include pneumonia, endocarditis (heart valve infection), osteomyelitis (bone infection), and sepsis (life-threatening bloodstream infection). These require immediate medical intervention, often with intravenous antibiotics. Factors like the specific Staph strain, the patient’s immune system, and the infection site influence treatment choices and outcomes. Rapid diagnosis is vital.
Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a rare but potentially fatal condition caused by toxins released by Staph bacteria. Symptoms include high fever, rash, low blood pressure, and organ failure. Immediate hospitalization and aggressive treatment are necessary for survival. TSS often requires long-term monitoring and support.
Factors Influencing Severity
The severity of a Staph infection depends on several factors. The location of the infection plays a crucial role; infections involving the bloodstream or internal organs are inherently more dangerous. The patient’s overall health and immune status also significantly influence the course and outcome of the infection. Furthermore, the specific strain of S. aureus, particularly its antibiotic resistance, dictates treatment strategy. Antibiotic resistance patterns vary regionally and require careful laboratory testing to guide treatment decisions.
Ciprofloxacin’s Effectiveness Against Different Staph Strains
Ciprofloxacin’s ability to combat Staphylococcus infections varies significantly depending on the specific strain. Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) is generally susceptible, while methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) often shows resistance.
MSSA Susceptibility
Ciprofloxacin typically demonstrates good activity against MSSA. However, increasing resistance is observed, necessitating susceptibility testing before treatment.
MRSA Resistance
Most MRSA strains exhibit resistance to ciprofloxacin. This resistance often stems from mutations in the bacterial DNA gyrase, the target of ciprofloxacin’s action. Consequently, ciprofloxacin is rarely a first-line choice for MRSA infections.
Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CoNS)
Ciprofloxacin’s activity against CoNS strains is inconsistent. Some species show susceptibility, while others are inherently resistant. Laboratory testing is crucial to guide treatment decisions.
Susceptibility Testing: A Critical Step
Before prescribing ciprofloxacin for a staph infection, performing susceptibility testing is vital. This ensures optimal treatment and minimizes the risk of treatment failure and the development of further resistance.
| Staphylococcus Strain | Ciprofloxacin Susceptibility | Treatment Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| MSSA | Generally susceptible, but resistance increasing | Consider susceptibility testing; may be appropriate in some cases |
| MRSA | Frequently resistant | Generally not recommended; alternative antibiotics are necessary |
| CoNS | Variable; dependent on species | Susceptibility testing is mandatory |
Alternative Antibiotics
For MRSA and ciprofloxacin-resistant strains, alternative antibiotics like vancomycin, linezolid, or daptomycin are usually recommended. Physician guidance is essential for choosing the appropriate treatment.
When Ciprofloxacin is Prescribed for Staph Infections
Ciprofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, is sometimes prescribed for Staphylococcus infections, but only under specific circumstances. Its use is generally reserved for infections caused by Ciprofloxacin-susceptible strains of Staphylococcus bacteria.
Doctors primarily consider Ciprofloxacin when other antibiotics, like first-line options such as penicillinase-resistant penicillins or cephalosporins, are ineffective or contraindicated. This often involves situations where the staph infection is resistant to these drugs or the patient has an allergy.
Specific examples include some cases of complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI) or urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by susceptible Staphylococcus strains. However, many Staphylococcus species, notably Staphylococcus aureus, frequently exhibit resistance to Ciprofloxacin. Therefore, susceptibility testing is critical before prescribing Ciprofloxacin.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions diligently. This includes completing the full course of antibiotics, even if you feel better sooner. Failing to finish your prescription increases the risk of recurrence and the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Remember, Ciprofloxacin carries potential side effects, including diarrhea, nausea, and tendonitis. Discuss these risks and any other concerns with your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin, while effective against many bacterial infections, carries potential side effects. Understanding these risks helps you make informed decisions with your doctor.
