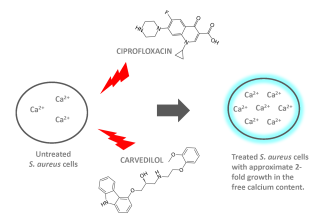
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) treats specific bacterial infections. It’s crucial to understand its targeted applications to ensure safe and effective treatment. Primarily, Cipro combats infections caused by susceptible bacteria in various parts of the body.
Respiratory tract infections like bronchitis and pneumonia are common indications. However, Cipro is not a first-line treatment for all respiratory ailments; your doctor determines its suitability based on the specific bacteria identified. Skin and soft tissue infections also respond well to Cipro, particularly those caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Escherichia coli.
Ciprofloxacin also targets urinary tract infections (UTIs) effectively. Remember, appropriate antibiotic use is vital for UTI management, and Cipro’s suitability depends on the infecting bacteria. Furthermore, Cipro finds application in treating certain types of bone and joint infections, and some sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea. Always consult a physician to determine if Cipro is the right treatment for your specific condition.
Important Note: Cipro is a prescription drug, and self-medication is dangerous. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern; therefore, responsible antibiotic use is paramount.
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro): Indications for Use
- Bacterial Infections Treated with Ciprofloxacin
- Respiratory Tract Infections
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Gastrointestinal Infections
- Other Infections
- Important Considerations
- Bone and Joint Infections
- Specific Conditions Where Ciprofloxacin is Prescribed
- Ciprofloxacin Use: Considerations and Limitations
- When to Seek Medical Attention for Infections
- Severe or Unresponsive Infections
- Specific Infection Concerns
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro): Indications for Use
Ciprofloxacin, commonly known as Cipro, is a powerful antibiotic effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria. Doctors prescribe it to treat various bacterial infections.
Respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia and bronchitis, frequently respond well to Ciprofloxacin treatment. Severe cases often benefit from its strong antibacterial action.
Skin and soft tissue infections, including cellulitis and wound infections, are another common application. Cipro’s ability to penetrate tissues makes it highly effective in these situations.
Bone and joint infections, often requiring long-term antibiotic therapy, may be treated with Ciprofloxacin. This is especially true for infections resistant to other antibiotics.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), both uncomplicated and complicated, are frequently treated with Cipro. Its high concentration in the urine makes it a suitable choice for these infections.
Certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as gonorrhea and some types of prostatitis, are responsive to Ciprofloxacin treatment. Always consult your physician for appropriate STI treatment.
Ciprofloxacin is also used to prevent anthrax infection post-exposure and in certain cases, to treat plague. These are typically high-risk situations requiring specific medical guidance.
Important Note: Ciprofloxacin is a prescription medication. Always consult a healthcare professional before using Ciprofloxacin or any other medication to ensure its suitability for your specific health condition and to discuss potential side effects.
Bacterial Infections Treated with Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin effectively treats various bacterial infections. Its broad spectrum targets both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Respiratory Tract Infections
Ciprofloxacin combats infections like pneumonia and bronchitis caused by susceptible bacteria, offering a valuable treatment option when other antibiotics fail. Always follow your doctor’s prescription precisely.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
This antibiotic is frequently used for skin infections such as cellulitis and wound infections. Prompt treatment with Ciprofloxacin can often prevent complications. Consult a physician for diagnosis and treatment plan.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Ciprofloxacin is a common choice for UTIs. It targets common UTI-causing bacteria like E. coli and Proteus mirabilis. However, antibiotic resistance is a concern; your doctor will consider this during diagnosis.
Gastrointestinal Infections
Ciprofloxacin can treat certain gastrointestinal infections caused by bacteria like Salmonella and Campylobacter. It is vital to differentiate between bacterial and viral causes of gastrointestinal illness before starting treatment.
Other Infections
Ciprofloxacin has applications in treating infections of the bones and joints (osteomyelitis), as well as some sexually transmitted infections. Your doctor will determine the best course of action based on your specific needs.
Important Considerations
| Infection Type | Bacteria Targeted | Treatment Duration (Typical) |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia | Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae | 7-14 days |
| Cellulitis | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes | 7-14 days |
| UTI | Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis | 7-14 days |
Remember, Ciprofloxacin is a prescription medication. Always seek professional medical advice before using it and strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration. Misuse can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Bone and Joint Infections
Ciprofloxacin is used in treating infections like osteomyelitis, particularly when other antibiotics are ineffective. Appropriate imaging and laboratory tests are crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment selection.
Specific Conditions Where Ciprofloxacin is Prescribed
Ciprofloxacin effectively treats various bacterial infections. Doctors frequently prescribe it for urinary tract infections (UTIs), including complicated UTIs and pyelonephritis (kidney infection).
Respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia, caused by susceptible bacteria, also respond well to Ciprofloxacin treatment. This includes cases of community-acquired pneumonia.
Skin and soft tissue infections, such as cellulitis and abscesses, are another common application. Ciprofloxacin can target the bacteria responsible for these infections.
Certain types of bone and joint infections benefit from Ciprofloxacin’s antibacterial properties. This is especially true in cases involving specific bacteria.
Gastrointestinal infections, particularly those caused by Salmonella or Shigella, are often treated with Ciprofloxacin. However, always consult a doctor before using Ciprofloxacin for digestive issues.
Additionally, Ciprofloxacin plays a role in treating infections in patients with compromised immune systems. It may be used for prophylaxis in certain surgical procedures where bacterial contamination is a risk.
Remember, Ciprofloxacin is a prescription-only medication. A doctor must determine its appropriateness for your specific condition and health status.
Ciprofloxacin Use: Considerations and Limitations
Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including herbal remedies and supplements, as interactions can occur. This is especially important with Ciprofloxacin.
Monitor for side effects. Common ones include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Serious but less frequent side effects include tendonitis and rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Report any unusual symptoms immediately.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Use Ciprofloxacin during pregnancy or breastfeeding only if the benefits outweigh the potential risks. Discuss this carefully with your doctor.
- Children: Ciprofloxacin use in children is generally restricted due to the risk of cartilage damage. Use should be reserved for serious infections where alternatives are ineffective.
- Liver and Kidney Problems: Dosage adjustments may be necessary for individuals with impaired liver or kidney function. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose.
- Photosensitivity: Ciprofloxacin can increase your skin’s sensitivity to sunlight. Use sunscreen and protective clothing when exposed to sunlight.
Ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness against certain bacteria is declining due to increasing antibiotic resistance. Your doctor will consider this when prescribing.
- Antibiotic resistance is a serious global health issue.
- Only use Ciprofloxacin when prescribed for a bacterial infection; it’s ineffective against viral infections.
- Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before finishing.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions for dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking Ciprofloxacin prematurely or change the dosage without consulting your physician. Ignoring this can lead to treatment failure and increased resistance.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Infections
See a doctor immediately if you experience a high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C), severe chills, or difficulty breathing. These symptoms could indicate a serious infection requiring immediate medical intervention.
Severe or Unresponsive Infections
Seek prompt medical attention if an infection doesn’t improve after a few days of home treatment, including over-the-counter medications. This applies to skin infections showing signs of spreading, worsening pain, or increased redness. Similarly, persistent diarrhea or vomiting warrants a doctor’s visit, especially if accompanied by fever or dehydration.
Specific Infection Concerns
Eye infections causing significant vision impairment or severe pain require immediate attention. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) with severe pain during urination or blood in the urine need prompt medical evaluation. Similarly, any infection accompanied by persistent nausea, severe abdominal pain, or disorientation necessitates immediate medical care.