Gastrointestinal Issues
- Nausea and vomiting are common. Drink plenty of fluids and consider bland foods to manage these symptoms.
- Diarrhea can occur; in rare cases, it can be severe (Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea). Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe or persistent diarrhea.
- Abdominal pain is another possibility. Over-the-counter pain relievers may provide some relief, but consult your doctor if pain is intense or persistent.
Nervous System Effects
- Headache is a relatively frequent side effect. Adequate hydration and rest can help.
- Dizziness and lightheadedness can occur. Avoid driving or operating machinery if affected.
- In rare instances, more serious neurological effects, such as seizures, have been reported. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience seizures or unusual neurological symptoms.
Other Potential Side Effects
- Skin reactions, ranging from mild rash to more serious allergic reactions. Stop taking Ciprofloxacin and seek immediate medical attention if you develop a severe allergic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling).
- Tendon problems, including tendonitis and tendon rupture, are possible, particularly in older adults or those taking corticosteroids. Report any tendon pain to your doctor immediately.
- Photosensitivity: Ciprofloxacin can increase your skin’s sensitivity to sunlight. Use sunscreen and protective clothing when exposed to sun.
- Changes in blood sugar levels have been reported in some patients with diabetes. Monitor your blood sugar closely if you are diabetic.
Important Considerations
This is not an exhaustive list. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Report any unusual symptoms promptly. Your doctor can assess your individual risk factors and determine if Ciprofloxacin is the appropriate treatment for your condition.
Alternative Treatments for Staph Infections Resistant to Ciprofloxacin
If ciprofloxacin fails, your doctor will likely prescribe a different antibiotic. Common alternatives include daptomycin, linezolid, vancomycin, and ceftaroline. The choice depends on the specific strain of staph and your overall health.
Surgical Drainage
For localized infections like abscesses, surgical drainage often plays a crucial role. This procedure removes pus and infected tissue, allowing the antibiotics to work more effectively. Prompt drainage significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Antibiotic Combinations
Sometimes, combining two or more antibiotics proves superior to using a single drug. This approach can tackle resistant bacteria more effectively. Your physician will determine the most suitable combination based on laboratory results.
Bacteriophage Therapy
Bacteriophages are viruses that infect and kill bacteria. This emerging therapy shows promise against antibiotic-resistant staph infections. Research continues, and it’s not yet a standard treatment, but it may be an option in some cases.
Immunomodulatory Therapies
These therapies aim to boost your immune system’s ability to fight the infection. This can involve various approaches, including targeted therapies designed to support your body’s natural defenses against staphylococcus aureus. Your doctor will assess the suitability of this approach.
Important Considerations Before Taking Ciprofloxacin
Tell your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Interactions can occur, affecting how Ciprofloxacin works or causing unwanted side effects.
Inform your doctor of any allergies you have, especially to antibiotics. Ciprofloxacin belongs to a class of drugs with potential cross-reactivity.
Discuss your medical history, including kidney or liver problems, heart conditions, or seizures. These conditions can influence Ciprofloxacin’s safety and efficacy.
Women should inform their doctor if they are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant. Ciprofloxacin use during pregnancy or breastfeeding requires careful consideration.
Be aware of potential side effects such as tendonitis or tendon rupture, especially in older adults or those taking corticosteroids. Report any pain or swelling in your tendons immediately.
Understand that Ciprofloxacin can affect your nervous system. Report any unusual sensations, dizziness, or confusion promptly.
This antibiotic may cause photosensitivity. Limit sun exposure and use sunscreen to avoid sunburn.
| Potential Side Effect | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe diarrhea | Contact your doctor immediately; this could indicate Clostridium difficile infection. |
| Allergic reaction (rash, itching, swelling) | Stop taking Ciprofloxacin and seek medical attention immediately. |
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking the medication early, even if you feel better. This can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Drink plenty of fluids while taking Ciprofloxacin to help prevent kidney problems.